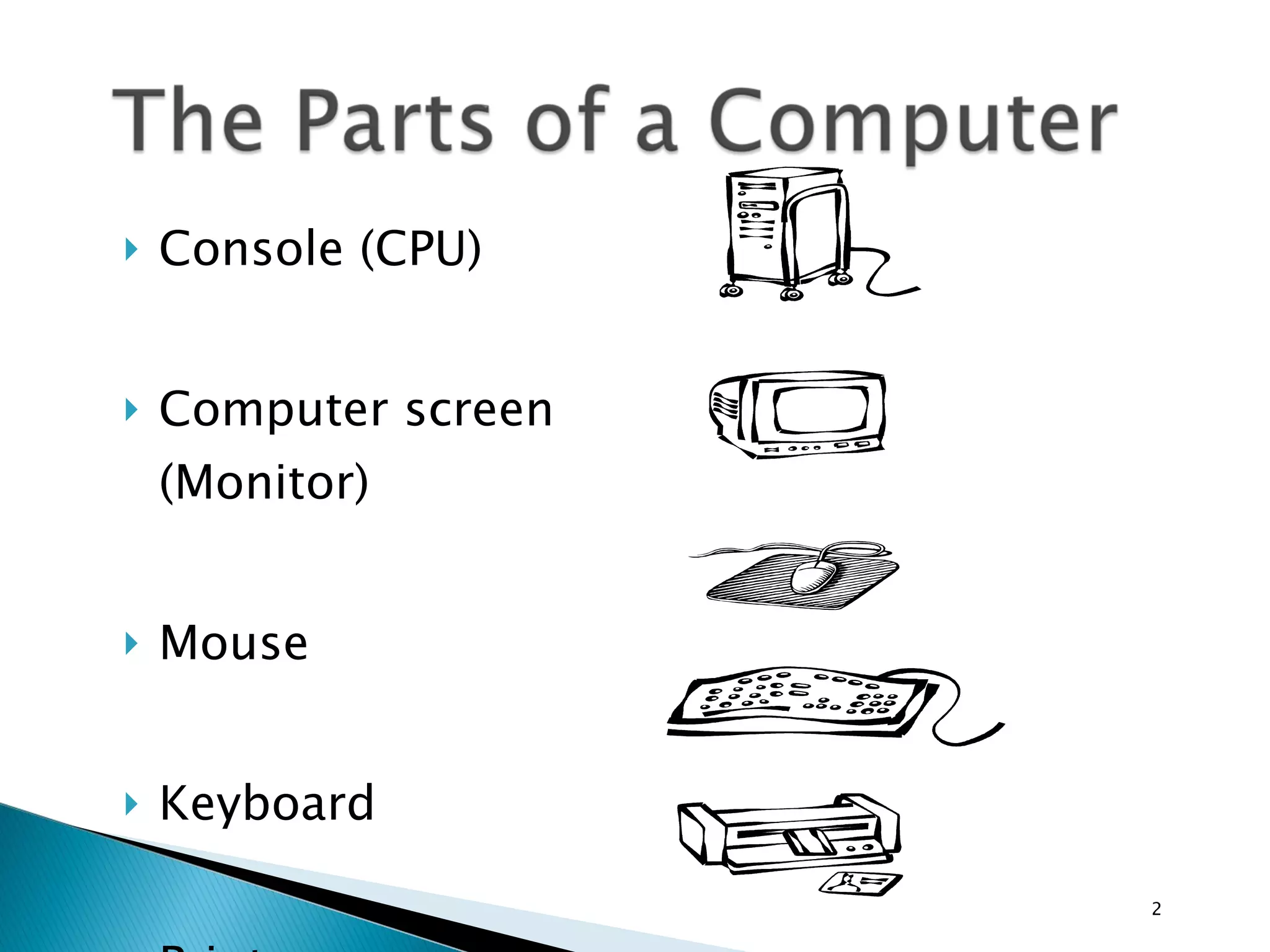
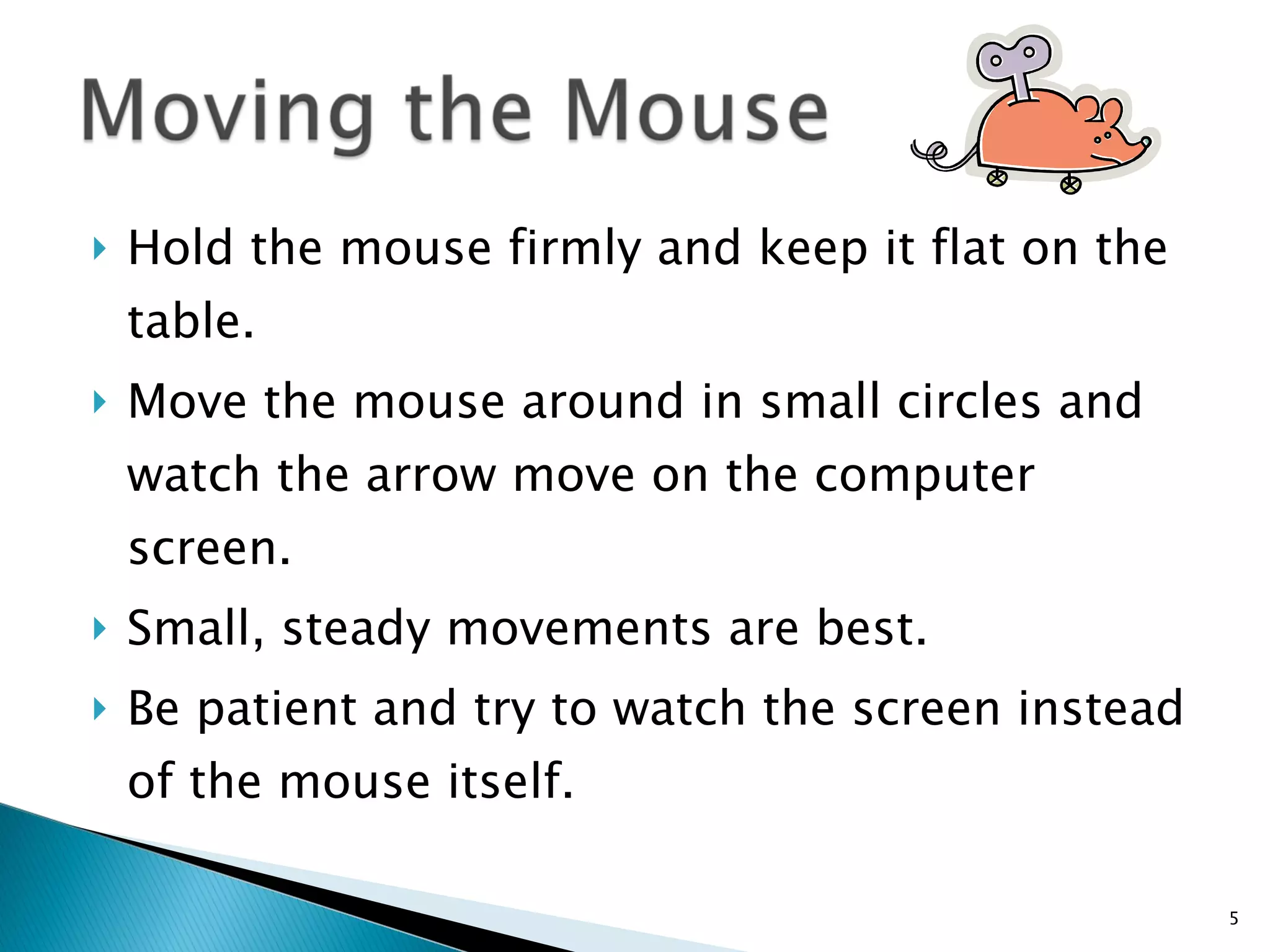
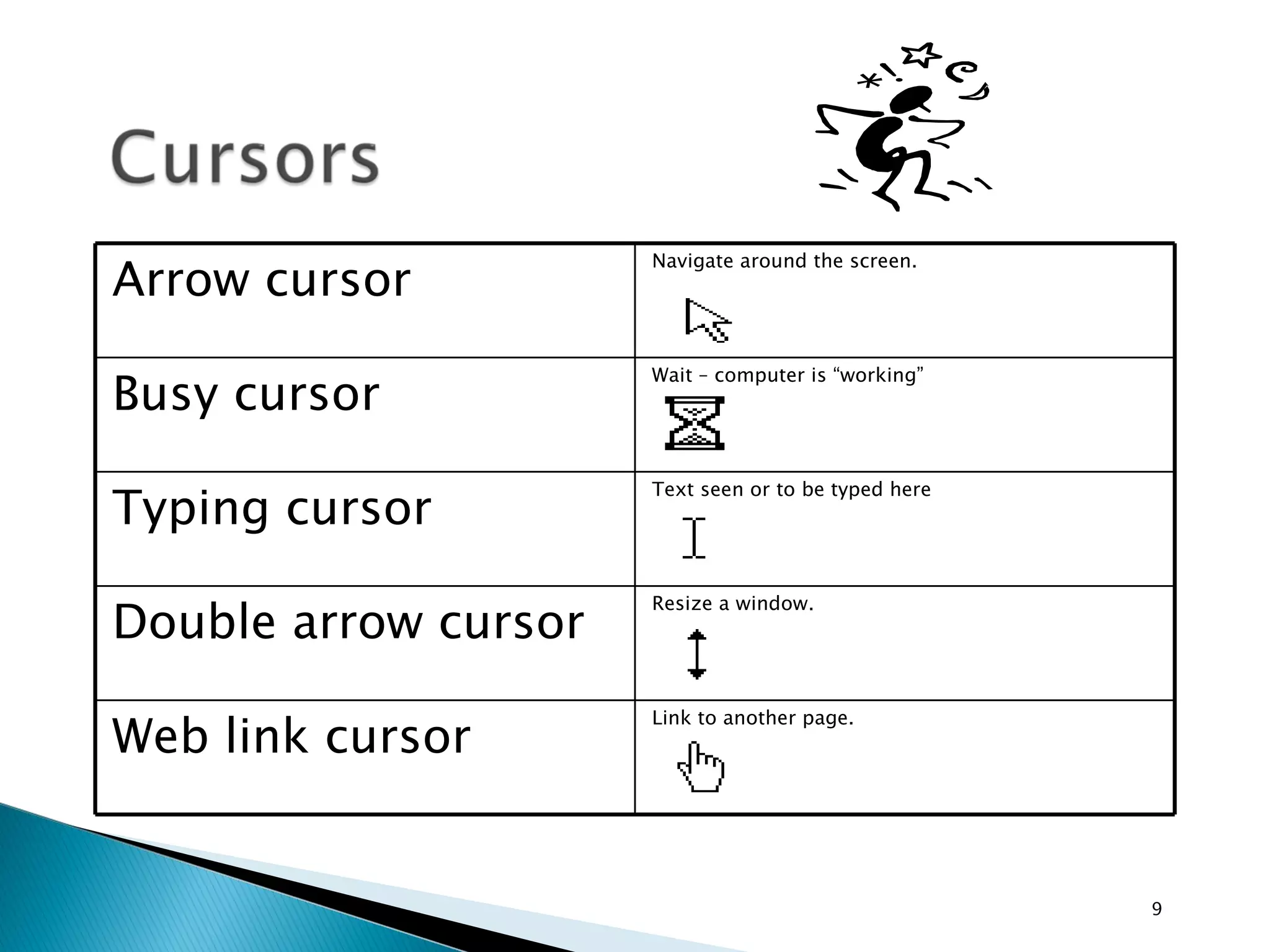
