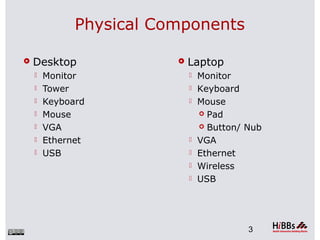
This document provides an overview of basic computer components, functions, and usage for Windows operating systems. It describes physical components such as the monitor, tower, keyboard, mouse, and ports. It explains how to power on the computer, log in, use input devices, and perform basic functions like opening programs. It also covers file systems, storage media, printers, and how to safely shut down the computer. The goal is to introduce general computer literacy to users new to Windows computers.