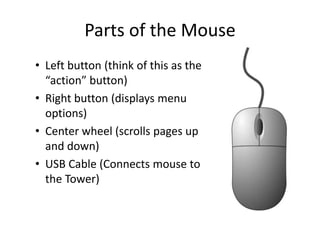
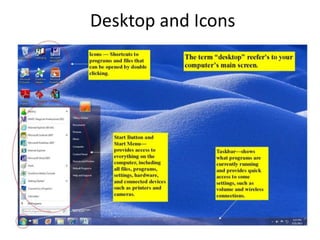
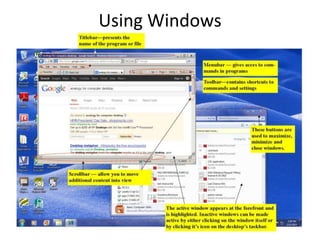
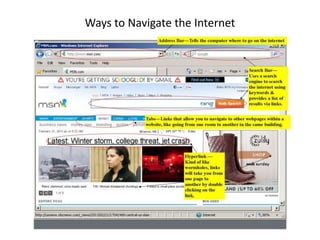
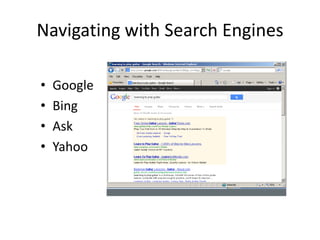
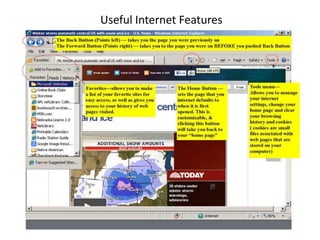
This document provides an introduction to basic computer skills, including identifying computer parts like the monitor, keyboard, and mouse. It describes how to use the mouse for common functions like clicking, dragging and dropping, and right-clicking. Keyboard functions like typing letters, numbers, and special keys are explained. The desktop and icons are introduced, as well as how to open and use windows. An overview of the internet is given along with methods for navigating it, including the address bar, search engines, hyperlinks, and tabs. Useful internet features like email are described. The document concludes with safety tips for using the internet.