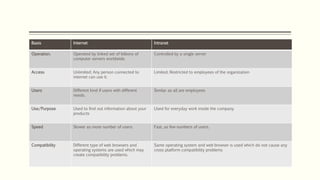
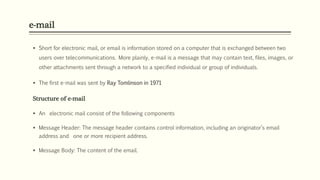
The document provides information on basics of internet, intranet, email, audio and video conferencing. It defines internet as a worldwide network of interconnected computer networks that transmit data. An intranet is a private network within an organization that uses internet protocols. Email consists of a header with sender/recipient fields and a message body. Audio and video conferencing allow real-time communication over the internet.