Basic ap chapter 25 powerpoint 2017
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
1 like•2,607 views
The urinary system filters blood through glomeruli in the kidneys, which filter out large particles but allow small molecules like water, salts, and wastes to pass into the urine. Urine characteristics provide information about hydration and health status, and urinalysis can detect diseases. The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra work together to collect, store, and eliminate urine from the body, maintaining homeostasis of water and electrolyte levels. Dysfunction of the urinary system can disrupt this homeostasis and impact other body systems and health.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Anatomy of Circulatory system and lymphatic system 

lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body by collecting excess fluid and particulate matter from tissues and depositing them in the bloodstream
Splanchnic circulation

The splanchnic circulation supplies blood to the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, and liver. It has unique features like blood from the mesenteric bed and spleen draining primarily to the liver via the portal vein. Mesenteric blood flow is regulated by local autoregulation, gastrointestinal activity, nerves, and chemicals like hormones. The spleen stores a large blood volume and its flow is regulated by sympathetic nerves. The liver receives substantial blood flow from the hepatic artery and portal vein, and its flow is regulated by various systemic and local factors. Cutaneous circulation regulates heat loss and is controlled by the hypothalamus in response to body temperature changes. The Lewis triple response describes the local vascular response to skin stimuli.
Basic ap chapter 26 powerpoint 2017

The document discusses body fluids and electrolyte balance in the human body. It explains that the chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions inside and outside of cells. Water and solutes move between compartments through osmosis and filtration. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are important for nerve function, hormone secretion, and fluid balance. The kidneys play a key role in regulating water balance and electrolyte levels in the blood.
Cardiovascular System, Heart, Blood Vessel, ECG, Hypertension, Arrhythmia 

Cardiovascular System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology-I,
The Blood Vessels,
The Heart,
The Electrocardiogram,
The Vascular Pathways,
As per PCI syllabus,
Atherosclerosis,
Coronary bypass operation,
Heart Transplants and Artificial Hearts
Anatomy of Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and immune system. It is composed of a network of lymphatic vessels that carry lymph fluid towards the heart. Lymph contains plasma constituents too large to pass through blood capillaries, such as macroparticles from damaged areas. Lymphatic vessels originate as blind-ended tubes and contain valves to prevent backflow. They join to form larger vessels and ducts that drain into veins. Lymph nodes filter lymph and activate immune cells. Key lymphatic organs include the spleen, bone marrow, thymus gland and tonsils, which help generate and select lymphocytes.
URINARY SYSTEM. PHYSİCAL

The urinary system functions to maintain homeostasis by filtering the blood and regulating fluid balance, electrolyte and acid-base levels. The kidneys filter blood to form urine through glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied during micturition, which is facilitated by spinal and brain centers.
6. urinary system

Urinary System, Kidney, Nephron, Function of Kidney, Urinary System Disease, Process of urine formation- Glomerular Filtration, Re absorption, Secretion
Unit III, chapter-1-Body fluids and Blood

Body fluids serve as a medium for transporting nutrients and waste throughout the body. The most abundant body fluids are interstitial fluid and blood plasma. Total body fluid is distributed between extracellular fluid, containing interstitial fluid and plasma, and intracellular fluid within cells. Blood transports gases, nutrients, waste products, and helps regulate pH and temperature. Blood is composed of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Hematopoiesis is the formation of blood cells in the bone marrow from stem cells. Blood groups are classified by antigens on red blood cells in the ABO and Rh systems, which determine transfusion compatibility.
Recommended
Anatomy of Circulatory system and lymphatic system 

lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body by collecting excess fluid and particulate matter from tissues and depositing them in the bloodstream
Splanchnic circulation

The splanchnic circulation supplies blood to the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, and liver. It has unique features like blood from the mesenteric bed and spleen draining primarily to the liver via the portal vein. Mesenteric blood flow is regulated by local autoregulation, gastrointestinal activity, nerves, and chemicals like hormones. The spleen stores a large blood volume and its flow is regulated by sympathetic nerves. The liver receives substantial blood flow from the hepatic artery and portal vein, and its flow is regulated by various systemic and local factors. Cutaneous circulation regulates heat loss and is controlled by the hypothalamus in response to body temperature changes. The Lewis triple response describes the local vascular response to skin stimuli.
Basic ap chapter 26 powerpoint 2017

The document discusses body fluids and electrolyte balance in the human body. It explains that the chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions inside and outside of cells. Water and solutes move between compartments through osmosis and filtration. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are important for nerve function, hormone secretion, and fluid balance. The kidneys play a key role in regulating water balance and electrolyte levels in the blood.
Cardiovascular System, Heart, Blood Vessel, ECG, Hypertension, Arrhythmia 

Cardiovascular System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology-I,
The Blood Vessels,
The Heart,
The Electrocardiogram,
The Vascular Pathways,
As per PCI syllabus,
Atherosclerosis,
Coronary bypass operation,
Heart Transplants and Artificial Hearts
Anatomy of Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and immune system. It is composed of a network of lymphatic vessels that carry lymph fluid towards the heart. Lymph contains plasma constituents too large to pass through blood capillaries, such as macroparticles from damaged areas. Lymphatic vessels originate as blind-ended tubes and contain valves to prevent backflow. They join to form larger vessels and ducts that drain into veins. Lymph nodes filter lymph and activate immune cells. Key lymphatic organs include the spleen, bone marrow, thymus gland and tonsils, which help generate and select lymphocytes.
URINARY SYSTEM. PHYSİCAL

