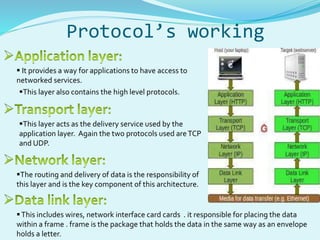
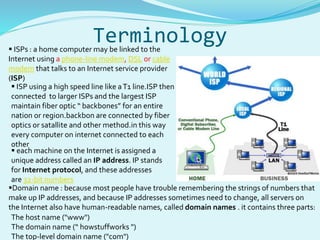
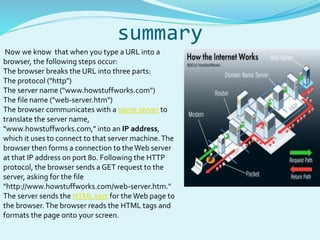
The document provides an overview of the internet, detailing its components, protocols, and workings, including hardware like routers and servers, as well as essential protocols such as TCP/IP and HTTP. It describes the processes involved when a browser accesses a website, translating URLs to IP addresses, and how information is transmitted over the internet. Terminology related to internet service providers, domain names, and the role of DNS servers is also explained.