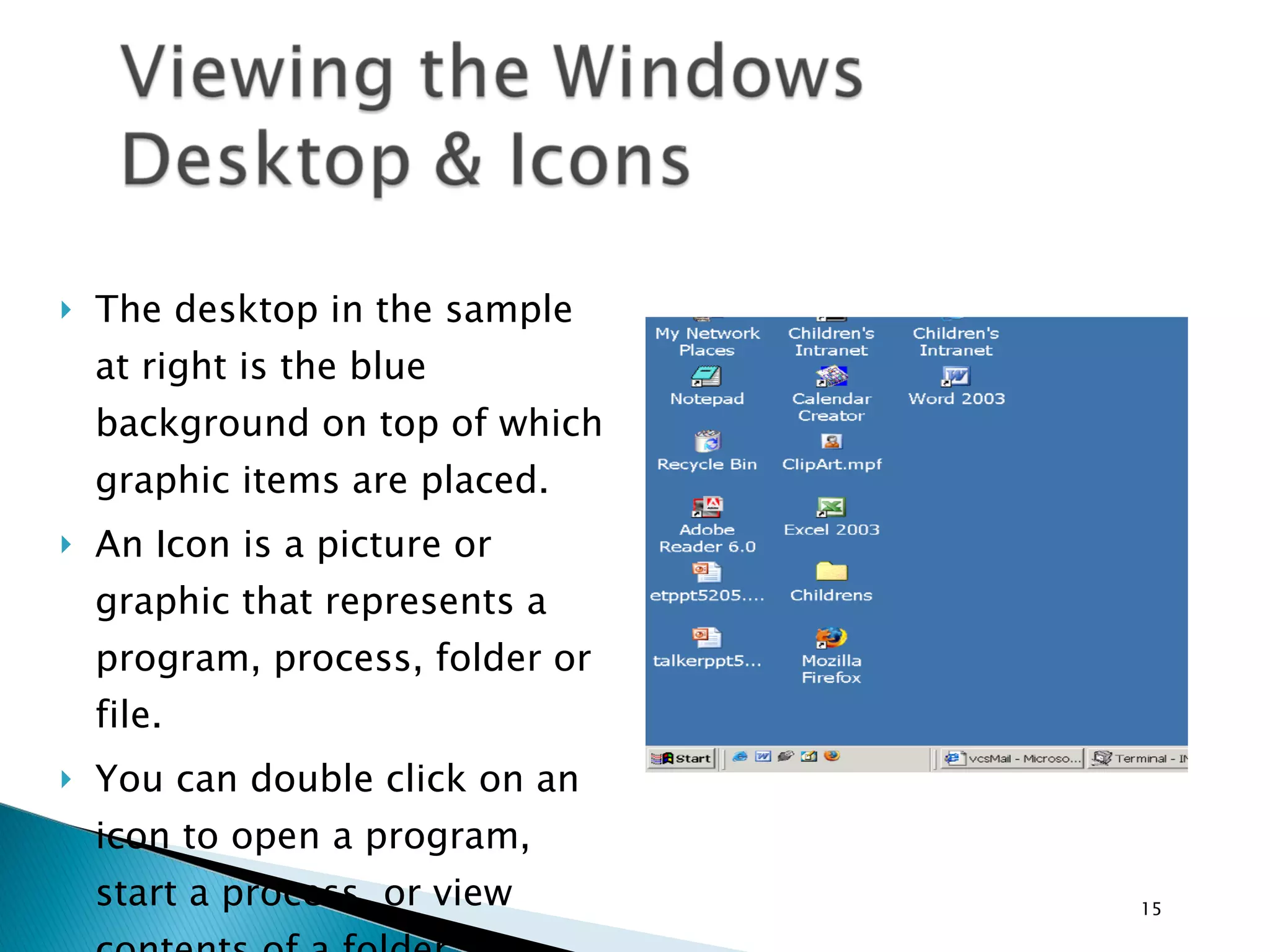
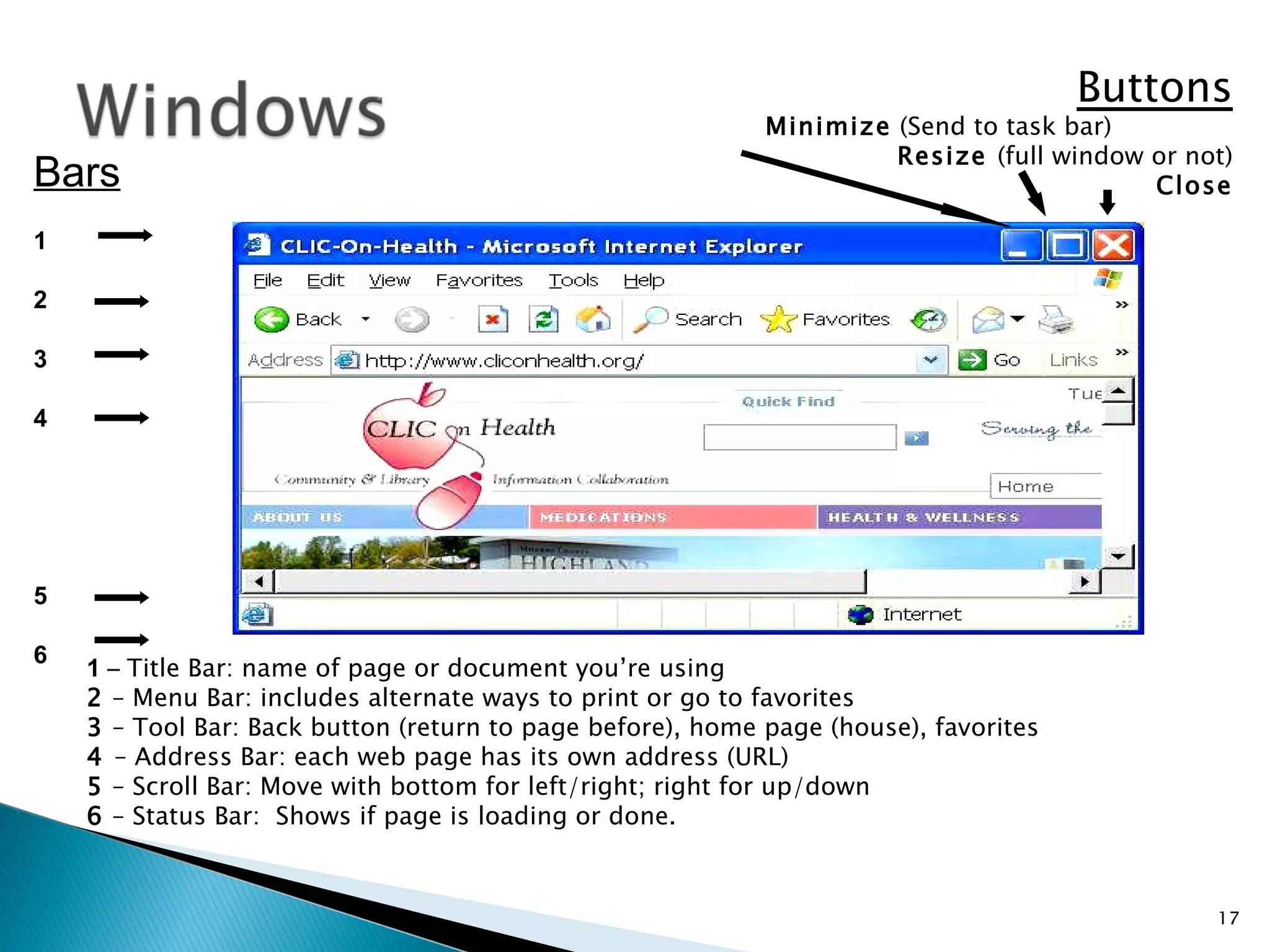