The urinary system functions to maintain homeostasis by filtering the blood and regulating fluid balance, electrolyte and acid-base levels. The kidneys filter blood to form urine through glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied during micturition, which is facilitated by spinal and brain centers.
6. urinary system

Urinary System, Kidney, Nephron, Function of Kidney, Urinary System Disease, Process of urine formation- Glomerular Filtration, Re absorption, Secretion
Unit III, chapter-1-Body fluids and Blood

Body fluids serve as a medium for transporting nutrients and waste throughout the body. The most abundant body fluids are interstitial fluid and blood plasma. Total body fluid is distributed between extracellular fluid, containing interstitial fluid and plasma, and intracellular fluid within cells. Blood transports gases, nutrients, waste products, and helps regulate pH and temperature. Blood is composed of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Hematopoiesis is the formation of blood cells in the bone marrow from stem cells. Blood groups are classified by antigens on red blood cells in the ABO and Rh systems, which determine transfusion compatibility.
Review on Anatomy and Physiology of cardiovascular system.

This system has three main components: the heart, the blood vessel and the blood itself. The heart is the system's pump and the blood vessels are like the delivery routes. Blood can be thought of as a fluid which contains the oxygen and nutrients the body needs and carries the wastes which need to be removed
4. body fluid & blood

Body fluids and blood
Body fluids, composition and functions of blood, hemopoeisis, formation of
hemoglobin, anemia, mechanisms of coagulation, blood grouping, Rh factors,
transfusion, its significance and disorders of blood, Reticulo endothelial system.
Circulatory System 

The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body via blood vessels. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - systemic circulation carries blood to the body and pulmonary circulation carries blood to and from the lungs. Blood flows from the heart through arteries, then narrows into smaller arterioles and capillaries where nutrients and gases are exchanged with body tissues before returning to the heart through veins. Maintaining healthy blood pressure can prevent circulatory diseases like heart attacks and strokes.
Group 3

The renal system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate electrolytes and fluid balance. They produce erythropoietin to stimulate red blood cell production and activate vitamin D to regulate calcium levels. Renal failure occurs when kidney function declines, leading to the buildup of waste and imbalances in fluid, electrolytes and acid-base levels. Treatment options for renal failure include dialysis and transplantation.
Urinary system

Urinary system
a) Anatomy and physiology of urinary system
b) Formation of urine
c) Renin Angiotensin system – Juxtaglomerular apparatus - acid base Balance
d) Clearance tests and micturition
Urinary System

The document provides an overview of the urinary system and kidney functions. It discusses the key parts of the urinary system including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. It then describes the internal anatomy and functions of the kidneys, including nephron structure and urine formation processes like glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. Key associated organs and blood supply to the kidneys are also outlined. The document concludes with discussing urinary tract disorders like kidney stones, infections, and renal failure.
Urinary system

The urinary system functions to maintain homeostasis by filtering the blood and regulating fluid balance, electrolyte and acid-base levels. The kidneys filter around 180 liters of plasma per day to form urine through glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied through the urethra in a process called micturition which is controlled by the brain and spinal cord.
Urinary system

The document provides an overview of the human urinary system including its main components and functions. It discusses the anatomy and physiology of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage. The bladder expels urine through the urethra under voluntary control. The document also describes urine composition and the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion involved in urine formation in the nephrons of the kidneys.
Biology:Transport in Humans (JYSS)

The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through a closed system of arteries, veins, and capillaries. It has four chambers - two atria which collect blood and two ventricles which pump blood. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones and waste products as it circulates. It contains plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The circulatory system transports these substances between tissues and organs via a network of blood vessels, and returns waste products to the kidneys and lungs.
Chapter 9 powerpoint

The document summarizes key aspects of the kidney and urinary system. It discusses the location and functions of the kidneys, components of urine like water and electrolytes. It further describes kidney conditions like Acute Tubular Necrosis, treatments for kidney failure including hemodialysis and access methods. It also outlines urinary tract infections and bladder neck obstruction, defining each and their associated symptoms and treatments.
BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION

This document summarizes the structure and function of blood and the circulatory system. It describes that blood is a connective tissue composed of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It also discusses the different blood types based on antigens on red blood cells. Furthermore, it explains the closed double circulatory system in humans, describing the structure and function of the heart in pumping blood through the arteries and veins to oxygenate tissues before returning to the heart.
ppt on Excretory system akki

The document discusses the key components and functions of the urinary system. It describes the kidneys, which filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine travels from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters. The bladder stores urine temporarily before it is excreted through the urethra. In addition to excretion, the kidneys play an important role in regulating fluid balance and blood pressure in the body.
The urinary system

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder, where it is stored until urination. When the bladder fills to a certain volume, urine is expelled through the urethra. The kidneys contain millions of nephrons, which are the functional filtering units that produce urine from blood plasma via glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Human urinary system

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood and produce urine by removing waste through small filtering units called nephrons. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder, where it is stored until excretion through the urethra. The main functions of the urinary system are to excrete waste, regulate water balance and electrolyte levels, and produce hormones to regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production.
Anatomy and Physilogy of Urinary System (Renal System)

The urinary system is responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine, while regulating water and electrolyte levels. Urine travels from the kidneys through ureters to the bladder, where it is stored until excreted through the urethra. The key parts are the kidneys, which contain nephrons that filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances; ureters, which transport urine from kidneys to bladder; and bladder, which stores urine until excretion. Together this system eliminates wastes and regulates fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
Blood and lymphatic system

