Embed presentation

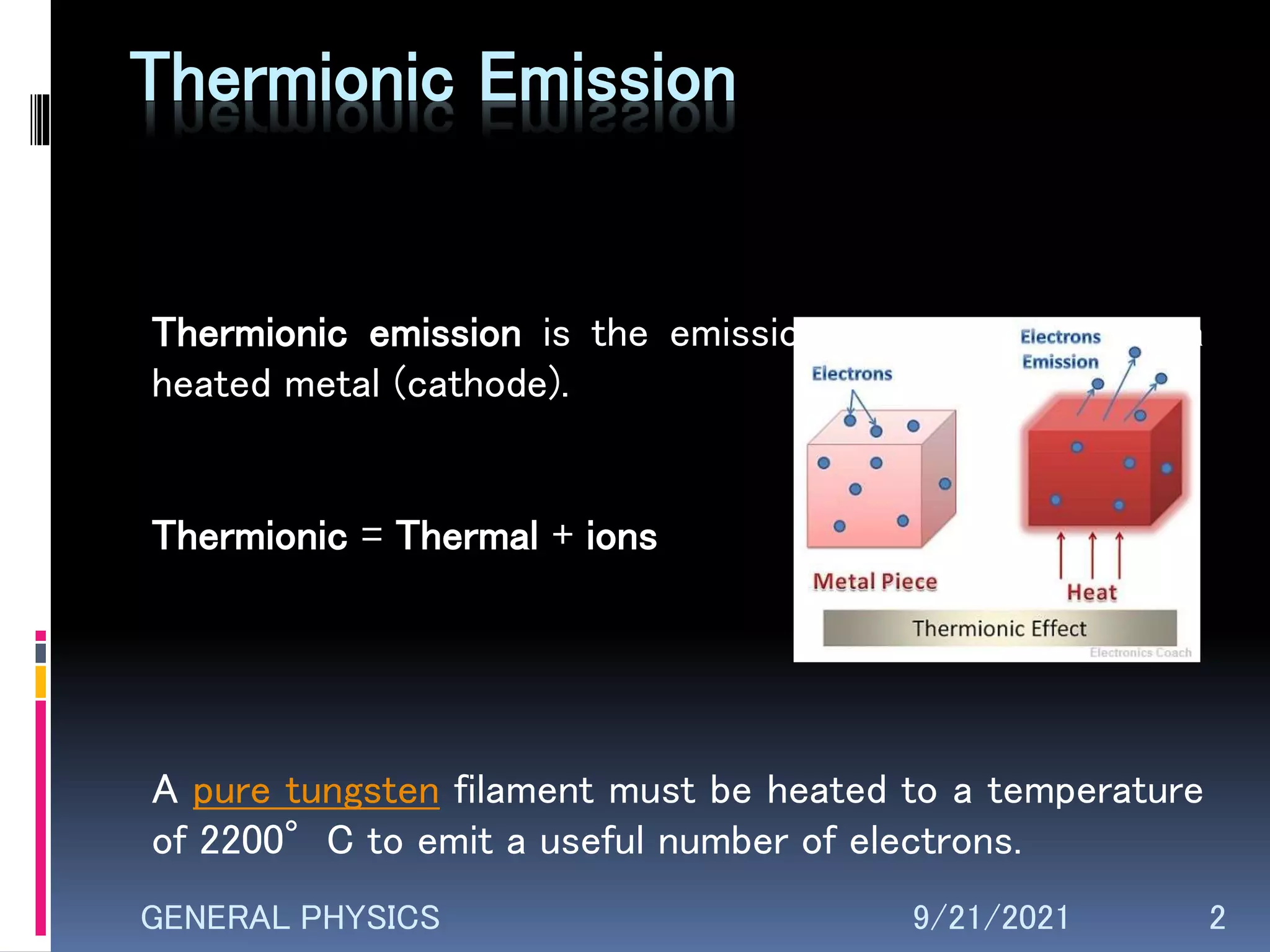

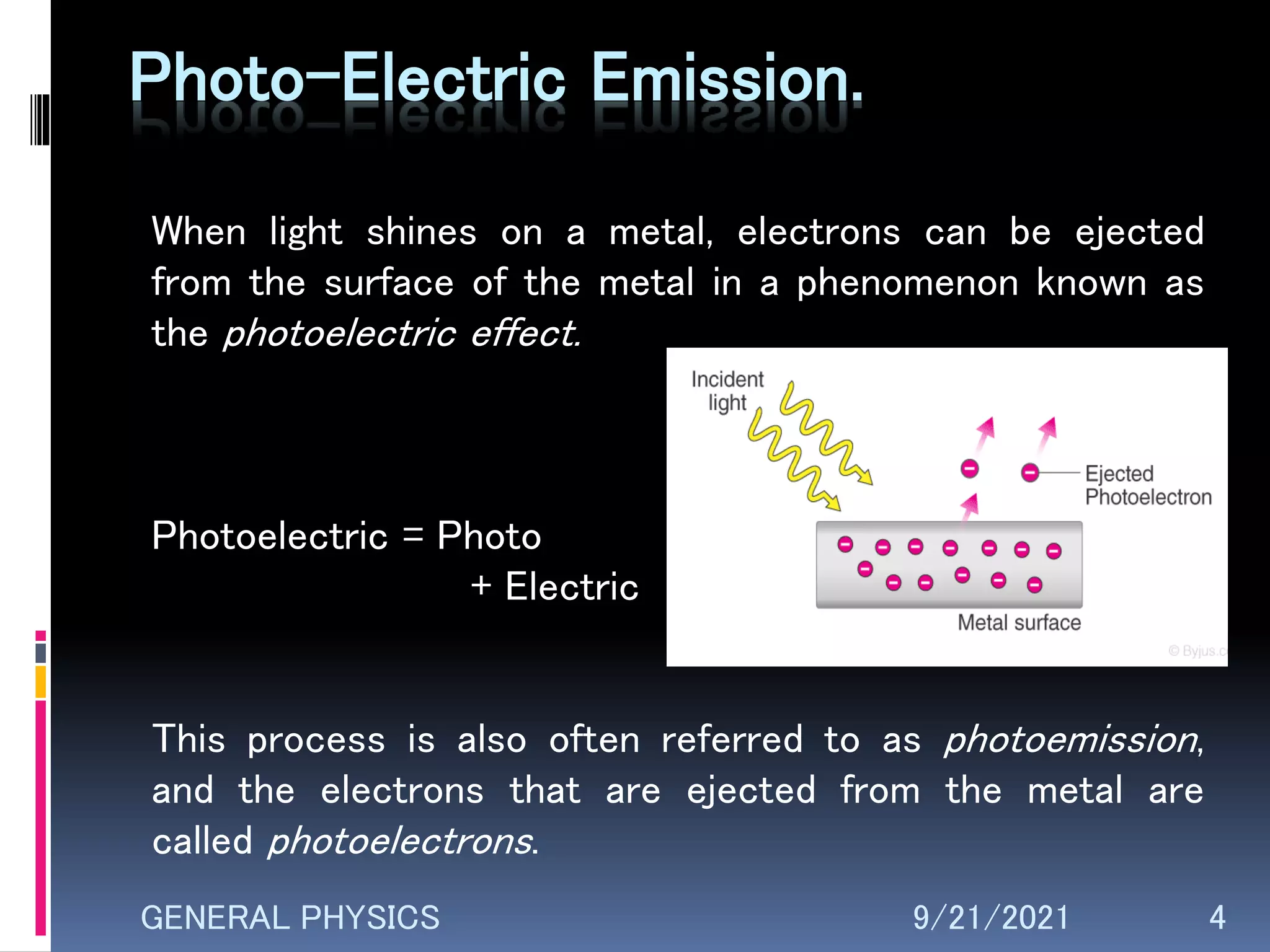
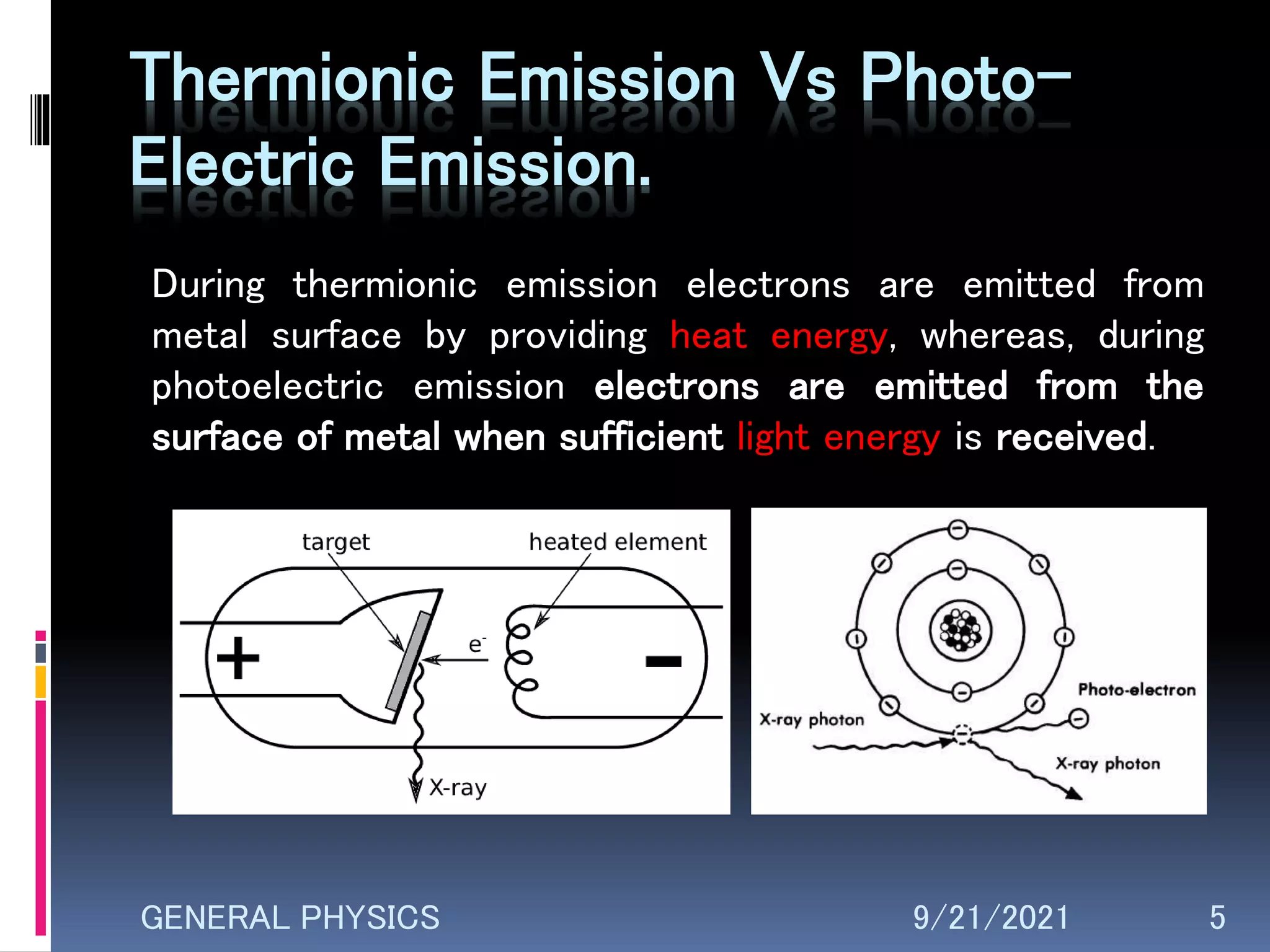

Thermionic emission is the emission of electrons from heated metal caused by thermal excitation. A pure tungsten filament must reach 2200°C to emit useful electrons. Factors like temperature, area, and work function affect emission. Thermionic emitters are used in electronics, instrumentation, power systems and energy conversion. Photoelectric emission ejects electrons from metals hit by light, also called the photoelectric effect. It differs from thermionic emission which uses heat rather than light to release electrons.




