This document provides an overview of topics related to the internet and computer programming. It discusses the internet and types of connectivity like analog modems, DSL, and wireless. It describes the OSI model and protocols like email, SMTP, POP3, DNS, and FTP. It also covers intranets and extranets. Other topics include the world wide web, HTML, and search engines. Presentation slides are included on each of these topics with details on definitions, components, benefits, and limitations.




![INTERNET AND ITS APPLICATIONS…
E-MAIL
ONLINE EDUCATION
TELNET[telecommunications and networks]
VIDEO CONFERENCING
E-COMMERCE
E-MARKETING
E-CRM[customer relationship management]
EFT[electronic fund transfer]
SEARCH ENGINES[global data search]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-5-320.jpg)
![ANALOG MODEMS
ISDN [integrated services digital network]
DSL [digital subscriber lines]
ADSL [asymmetrical digital subscriber lines]
SDSL [symmetrical digital subscriber lines]
HDSL [high-data-rate digital subscriber lines]
LEASED LINES
WIRE-LESS [Wi-Fi and VPN]
SATELLITE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-7-320.jpg)

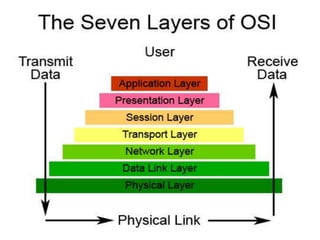
![OSI MODEL [INTRODUCTION]
The OPEN SYSTEM INTERCONNECTION (OSI) model
includes a set of protocols that attempt to define and
standardization the data communication process.
The OSI model is a concept that describes, how data
communications should take place.
It divides the process into seven steps called layers.
The OSI protocols were defined by the International
Standard Organization (ISO) [INCLUDING IEEE].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-9-320.jpg)


![Email [electronic-mail] allows the user to send
data in the form of text, pictures, sound and video
to a remote computer on the Internet.
These Email services are created by companies on
specific web services and can be accessed by
anyone anywhere in the world at anytime.
Files and data can also be sent through an Email as
like an attachment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-13-320.jpg)
![SMTP[simple mail transfer protocol]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-14-320.jpg)
![SMTP is a member of the TCP/IP suite of
protocols that governs the exchange of
electronic mail between message transfer
agents.
It uses a ‘MAIL TRANSFER AGENT’ [MTA] to
transfer the commands, replies, e-mails
across the internet.
It has a set of predefined rules through
which it handles the mail traffic across a
particular network.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-15-320.jpg)
![POP3[post office protocol {ver.3}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-16-320.jpg)


![FTP[file transfer protocol]
TCP/IP
USER
FTP
DATA FLOW
RECIEVER
[WEB SERVER]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-21-320.jpg)




![WORLD WIDE WEB
[WWW]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-26-320.jpg)


![HTML
[Hyper text markup
language]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-29-320.jpg)
![ Most Web documents are expressed by means of a special
language called [Hyper Text Markup Language ] or simply
HTML.
Being a markup language means that HTML provides
keywords to structure a document into different sections.
It is also possible to insert images or animations at
specific positions in a document.
Besides these structural elements, HTML provides various
keywords to instruct the browser how to present the
document.
One of its most powerful features is the ability to express
parts of a document in the form of a script [JAVA SCRIPT].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-30-320.jpg)


![VIJAY KUMAR L. SAROJ
ABHINAV AWASTHI
[S.Y.Bcom]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itassign-140303105422-phpapp02/85/basic-it-presentation-33-320.jpg)