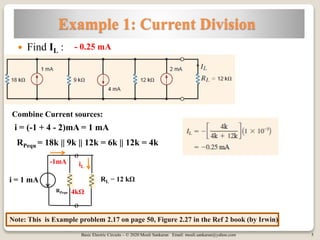
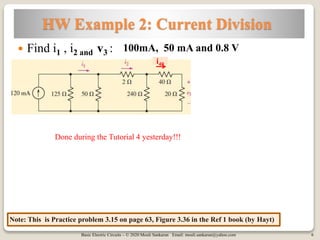
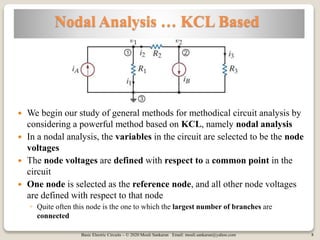
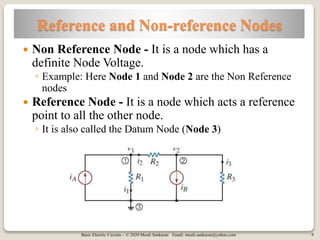
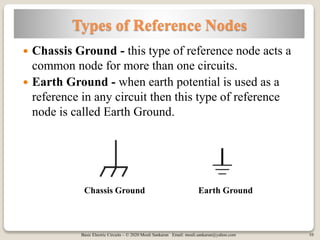
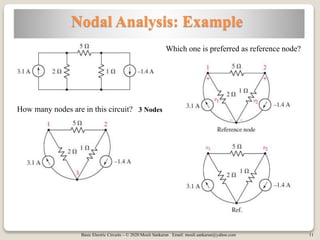
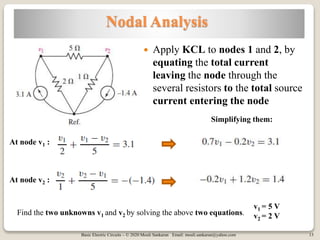
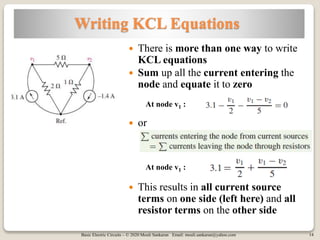
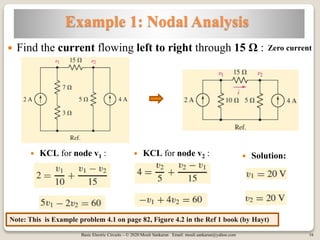
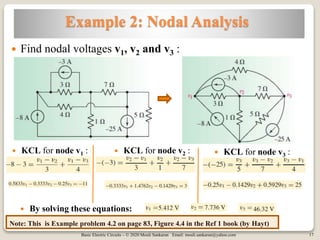
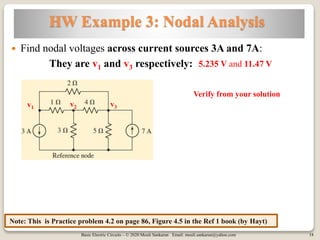
The document covers key concepts in basic electric circuits, focusing on current division and nodal analysis techniques. It discusses how to apply Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) to determine node voltages, including examples and practice problems. Additionally, it distinguishes between reference and non-reference nodes, highlighting the importance of selecting a reference node for circuit analysis.