Blood has four main functions: carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide, removing waste, transporting nutrients, and fighting infections. It contains red blood cells, which carry oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein. White blood cells help fight infection as part of the immune system. Platelets help blood clot to prevent excessive bleeding from injuries. Blood type is determined by antigens, and certain types cannot be mixed in transfusions. Diseases of the blood include anemias like sickle cell anemia and leukemias, in which too many white blood cells are produced. The lymphatic system carries lymph containing white blood cells and filters it through lymph nodes to fight infection. AIDS weakens this system by infect
Excretory system in Human (Class 10)

Life of every organism depends on certain basic processes. Excretion is one among them. Different organisms follow different modes of excretion. In complex organisms including humans, there is a specialized system for excretion called human excretory system.
Excretory system

The document summarizes the human excretory system. The skin and kidneys are the main excretory organs, with the kidneys filtering blood and removing waste from the body. The kidneys regulate water and salt concentrations in the body through a process called osmoregulation. The basic unit of the kidney is the nephron, which filters blood and selectively reabsorbs nutrients while excreting waste as urine. Urine is stored in the bladder and released through the urethra.
Kidney anatomy - Almaskhan .khorfakhan hospital

The document provides information about kidney anatomy, physiology, and imaging. It describes the location and external anatomy of the kidneys, their internal anatomy including the cortex and medulla, and their three surrounding tissue layers. Key functions of the kidneys including homeostasis, filtering blood, and excretion of waste are summarized. Common kidney conditions like stones, cysts, cancers, and failures are outlined. Imaging modalities for evaluating the kidneys like ultrasound, biopsy, x-ray, CT and MRI are listed, along with contrast administration protocols and tips for CT of the kidneys.
Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary System

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine passes from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters. The bladder stores urine until micturition. The urethra then carries urine out of the body. The urinary system regulates water balance and the levels of electrolytes, acids, and bases in the blood to maintain homeostasis. Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter blood and form urine through processes like filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Kidney structure & function

The kidney is made up of approximately 1 million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron contains a glomerulus for initial blood filtration and a tubule for reabsorption and waste excretion. The kidneys play crucial roles in regulating blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and removing waste from the blood in the form of urine. Common kidney functions include filtering the blood, reabsorbing necessary nutrients, and secreting hormones to support other bodily processes. Damage to the kidneys can impair these functions and potentially lead to serious health issues like kidney failure.
Nephrology

general nephrology, disorders of the male reproductive system, disorders of the female reproductive system
More Related Content
What's hot
Review on Anatomy and Physiology of cardiovascular system.

This system has three main components: the heart, the blood vessel and the blood itself. The heart is the system's pump and the blood vessels are like the delivery routes. Blood can be thought of as a fluid which contains the oxygen and nutrients the body needs and carries the wastes which need to be removed
4. body fluid & blood

Body fluids and blood
Body fluids, composition and functions of blood, hemopoeisis, formation of
hemoglobin, anemia, mechanisms of coagulation, blood grouping, Rh factors,
transfusion, its significance and disorders of blood, Reticulo endothelial system.
Circulatory System 

The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body via blood vessels. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - systemic circulation carries blood to the body and pulmonary circulation carries blood to and from the lungs. Blood flows from the heart through arteries, then narrows into smaller arterioles and capillaries where nutrients and gases are exchanged with body tissues before returning to the heart through veins. Maintaining healthy blood pressure can prevent circulatory diseases like heart attacks and strokes.
Group 3

The renal system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate electrolytes and fluid balance. They produce erythropoietin to stimulate red blood cell production and activate vitamin D to regulate calcium levels. Renal failure occurs when kidney function declines, leading to the buildup of waste and imbalances in fluid, electrolytes and acid-base levels. Treatment options for renal failure include dialysis and transplantation.
Urinary system

Urinary system
a) Anatomy and physiology of urinary system
b) Formation of urine
c) Renin Angiotensin system – Juxtaglomerular apparatus - acid base Balance
d) Clearance tests and micturition
Urinary System

The document provides an overview of the urinary system and kidney functions. It discusses the key parts of the urinary system including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. It then describes the internal anatomy and functions of the kidneys, including nephron structure and urine formation processes like glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. Key associated organs and blood supply to the kidneys are also outlined. The document concludes with discussing urinary tract disorders like kidney stones, infections, and renal failure.
Urinary system

The urinary system functions to maintain homeostasis by filtering the blood and regulating fluid balance, electrolyte and acid-base levels. The kidneys filter around 180 liters of plasma per day to form urine through glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied through the urethra in a process called micturition which is controlled by the brain and spinal cord.
Urinary system

The document provides an overview of the human urinary system including its main components and functions. It discusses the anatomy and physiology of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage. The bladder expels urine through the urethra under voluntary control. The document also describes urine composition and the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion involved in urine formation in the nephrons of the kidneys.
Biology:Transport in Humans (JYSS)

The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through a closed system of arteries, veins, and capillaries. It has four chambers - two atria which collect blood and two ventricles which pump blood. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones and waste products as it circulates. It contains plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The circulatory system transports these substances between tissues and organs via a network of blood vessels, and returns waste products to the kidneys and lungs.
Chapter 9 powerpoint

The document summarizes key aspects of the kidney and urinary system. It discusses the location and functions of the kidneys, components of urine like water and electrolytes. It further describes kidney conditions like Acute Tubular Necrosis, treatments for kidney failure including hemodialysis and access methods. It also outlines urinary tract infections and bladder neck obstruction, defining each and their associated symptoms and treatments.
BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION

