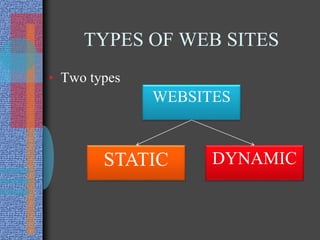
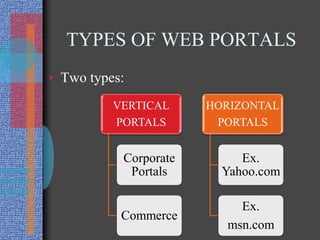
The document provides an introduction to the Internet. It describes the Internet as the largest network in the world that connects hundreds of thousands of individual networks. It moves ideas and information through cyberspace rather than physical space. The Internet has no single owner or formal management, and was originally developed by the Department of Defense. Common uses of the Internet include email, file transfers, discussion groups, and surfing the World Wide Web.