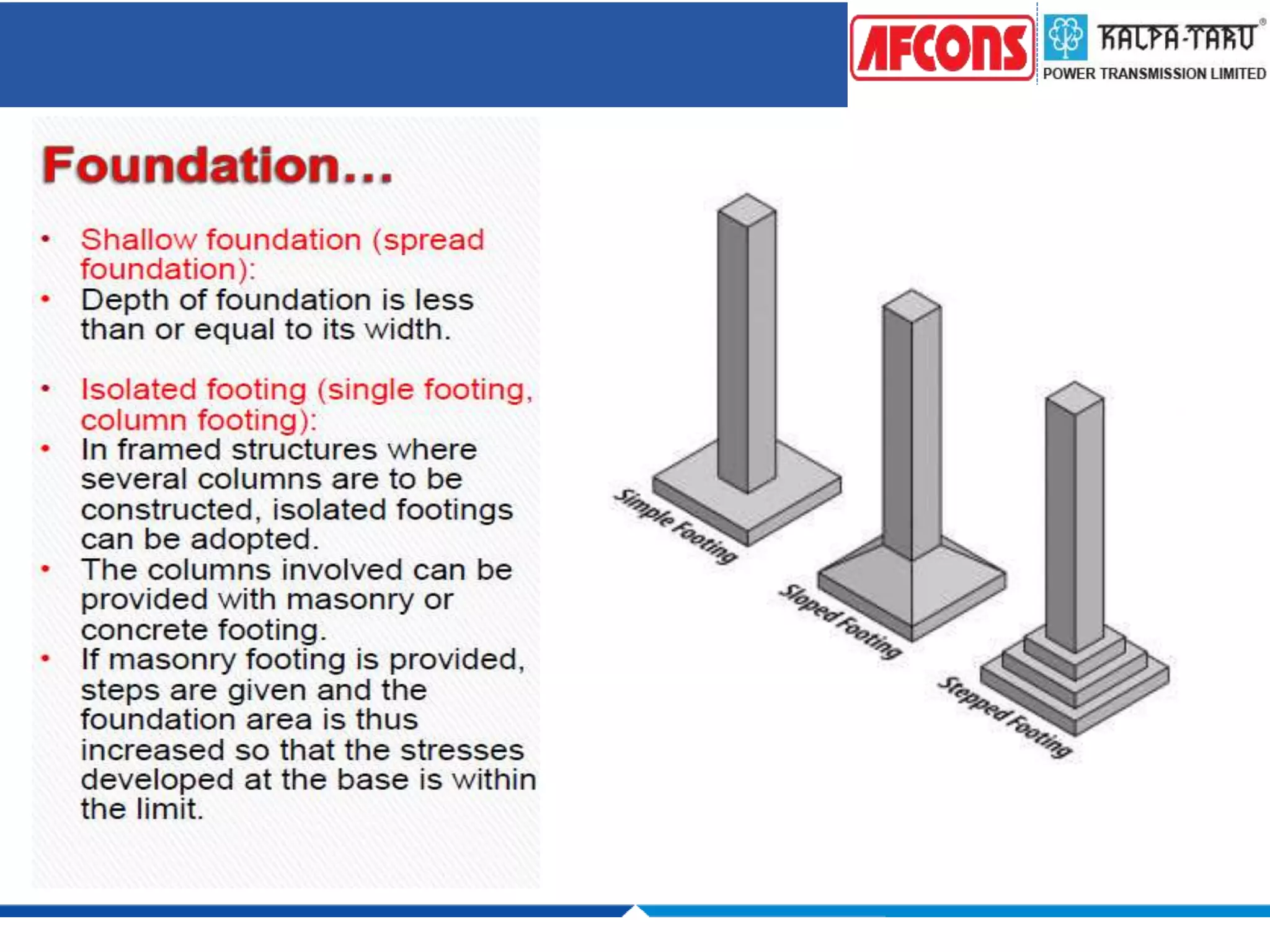
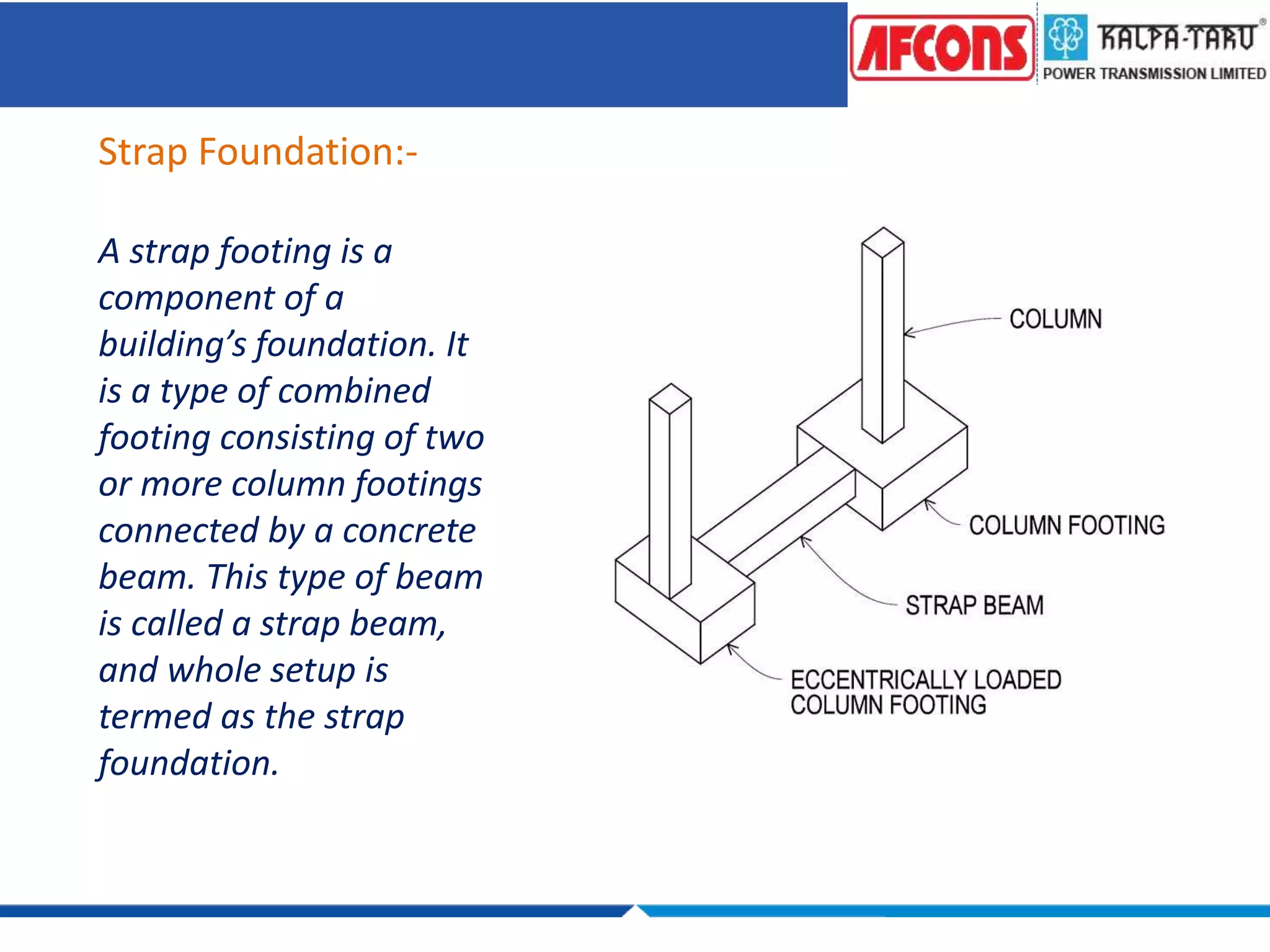
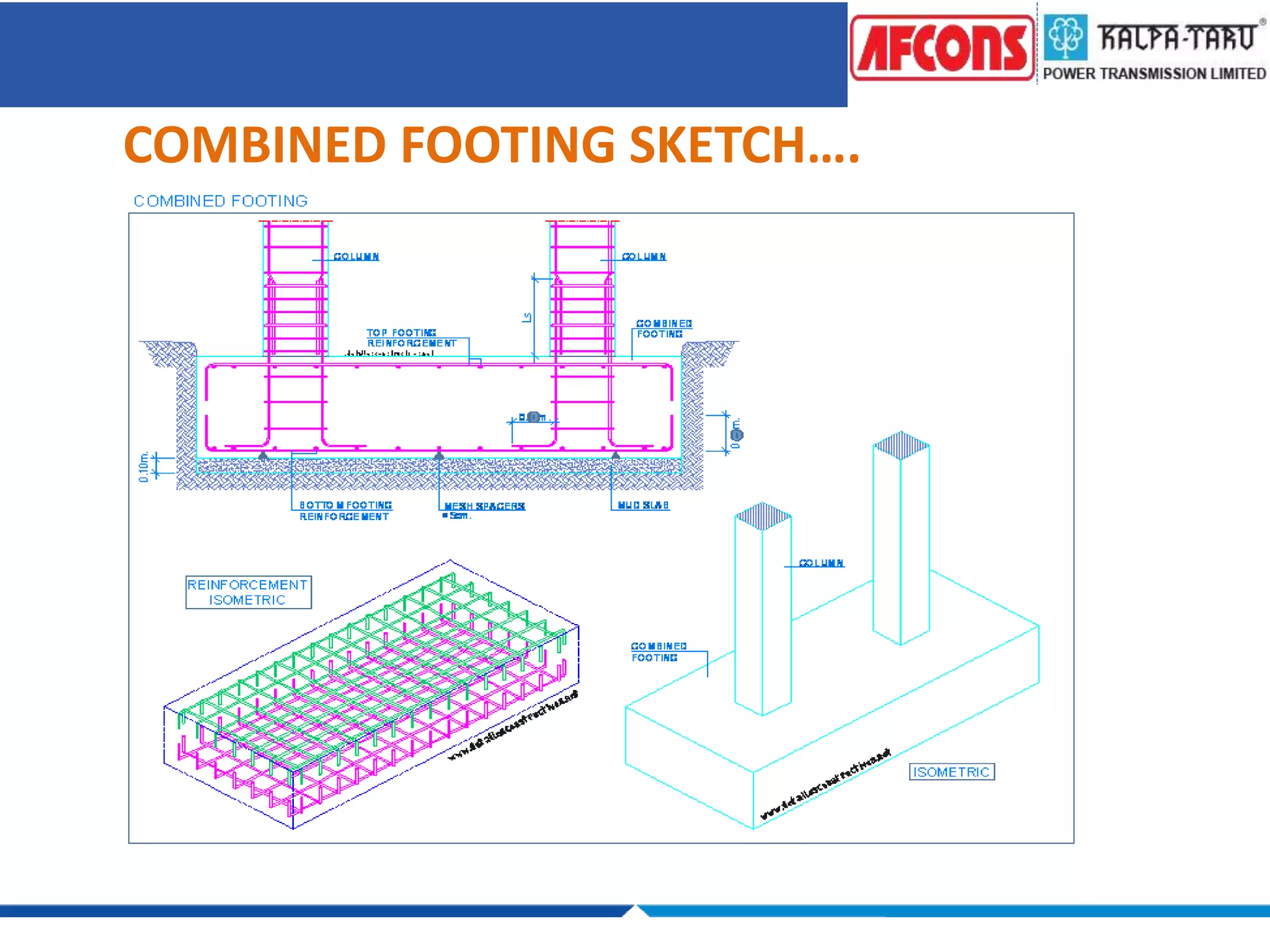
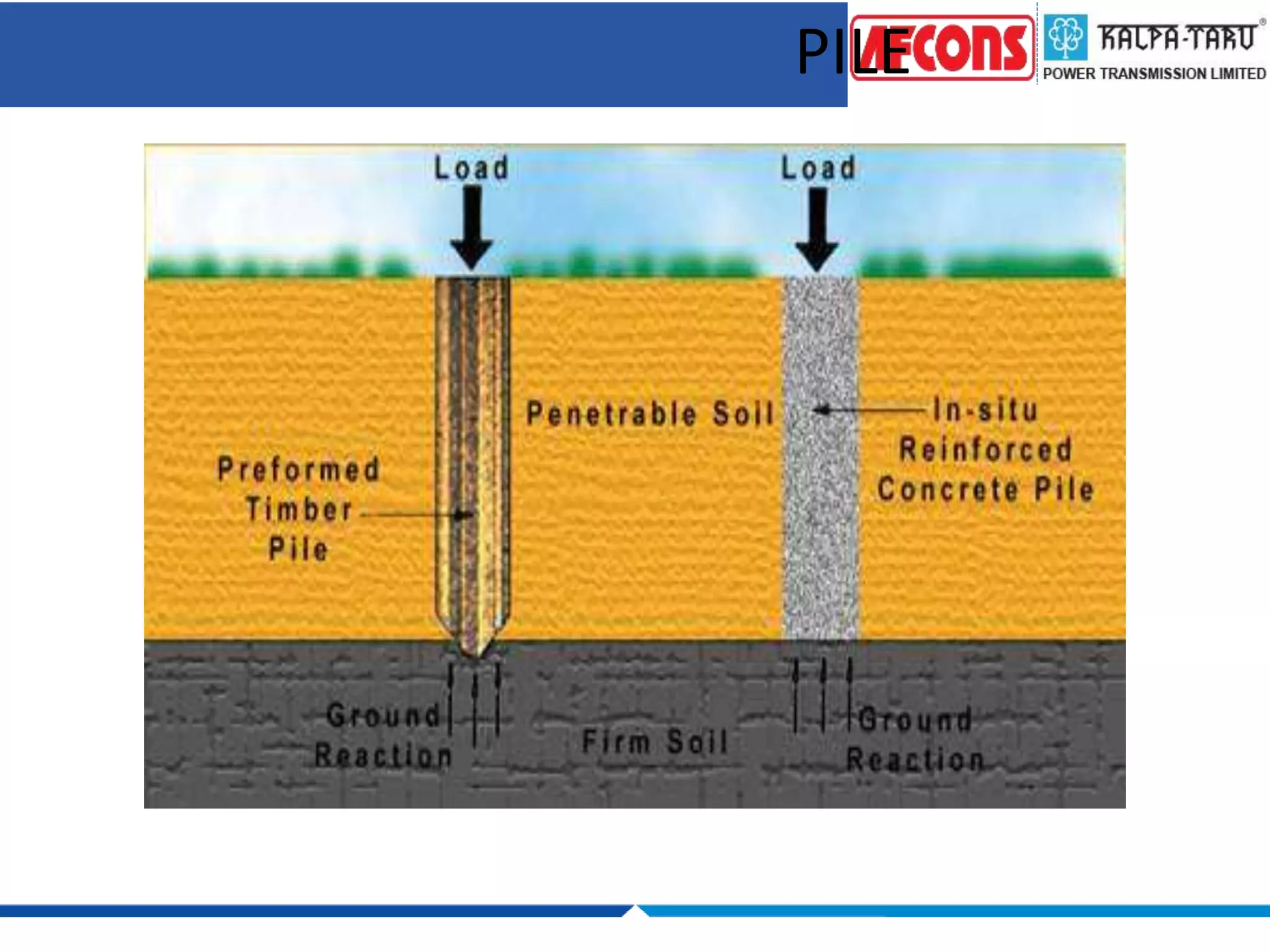
