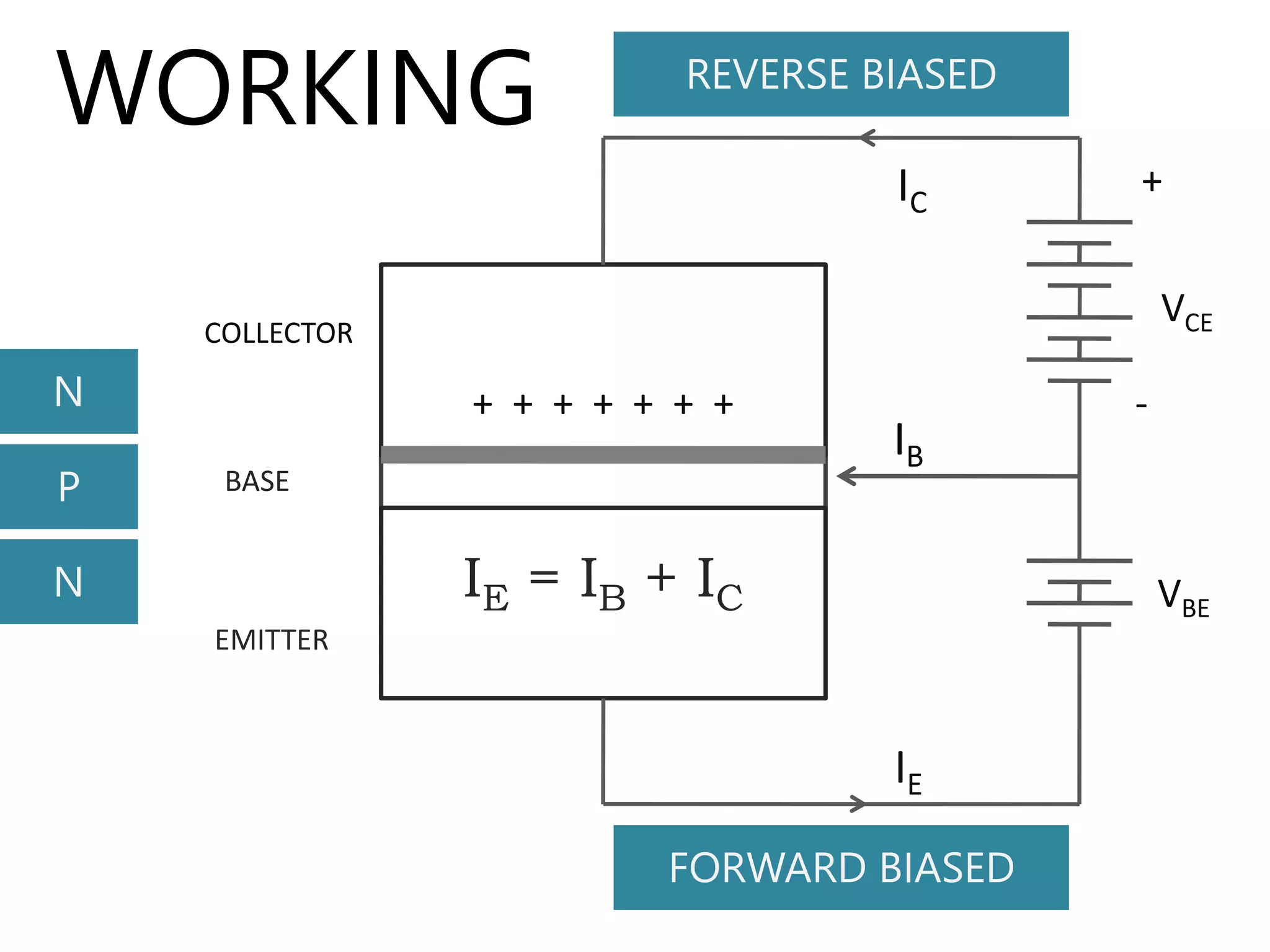
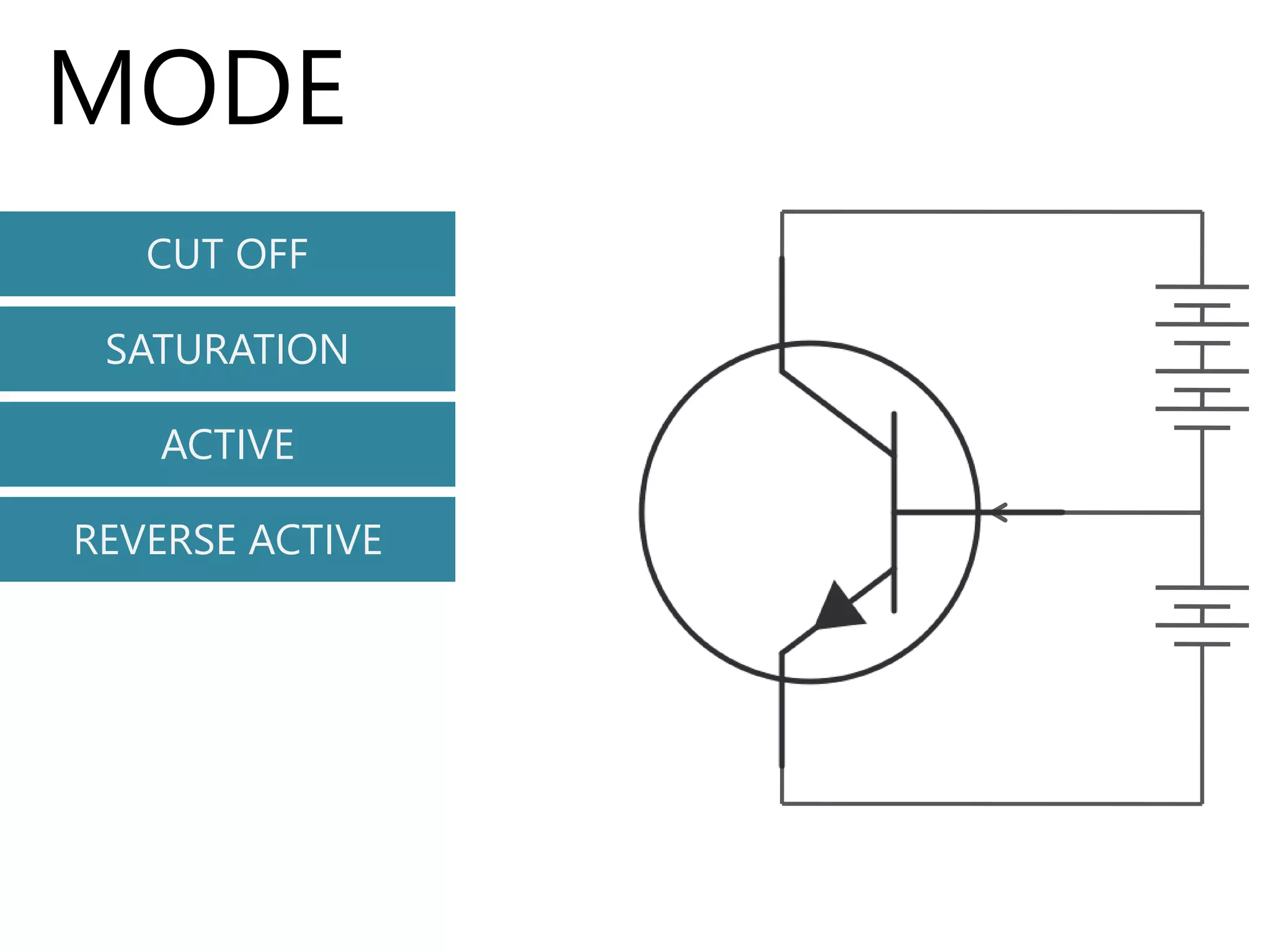
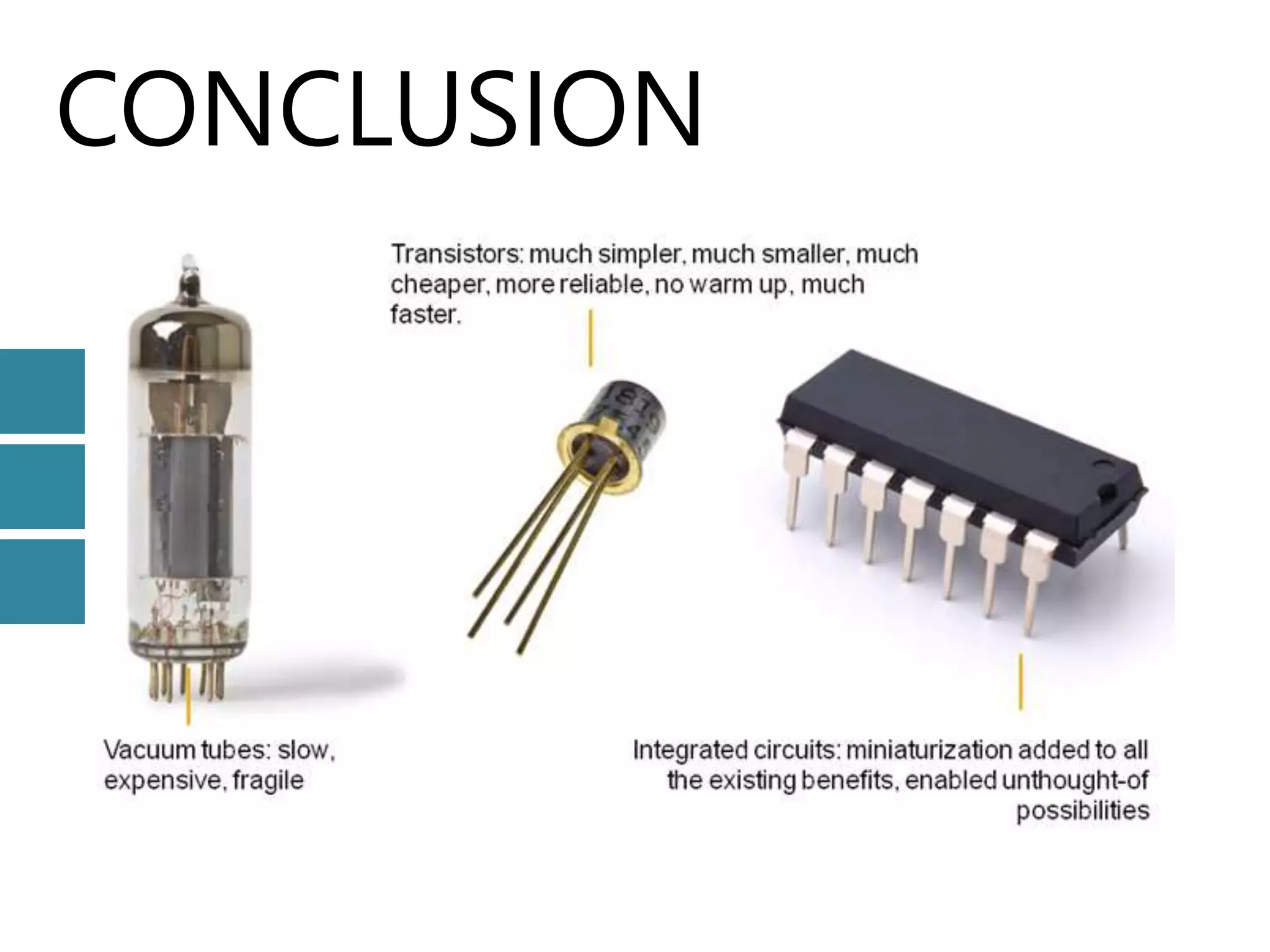
The document discusses the bipolar junction transistor (BJT), an important electronic device invented in 1947 at Bell Labs by Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley. It summarizes the BJT's construction using either PNP or NPN semiconductor materials, its basic working involving forward and reverse biasing of the base-emitter and collector-emitter junctions, and its three main modes of operation - cutoff, saturation, and active. The document also covers BJT configurations like common base, common collector, and common emitter; and concludes with references.