This document provides an overview of intermediate computer skills, including:
- Using keyboard shortcuts like Ctrl+Alt+Del to manage programs and restart the computer.
- Connecting and using external devices like printers, scanners, and storage drives.
- Creating, organizing, moving, and deleting files on the computer and connected devices.
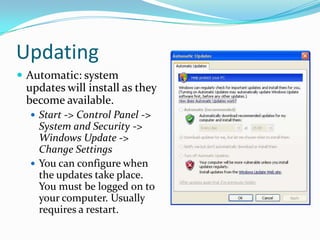
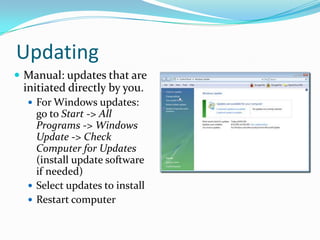
- Installing, uninstalling, and updating programs on the computer.
- Understanding the basics of Microsoft applications like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Publisher.
- Protecting the computer from malware and unauthorized access through software and physical security measures.