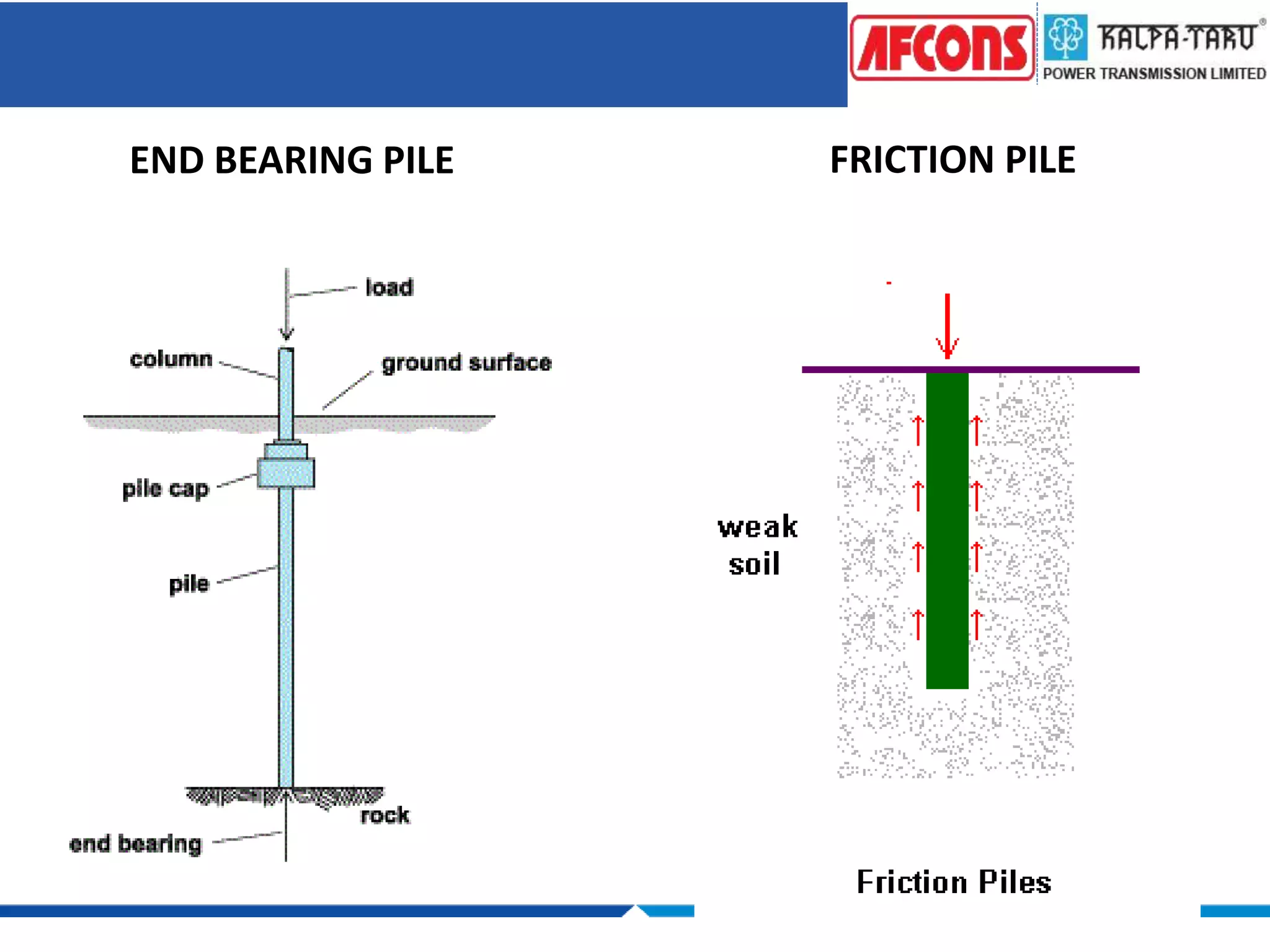
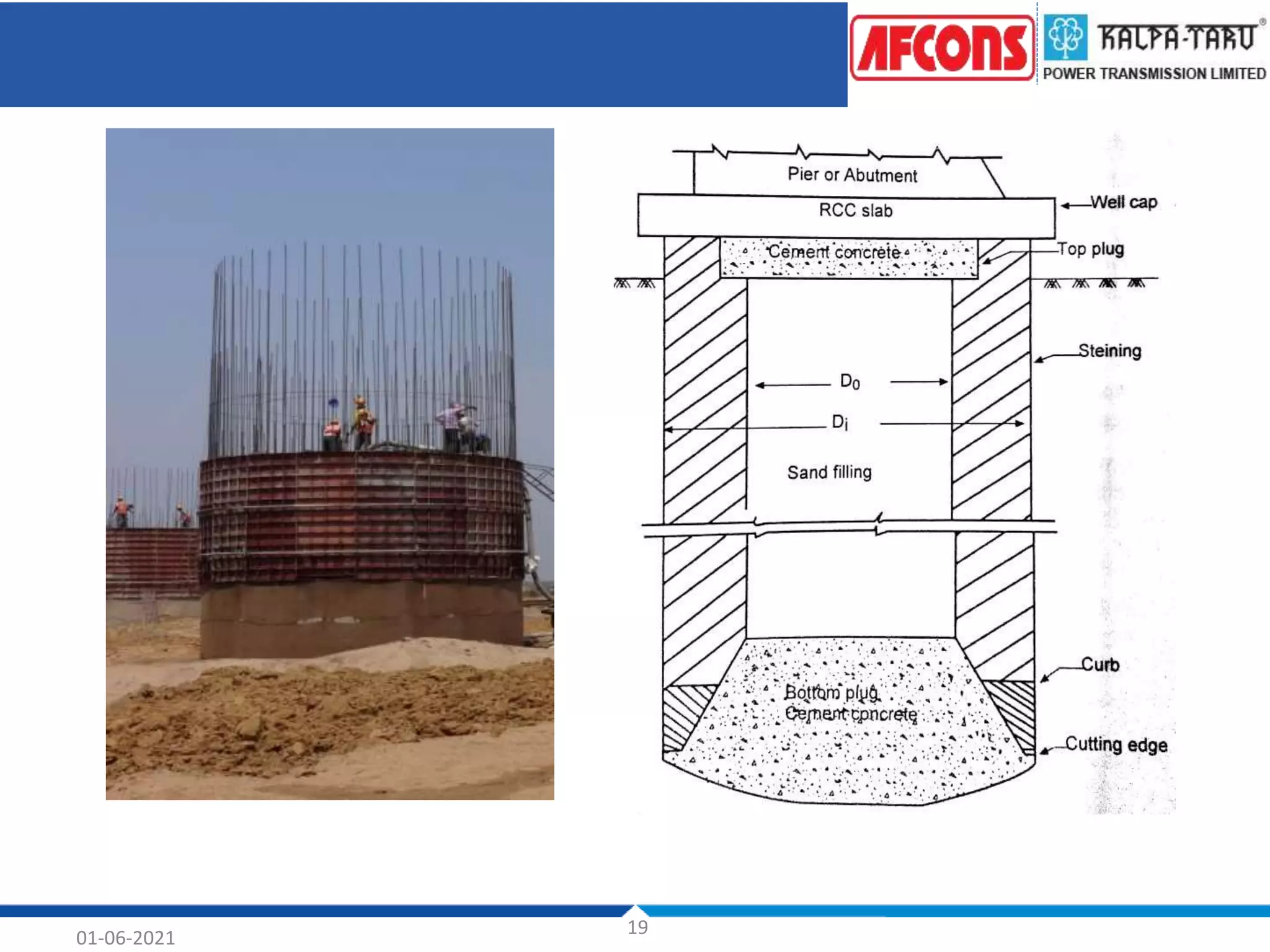
This document provides an overview of foundations and their design considerations. It discusses the key functions of foundations as transmitting loads to the soil below a structure. Foundations can be either shallow, such as isolated or combined footings, or deep such as pile or well foundations. Design is influenced by soil type, groundwater, and structural requirements. Pile foundations transmit loads through end bearing and friction, and can be made of materials like concrete, timber, steel, or composites.




![Where ,
p=safe bearing capacity of soil
w=unit weight of foundation soil
ᶲ=angle of internal friction
Depth of foundation:-
D=p/w[1-sinᶲ/1+sinᶲ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foundationppt-230128040158-c8db4f94/75/Foundation-and-types-7-2048.jpg)