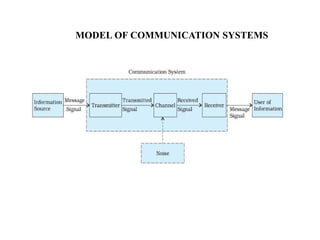
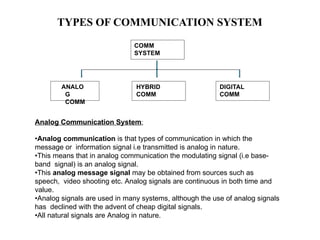
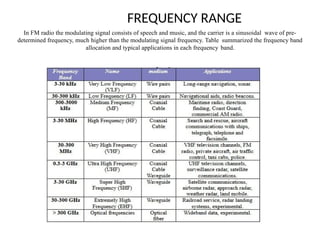
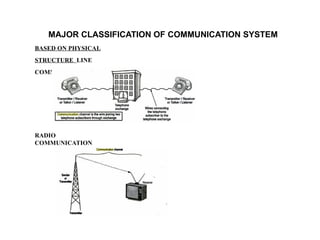
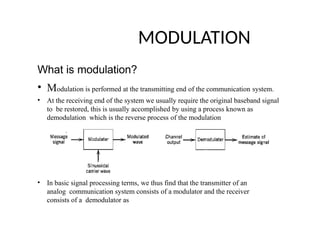
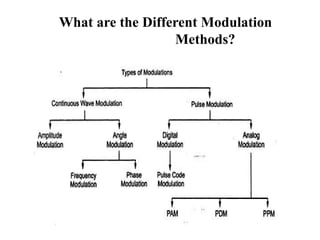
The document provides an overview of analog communication systems, explaining their purpose and functionality, which includes transmitting information-bearing signals from a source to a destination. It discusses the fundamentals of communication, modulation, and the classification of various communication systems. Additionally, it highlights key aspects of analog signals, their continuous nature, and the importance of modulation for effective communication.