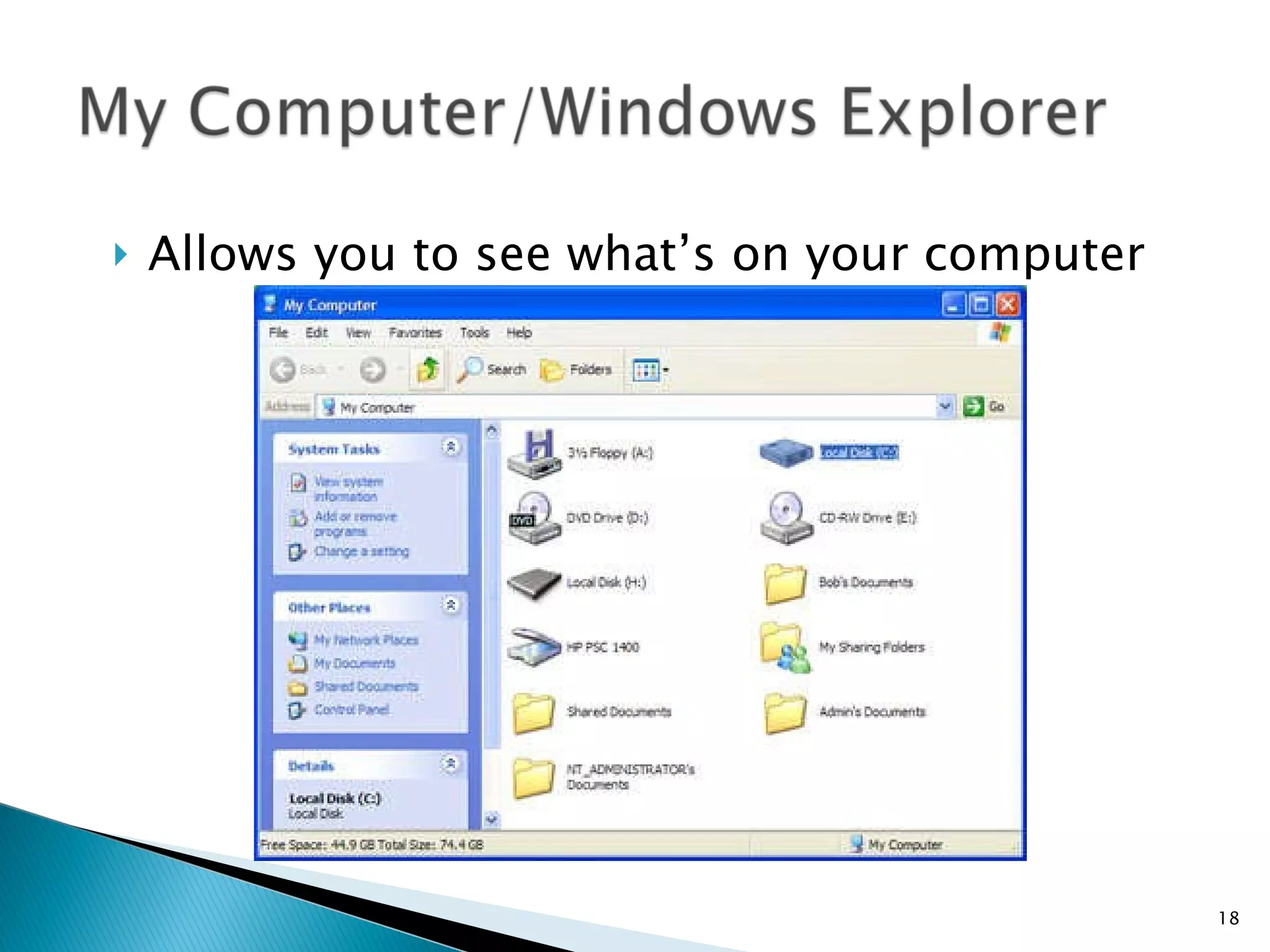
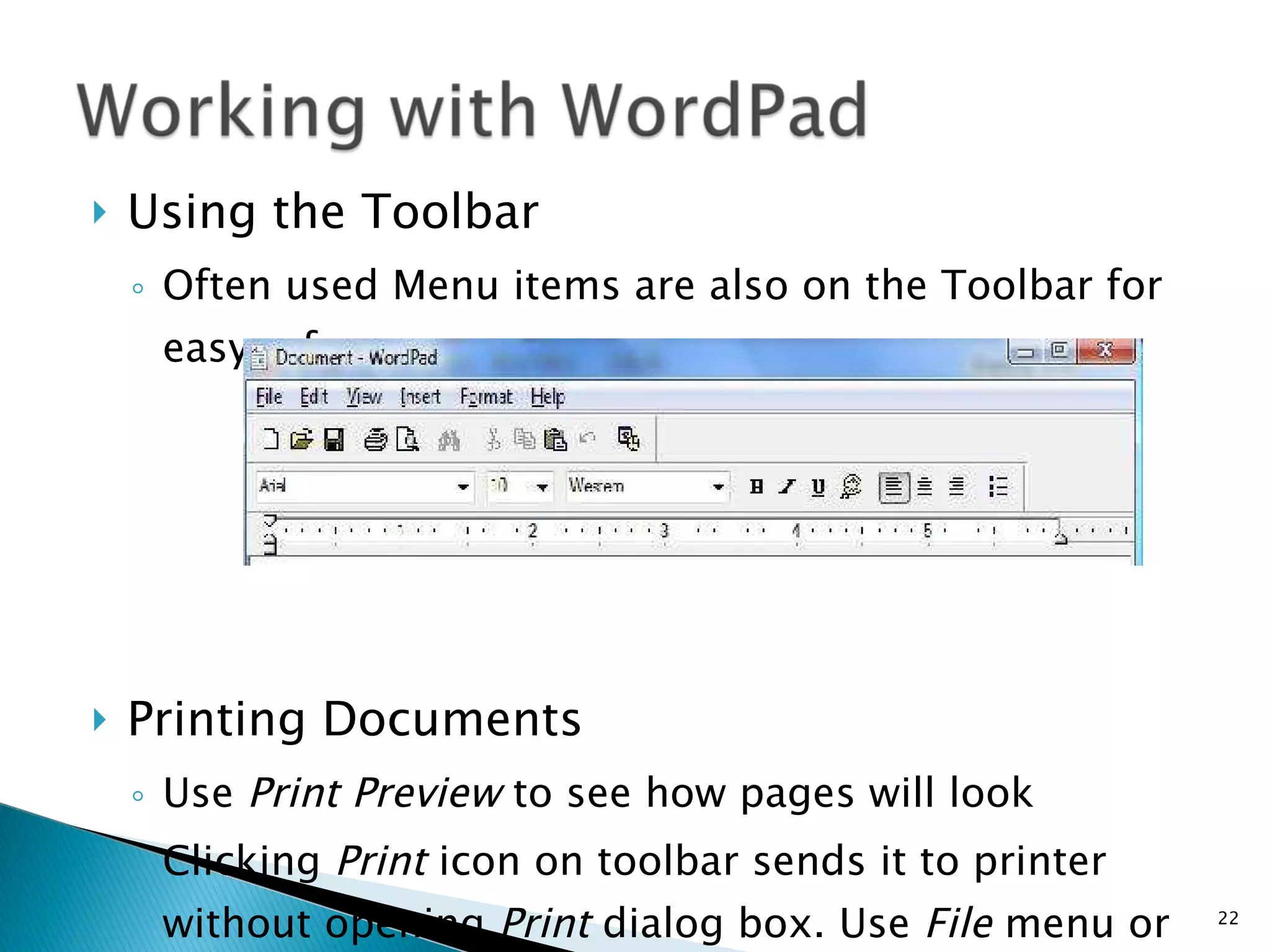
This document provides instructions for basic computer use, including an overview of common computer components like the monitor, mouse, and keyboard. It describes how to hold and move the mouse, the functions of the left and right mouse buttons. It also summarizes how to use icons, windows, menus and toolbars, and how to perform tasks like opening programs, selecting files, copying and pasting, using WordPad, and printing documents.