This document summarizes the structure and function of blood and the circulatory system. It describes that blood is a connective tissue composed of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It also discusses the different blood types based on antigens on red blood cells. Furthermore, it explains the closed double circulatory system in humans, describing the structure and function of the heart in pumping blood through the arteries and veins to oxygenate tissues before returning to the heart.
ppt on Excretory system akki

The document discusses the key components and functions of the urinary system. It describes the kidneys, which filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine travels from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters. The bladder stores urine temporarily before it is excreted through the urethra. In addition to excretion, the kidneys play an important role in regulating fluid balance and blood pressure in the body.
The urinary system

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder, where it is stored until urination. When the bladder fills to a certain volume, urine is expelled through the urethra. The kidneys contain millions of nephrons, which are the functional filtering units that produce urine from blood plasma via glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Human urinary system

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood and produce urine by removing waste through small filtering units called nephrons. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder, where it is stored until excretion through the urethra. The main functions of the urinary system are to excrete waste, regulate water balance and electrolyte levels, and produce hormones to regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production.
Anatomy and Physilogy of Urinary System (Renal System)

The urinary system is responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine, while regulating water and electrolyte levels. Urine travels from the kidneys through ureters to the bladder, where it is stored until excreted through the urethra. The key parts are the kidneys, which contain nephrons that filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances; ureters, which transport urine from kidneys to bladder; and bladder, which stores urine until excretion. Together this system eliminates wastes and regulates fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
Blood and lymphatic system

Blood has four main functions: carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide, removing waste, transporting nutrients, and fighting infections. It contains red blood cells, which carry oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein. White blood cells help fight infection as part of the immune system. Platelets help blood clot to prevent excessive bleeding from injuries. Blood type is determined by antigens, and certain types cannot be mixed in transfusions. Diseases of the blood include anemias like sickle cell anemia and leukemias, in which too many white blood cells are produced. The lymphatic system carries lymph containing white blood cells and filters it through lymph nodes to fight infection. AIDS weakens this system by infect
Excretory system in Human (Class 10)

Life of every organism depends on certain basic processes. Excretion is one among them. Different organisms follow different modes of excretion. In complex organisms including humans, there is a specialized system for excretion called human excretory system.
Excretory system

The document summarizes the human excretory system. The skin and kidneys are the main excretory organs, with the kidneys filtering blood and removing waste from the body. The kidneys regulate water and salt concentrations in the body through a process called osmoregulation. The basic unit of the kidney is the nephron, which filters blood and selectively reabsorbs nutrients while excreting waste as urine. Urine is stored in the bladder and released through the urethra.
Kidney anatomy - Almaskhan .khorfakhan hospital

The document provides information about kidney anatomy, physiology, and imaging. It describes the location and external anatomy of the kidneys, their internal anatomy including the cortex and medulla, and their three surrounding tissue layers. Key functions of the kidneys including homeostasis, filtering blood, and excretion of waste are summarized. Common kidney conditions like stones, cysts, cancers, and failures are outlined. Imaging modalities for evaluating the kidneys like ultrasound, biopsy, x-ray, CT and MRI are listed, along with contrast administration protocols and tips for CT of the kidneys.
Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary System

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The urine passes from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters. The bladder stores urine until micturition. The urethra then carries urine out of the body. The urinary system regulates water balance and the levels of electrolytes, acids, and bases in the blood to maintain homeostasis. Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter blood and form urine through processes like filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
What's hot (20)
Review on Anatomy and Physiology of cardiovascular system.

Review on Anatomy and Physiology of cardiovascular system.
Anatomy and Physilogy of Urinary System (Renal System)

Anatomy and Physilogy of Urinary System (Renal System)
Similar to Basic ap chapter 25 powerpoint 2017
Kidney structure & function

The kidney is made up of approximately 1 million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron contains a glomerulus for initial blood filtration and a tubule for reabsorption and waste excretion. The kidneys play crucial roles in regulating blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and removing waste from the blood in the form of urine. Common kidney functions include filtering the blood, reabsorbing necessary nutrients, and secreting hormones to support other bodily processes. Damage to the kidneys can impair these functions and potentially lead to serious health issues like kidney failure.
Nephrology

general nephrology, disorders of the male reproductive system, disorders of the female reproductive system
Acute and chronic renal failure 2.pptx

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, which then passes through the ureters into the bladder. The bladder stores urine until urination, when it passes through the urethra. Together this system eliminates waste from the body and regulates fluid and electrolyte balance. Chronic kidney disease results in the gradual loss of kidney function over time due to damage and scarring of the kidneys. It has multiple causes and stages of severity, eventually progressing to kidney failure if untreated.
Urinary elimination

The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, which work together to produce and excrete urine. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder. When full, the bladder empties through the urethra. Urine contains water and waste products like urea, salts, and other dissolved substances. Dysfunctions like incontinence, retention, infection, or changes in urine production can indicate underlying issues.
Presentation1

The kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate fluid balance and electrolytes. Kidney failure occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to adequately perform these functions. Symptoms of kidney failure include fatigue, shortness of breath, and edema. Diagnosis involves blood and urine tests to measure waste and electrolyte levels. Treatment options for kidney failure include managing the underlying cause, medications to control symptoms, dialysis to filter the blood, and kidney transplantation.
Water, Electrolyte and acid-base balance.pptx

