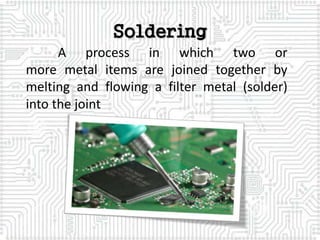
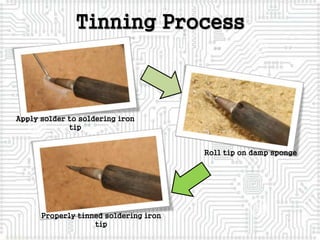
This document provides a comprehensive overview of soldering and desoldering processes, including tools needed and safety guidelines. It lays out the steps for properly soldering and desoldering electronic components, emphasizing the importance of technique and safety measures. The presentation also highlights common mistakes in soldering and provides references for further learning.