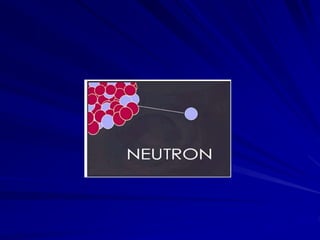
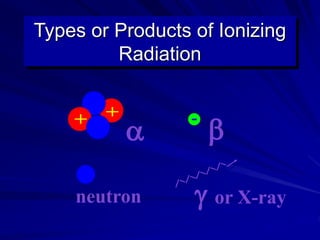
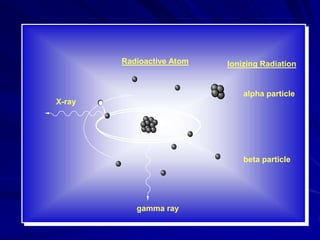
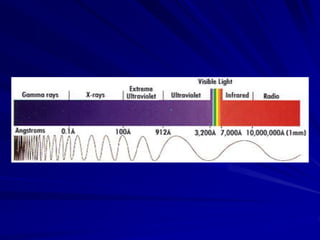
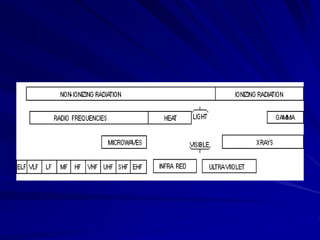
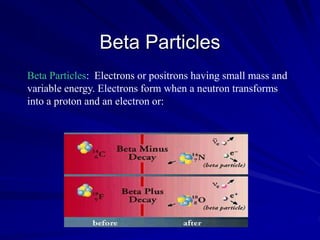
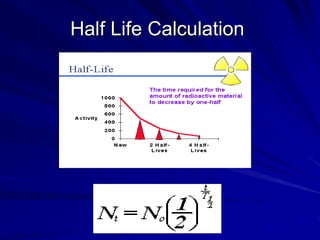
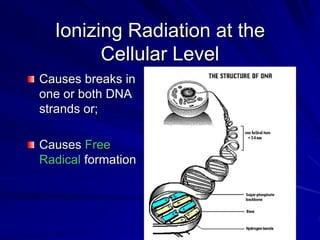
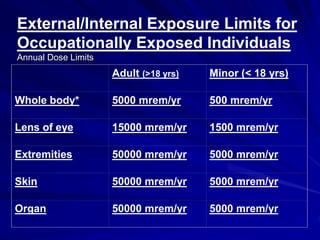
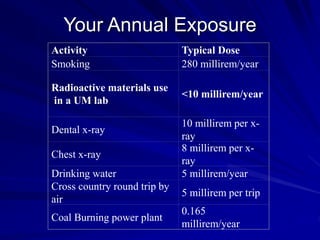
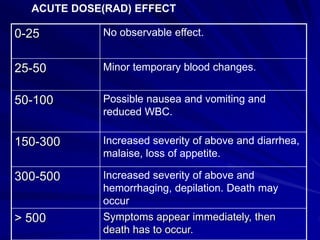
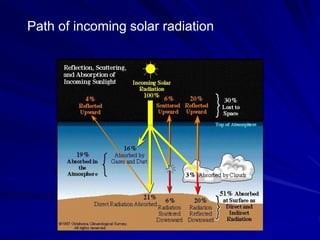
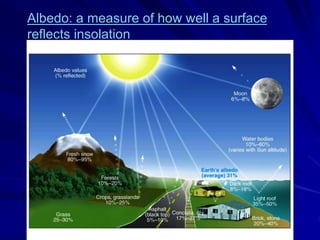
Radiation can be ionizing or non-ionizing. Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms and molecules and includes alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, x-rays, and neutrons. Non-ionizing radiation does not have enough energy to ionize but can excite electrons. Exposure to ionizing radiation can lead to cellular DNA damage and increased cancer risk over time depending on dose. Acute radiation sickness occurs above 100 rads while long term effects like cancer have no threshold. Occupational exposure limits aim to keep annual whole body dose below 5 rem (50 mSv) per year. Common sources of natural background radiation include radon gas and cosmic rays.