This document discusses water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance in the human body. It covers several key points:
- Water makes up about 60% of the human body and is essential for biochemical reactions and transport. The body carefully regulates water intake, output, and distribution between intracellular and extracellular fluid.
- Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are important for maintaining fluid balance and osmotic pressure. The kidneys play a key role in regulating electrolyte concentrations through hormones.
- Acid-base balance is critical and maintained through buffers, respiratory and renal systems that regulate bicarbonate and carbon dioxide levels to keep blood pH between 7.35-7.45. Dis
Human excretory system

The human excretory system removes waste from the body through organs like the lungs, skin, colon and kidneys. The kidneys play a key role by filtering the blood to remove urea and other toxins, regulating electrolyte and acid-base balance, and controlling blood pressure. Each kidney contains millions of nephrons, the functional units that filter blood via glomeruli and tubules to produce urine, which is then stored in the bladder and expelled via the urethra. The excretory system is vital for maintaining homeostasis by regulating water balance and removing metabolic waste.
Nutritional Management of Renal Diseases

The document provides information on the nutritional management of renal diseases. It discusses the structure and function of the kidneys, defines common renal diseases like glomerulonephritis and chronic renal failure, and their symptoms. It also describes the process of hemodialysis and dietary management for different kidney conditions like nephrotic syndrome and acute renal failure. The goal is to control waste levels, electrolyte balance, fluid retention and nutritional needs for patients with impaired renal function.
artificial kidney

The document summarizes a seminar presentation on artificial kidneys. It introduces the topic of artificial kidneys and dialysis machines, which are used to filter blood when the kidneys are damaged or failing. It describes how dialysis machines work by using a semi-permeable membrane to separate waste and excess water from the blood. The document also outlines some of the causes and symptoms of renal failure, as well as diet and treatment considerations for patients undergoing dialysis.
Mechanism of Urine formation in human beings.pdf

The document summarizes the mechanism of urine formation. It involves three main stages: glomerular filtration, selective reabsorption, and tubular secretion. In glomerular filtration, the kidneys filter blood in the glomerulus to form nephric filtrate. Then in selective reabsorption, the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule reabsorb useful substances like water, glucose and electrolytes. Finally, in tubular secretion unwanted substances are secreted into the filtrate to be excreted in urine. Through these stages, the kidneys eliminate waste from the body and regulate fluid and electrolyte balance.
lecture 7 renal system copy.ppt

This document provides an overview of renal physiology topics taught by Dr. Joseph Somuah Akuamoah at Kaaf University. It discusses multiple functions of the kidney including excretion of waste, regulation of fluids and electrolytes, and hormone regulation. It describes urine transport through the ureters and bladder. Key concepts covered include glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion, urine concentration and dilution, and causes of diseases like nephrotic syndrome and acute renal failure.
Fluid &electrolyte balance

This document discusses fluid and electrolyte balance in the human body. It covers the following key points:
- Approximately 60% of the adult body weight is made up of fluid and electrolytes.
- Fluids are regulated through processes like osmosis, diffusion, and filtration. Key organs like the kidneys, heart, lungs, and endocrine glands help maintain fluid homeostasis.
- Electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia and hyperkalemia are discussed in detail, including their causes, signs/symptoms, and treatment approaches.
- Proper fluid and electrolyte balance is essential for life and is tightly regulated through various physiological mechanisms.
renal

The document provides information on dietary modifications for renal disorders. It discusses the functions of the kidneys and defines acute and chronic renal diseases. For acute renal diseases, it outlines symptoms, risk factors, causes, diagnosis, treatment including diet modifications and dialysis. For chronic renal disease, it again discusses symptoms, causes and complications. It provides dietary guidelines for renal disease not requiring dialysis, including the DASH diet. Diet recommendations are tailored based on kidney disease stage and include limiting protein, sodium and phosphorus.
Urine and urinalysis

Urine is the body's liquid waste composed of water, salt urea and uric acid. Urine can be evaluated by its physical appearance (color, cloudiness, odor, clarity), also referred to as a macroscopic analysis. It can be also analyzed based on its chemical and molecular properties, including microscopic assessment.
Excretion 2015

The document summarizes key concepts about excretion and the urinary system. It discusses (1) how the kidneys produce urine through ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption, (2) how anti-diuretic hormone regulates water concentration in the blood through urine production, and (3) how dialysis can remove waste when the kidneys fail by diffusion across a semi-permeable membrane.
dietary modification of renal disorder

The document provides information on dietary modifications for renal disorders. It discusses the DASH diet which limits protein, sodium, and potassium and has been recommended for renal disease. It also outlines dietary guidelines based on stages of kidney disease, including limiting protein, sodium, and phosphorus. The guidelines provide daily serving recommendations from food groups for a 2,200 calorie renal diet.
Fluid and electrolyte balance

The document discusses fluid and electrolyte balance in the human body. It covers several key points:
1) Water and electrolytes like sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride must be balanced for normal bodily function. The kidneys and other organs work to maintain this balance.
2) Imbalances in various electrolytes can occur from medical conditions, medications, or diet. This can cause issues like abnormal heart rhythms or muscle problems.
3) Laboratory tests are used to diagnose electrolyte imbalances by measuring levels in blood and urine. Treatment focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause while restoring normal electrolyte levels.
Excretion system of urea in human revise by Ahmed Ghdhban Alziaydi

1. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate water and electrolyte levels.
2. The nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter blood and produce urine.
3. Urine travels from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder for temporary storage and then exits through the urethra.
APU6 Urinary System

