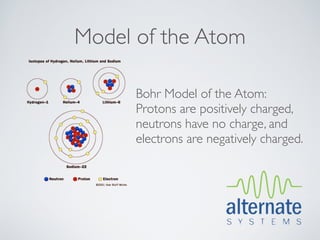
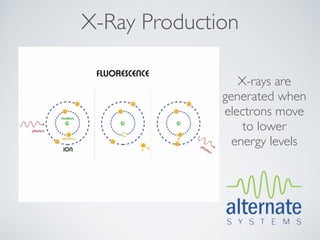
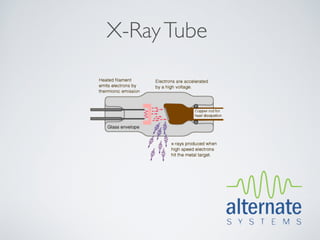
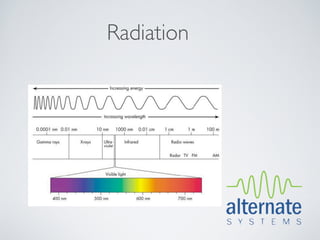
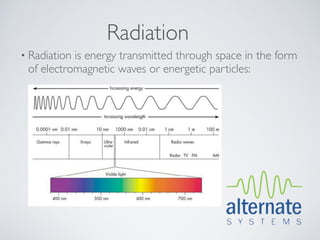
This document presents an overview of x-ray radiation safety, including types of radiation, generation of x-rays, potential health effects, and safety regulations. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing exposure to radiation through safety devices and procedures, highlighting health risks such as burns and cancer. The document also summarizes the necessity of adhering to health regulations and maintaining safety features when operating radiation-emitting devices.