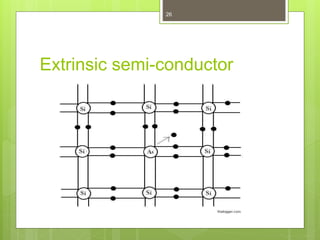
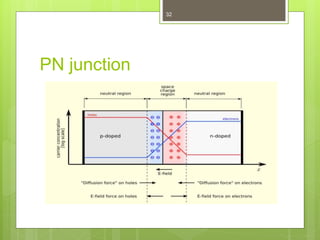
This document outlines the syllabus and content for a basic electronics course. It discusses that the course grade will be based on midterm, final, and sessional marks. Sessional marks depend on behavior, participation, assignments, presentations, attendance, and quizzes. Contact information for the instructor is provided. Recommended reference materials are listed. An introduction to electronics and its role in daily life is given. The history of electronics from vacuum tubes to integrated circuits is summarized. Fundamental electronics components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors are defined. Band theory, intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, and PN junctions are explained conceptually. Students will have a homework assignment on electricity and magnetism