The document provides an overview of the urinary system, including its general functions, major organs, urine formation process, urine composition, micturition, urinalysis, homeostasis, and aging effects. It describes the kidneys' roles in excretion, regulation of blood volume and pressure, electrolyte and pH balance, and hormone release. The major organs - kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra - and their structures and functions are defined. Urine formation via nephron filtration, reabsorption and secretion is explained in detail.
Similar to Basic ap chapter 25 powerpoint 2017 (20)
Excretion system of urea in human revise by Ahmed Ghdhban Alziaydi

Excretion system of urea in human revise by Ahmed Ghdhban Alziaydi
More from Kathy Richards
Basic ap chapter 28 powerpoint 2017

1. Fertilization occurs when a sperm and egg fuse, forming a single diploid cell called a zygote containing genetic material from both parents.
2. The journey of sperm is difficult, with millions being overcome by acidity or blocked, and thousands destroyed before reaching the egg.
3. During its journey, sperm undergo capacitation to prepare for fertilization by improving motility and membrane changes.
4. Fertilization must occur in the uterine tube, where the egg is swept after ovulation. Hundreds of sperm help make a path for one to fuse with the egg's membrane.
Basic ap chapter 27 powerpoint 2017

The document summarizes key aspects of the male and female reproductive systems. It describes how a child's birth requires healthy functioning of both the mother and father's reproductive systems, including hormone production and the union of male sperm and female eggs. It then provides details on male anatomy like the testes, sperm production, and role of the prostate and vas deferens. It also covers the female reproductive cycle, ovulation, menstruation, menopause, and the role of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Basic ap chapter 24 powerpoint 2017

This document discusses metabolism and nutrition. It explains that metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that break down molecules (catabolism) or build them up (anabolism) in the body. These reactions release or use energy. The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins - undergo digestion and are used to meet the body's energy demands. A balanced diet and sufficient intake of calories is important for health. The metabolic rate depends on factors like age, gender, activity level, and can be modified through diet and exercise.
Basic ap chapter 23 powerpoint 2017

The document provides an overview of the human digestive system. It describes the functions of key organs including the mouth, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The digestive process involves ingestion, propulsion, mechanical and chemical digestion, absorption and defecation. Each organ plays an important role in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream.
Basic ap chapter 22 powerpoint 2017

The respiratory system functions to provide oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide through gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. It includes both conducting zones that transport air, and respiratory zones involved in gas exchange. Key structures are the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and pleurae. Breathing occurs through changes in pressure between the atmosphere and lungs, driven by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, with inspiration occurring when the thoracic cavity volume increases and expiration when it decreases.
Basic ap chapter 21 powerpoint 2017

The lymphatic system drains excess fluid from tissues and returns it to the bloodstream. It also filters pathogens and transports immune cells. The lymphatic system consists of lymph vessels, lymph nodes, and organs that carry a fluid called lymph. Lymph is formed from interstitial fluid that leaks from blood vessels and is drained through the lymphatic system before returning to the bloodstream. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body and helps the immune system fight infection and disease.
Basic ap chapter 20 powerpoint 2017

This document summarizes the key components of the cardiovascular system, including different types of blood vessels and how blood flows through the body. It discusses arteries, veins, capillaries, and how they differ. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart at high pressure, while veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart at low pressure. Capillaries allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste. Blood pressure, flow, and the factors that influence them are also explained.
Basic ap chapter 19 powerpoint 2017

The document discusses the cardiovascular system and the heart. It describes the heart as a muscular pump located in the chest cavity that circulates blood through two circuits - the pulmonary and systemic circuits. The heart has four chambers, valves to ensure one-way blood flow, and a conduction system to coordinate contractions. It discusses the cardiac cycle, heart sounds, cardiac output, and factors that influence pumping like preload and afterload. An electrocardiogram is described as a tool to monitor the heart's electrical activity.
Basic ap chapter 18 powerpoint 2017

This document summarizes key components of the cardiovascular system, including blood, its composition and functions. It describes the three main components of blood - plasma, red blood cells, and white blood cells. Red blood cells transport oxygen, white blood cells help fight infection, and platelets help with clotting. The document outlines the roles of different white blood cell types and discusses conditions like sickle cell anemia and polycythemia. In summary, it provides an overview of the components and functions of blood within the cardiovascular system.
Basic ap chapter 17 powerpoint 2017

The document provides an overview of the endocrine system. It describes that the endocrine and nervous systems work together to maintain homeostasis. The endocrine system uses chemical signaling via hormones to regulate slower processes, while the nervous system uses both electrical and chemical signaling for rapid responses. Major glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones like insulin, adrenaline, estrogen and testosterone which target specific cells and regulate various bodily functions.
Basic ap chapter 15 powerpoint 2017

The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion. It has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The sympathetic system activates the fight or flight response while the parasympathetic system regulates resting functions like digestion. The autonomic system works with the endocrine system to maintain homeostasis and is controlled by the hypothalamus and other brain regions.
Basic ap chapter 14 powerpoint 2017

The somatic nervous system is responsible for conscious perception of the environment and voluntary responses through skeletal muscles. Sensation is the activation of sensory receptors by stimuli, while perception is the central processing of sensations into meaningful patterns in the brain. The major sensory receptors are chemoreceptors for taste and smell, mechanoreceptors for touch and balance, nociceptors for pain, and photoreceptors for vision.
Basic ap chapter 13 powerpoint 2017

The document summarizes the main components and functions of the central nervous system. It discusses the brain regions including the cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum. It also covers the spinal cord, protective coverings, blood supply, common disorders like strokes, and the cranial nerves.
Basic ap chapter 12 powerpoint 2017

