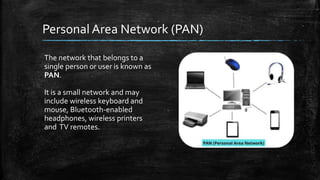
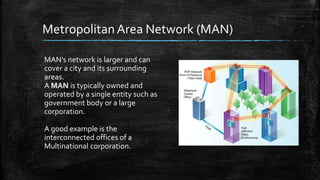
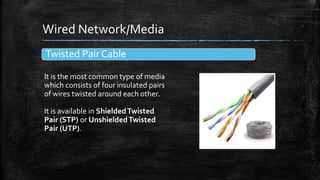
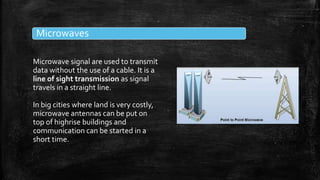
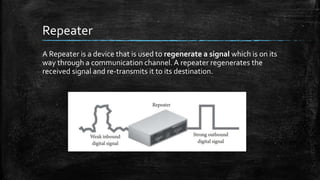
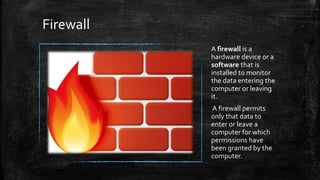
A computer network connects multiple devices together to share resources. The main advantages of a network include resource sharing, reliable data storage through backups, and centralized storage of files. There are different types of networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). Networks require transmission media like cables or wireless signals to connect devices and transfer data. Common network devices that help facilitate networking include network interface cards, hubs, switches, repeaters, and routers.