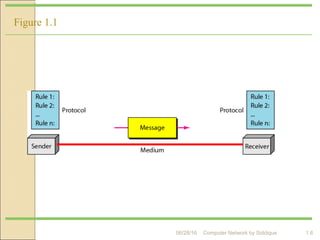
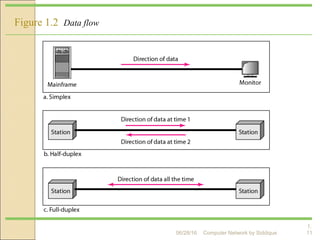
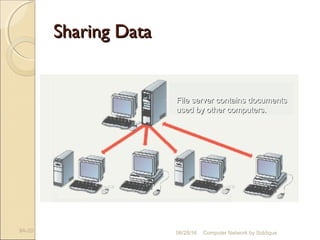
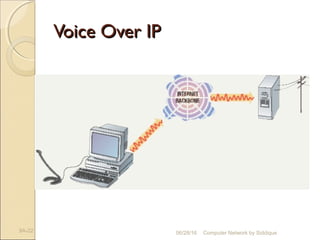
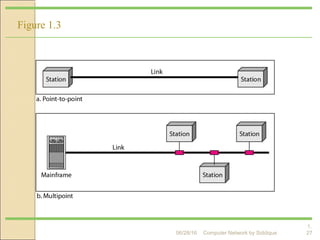
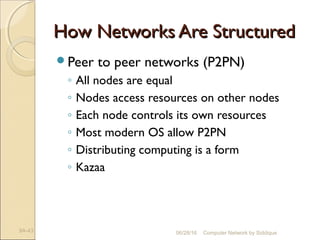
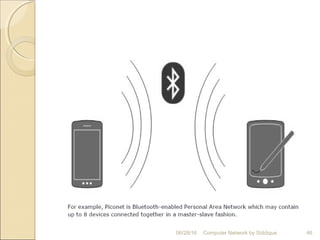
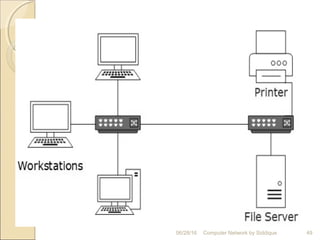
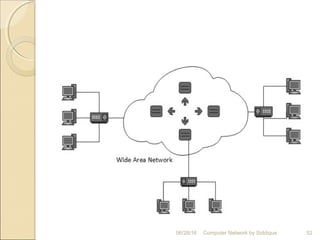
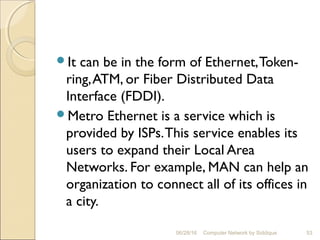
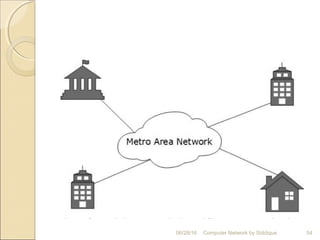
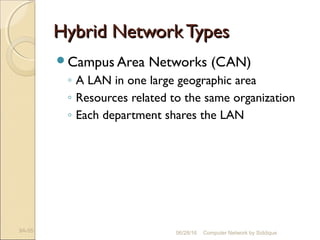
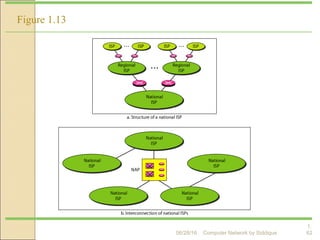
The document discusses basics of computer networks. It defines data communication and its key characteristics like delivery, accuracy and timeliness. The basic components of a communication model are identified as the message, protocol, sender, receiver and transmission medium. Different data types like text, numbers, images, audio and video are represented as bit patterns for transmission. Types of networks like personal area network, local area network, wide area network, campus area network and metropolitan area network are classified based on their geographical span, interconnectivity, administration and architecture.