The document discusses the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The two main cell types are neurons, which transmit electrical signals, and glial cells, which provide support. Neurons have a cell body and branched processes called dendrites that receive signals and axons that transmit signals. Axons may be wrapped in a fatty sheath called myelin for insulation. The CNS contains gray matter, with cell bodies, and white matter, with mostly axons. The nervous system functions include sensation, integration of information, and response.
Basic ap chapter 11 powerpoint 2017

The muscular system allows for movement of the body through contraction of skeletal muscles, which are attached to bones via tendons. There are two main types of skeletal muscles - the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which facilitate breathing by changing the size of the thoracic cavity. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens while the external intercostals elevate the ribs, expanding the cavity. Exhalation occurs when these muscles relax and the internal intercostals draw the ribs together to decrease cavity size.
B asic ap chapter 10 powerpoint 2017

1. The three main types of muscle tissue - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac - all exhibit excitability and the ability to generate action potentials.
2. Skeletal muscle is striated and controls voluntary movement by attaching to bones. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart and pumps blood, while smooth muscle controls involuntary functions like digestion.
3. Skeletal muscle contractions can be isotonic, involving movement, or isometric, involving tension without movement. Muscle tone maintains low-level contractions for posture and joint stability.
Basic ap chapter 9 powerpoint 2017

This document provides information on the different types of joints in the human body. It begins by explaining that joints are where bones connect and allow for varying degrees of movement. There are three main types of joints - fibrous joints which join bones through connective tissue, cartilaginous joints which join through cartilage, and synovial joints which have a fluid-filled cavity allowing movement. Within these categories there are further structural and functional classifications. The document then goes on to describe six specific types of synovial joints and three functional classifications of joints based on mobility. It concludes by discussing the different types of movements that can occur at synovial joints in the body.
Basic ap chapter 8 powerpoint 2017

The document summarizes key bones and structures of the appendicular skeleton. It describes how the 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are divided into the limb bones and girdle bones that attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. The upper and lower limbs each have distinct functional demands due to human bipedalism. Key bones of the upper limb include the humerus, ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. The lower limb attaches via the pelvic girdle, made of the fused hip bones that connect to the axial skeleton at the sacrum. The male and female pelvises differ in size and shape relating to functional demands.
Basic ap chapter 7 powerpoint 2017

The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages, and ligaments that provide structure and protection. The axial skeleton forms the central axis and includes the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The skull has multiple bones that form the cranium and face. Bones of the skull include the parietal, temporal, frontal, occipital, maxilla, zygomatic, nasal, and mandible. The appendicular skeleton includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs attached to the axial skeleton.
Basic ap chapter 6 powerpoint 2017

The skeletal system performs several critical functions:
1. It supports the body and facilitates movement by providing attachment points for muscles and acting as levers.
2. Bones protect internal organs such as the lungs, heart, and brain.
3. The skeletal system stores and releases minerals and produces blood cells. Bones store minerals like calcium and release them when needed, and bone marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
More from Kathy Richards (20)
Recently uploaded
Digital Artifact 1 - 10VCD Environments Unit

Digital Artifact 1 - 10VCD Environments Unit - NGV Pavilion Concept Design
Types of Herbal Cosmetics its standardization.

Physiology and chemistry of skin and pigmentation, hairs, scalp, lips and nail, Cleansing cream, Lotions, Face powders, Face packs, Lipsticks, Bath products, soaps and baby product,
Preparation and standardization of the following : Tonic, Bleaches, Dentifrices and Mouth washes & Tooth Pastes, Cosmetics for Nails.
How to Add Chatter in the odoo 17 ERP Module

In Odoo, the chatter is like a chat tool that helps you work together on records. You can leave notes and track things, making it easier to talk with your team and partners. Inside chatter, all communication history, activity, and changes will be displayed.
The History of Stoke Newington Street Names

Presented at the Stoke Newington Literary Festival on 9th June 2024
www.StokeNewingtonHistory.com
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

Odoo provides an option for creating a module by using a single line command. By using this command the user can make a whole structure of a module. It is very easy for a beginner to make a module. There is no need to make each file manually. This slide will show how to create a module using the scaffold method.
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

Discover the Simplified Electron and Muon Model: A New Wave-Based Approach to Understanding Particles delves into a groundbreaking theory that presents electrons and muons as rotating soliton waves within oscillating spacetime. Geared towards students, researchers, and science buffs, this book breaks down complex ideas into simple explanations. It covers topics such as electron waves, temporal dynamics, and the implications of this model on particle physics. With clear illustrations and easy-to-follow explanations, readers will gain a new outlook on the universe's fundamental nature.
Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS Template 2023-2024 by: Irene S. Rueco
DRUGS AND ITS classification slide share

Any substance (other than food) that is used to prevent, diagnose, treat, or relieve symptoms of a
disease or abnormal condition
PCOS corelations and management through Ayurveda.

This presentation includes basic of PCOS their pathology and treatment and also Ayurveda correlation of PCOS and Ayurvedic line of treatment mentioned in classics.
Hindi varnamala | hindi alphabet PPT.pdf

हिंदी वर्णमाला पीपीटी, hindi alphabet PPT presentation, hindi varnamala PPT, Hindi Varnamala pdf, हिंदी स्वर, हिंदी व्यंजन, sikhiye hindi varnmala, dr. mulla adam ali, hindi language and literature, hindi alphabet with drawing, hindi alphabet pdf, hindi varnamala for childrens, hindi language, hindi varnamala practice for kids, https://www.drmullaadamali.com
A Strategic Approach: GenAI in Education

Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies such as Generative AI, Image Generators and Large Language Models have had a dramatic impact on teaching, learning and assessment over the past 18 months. The most immediate threat AI posed was to Academic Integrity with Higher Education Institutes (HEIs) focusing their efforts on combating the use of GenAI in assessment. Guidelines were developed for staff and students, policies put in place too. Innovative educators have forged paths in the use of Generative AI for teaching, learning and assessments leading to pockets of transformation springing up across HEIs, often with little or no top-down guidance, support or direction.
This Gasta posits a strategic approach to integrating AI into HEIs to prepare staff, students and the curriculum for an evolving world and workplace. We will highlight the advantages of working with these technologies beyond the realm of teaching, learning and assessment by considering prompt engineering skills, industry impact, curriculum changes, and the need for staff upskilling. In contrast, not engaging strategically with Generative AI poses risks, including falling behind peers, missed opportunities and failing to ensure our graduates remain employable. The rapid evolution of AI technologies necessitates a proactive and strategic approach if we are to remain relevant.
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশের অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা ২০২৪ [Bangladesh Economic Review 2024 Bangla.pdf] কম্পিউটার , ট্যাব ও স্মার্ট ফোন ভার্সন সহ সম্পূর্ণ বাংলা ই-বুক বা pdf বই " সুচিপত্র ...বুকমার্ক মেনু 🔖 ও হাইপার লিংক মেনু 📝👆 যুক্ত ..
আমাদের সবার জন্য খুব খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটি বই ..বিসিএস, ব্যাংক, ইউনিভার্সিটি ভর্তি ও যে কোন প্রতিযোগিতা মূলক পরীক্ষার জন্য এর খুব ইম্পরট্যান্ট একটি বিষয় ...তাছাড়া বাংলাদেশের সাম্প্রতিক যে কোন ডাটা বা তথ্য এই বইতে পাবেন ...
তাই একজন নাগরিক হিসাবে এই তথ্য গুলো আপনার জানা প্রয়োজন ...।
বিসিএস ও ব্যাংক এর লিখিত পরীক্ষা ...+এছাড়া মাধ্যমিক ও উচ্চমাধ্যমিকের স্টুডেন্টদের জন্য অনেক কাজে আসবে ...
Recently uploaded (20)
Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf

Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...
Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf
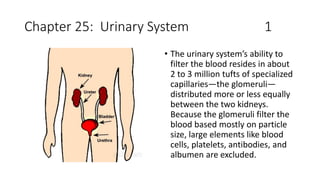
Basic ap chapter 25 powerpoint 2017
- 1. Chapter 25: Urinary System 1 • The urinary system’s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries—the glomeruli— distributed more or less equally between the two kidneys. Because the glomeruli filter the blood based mostly on particle size, large elements like blood cells, platelets, antibodies, and albumen are excluded.
- 2. Urine 2 • Characteristics of the urine change, depending on influences such as water intake, exercise, environmental temperature, nutrient intake, and other factors. • Some of the characteristics such as color and odor are rough descriptors of your state of hydration. • For example, if you exercise or work outside, and sweat a great deal, your urine will turn darker and produce a slight odor, even if you drink plenty of water. Athletes are often advised to consume water until their urine is clear. This is good advice; however, it takes time for the kidneys to process body fluids and store it in the bladder. • Another way of looking at this is that the quality of the urine produced is an average over the time it takes to make that urine. Producing clear urine may take only a few minutes if you are drinking a lot of water or several hours if you are working outside and not drinking much.
- 3. Urinalysis 3 • Urinalysis (urine analysis) often provides clues to renal disease. Normally, only traces of protein are found in urine, and when higher amounts are found, damage to the glomeruli is the likely basis. • Unusually large quantities of urine may point to diseases like diabetes mellitus or hypothalamic tumors that cause diabetes insipidus. • The color of urine is determined mostly by the breakdown products of red blood cell destruction. • The “heme” of hemoglobin is converted by the liver into water-soluble forms that can be excreted into the bile and indirectly into the urine. This yellow pigment is urochrome. • Urine color may also be affected by certain foods like beets, berries, and fava beans. • A kidney stone or a cancer of the urinary system may produce sufficient bleeding to manifest as pink or even bright red urine. • Diseases of the liver or obstructions of bile drainage from the liver impart a dark “tea” or “cola” hue to the urine. • Dehydration produces darker, concentrated urine that may also possess the slight odor of ammonia. • Most of the ammonia produced from protein breakdown is converted into urea by the liver, so ammonia is rarely detected in fresh urine. The strong ammonia odor you may detect in bathrooms or alleys is due to the breakdown of urea into ammonia by bacteria in the environment. • About one in five people detect a distinctive odor in their urine after consuming asparagus; other foods such as onions, garlic, and fish can impart their own aromas! These food-caused odors are harmless.
- 4. Urine Volumes 4 • Urine volume varies considerably. The normal range is one to two liters per day. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. • Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. 300-500 mL/day production a day. • Causes: Dehydration; blood loss; diarrhea; cardiogenic shock; kidney disease; enlarged prostate • The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. Production of less than 50 mL/day. Causes: Kidney failure; obstruction, such as kidney stone or tumor; enlarged prostate. • Excessive urine production is polyuria. Production of greater than 2.5 L/day. Causes: Diabetes mellitus; diabetes insipidus; excess caffeine or alcohol; kidney disease; certain drugs, such as diuretics; sickle cell anemia; excessive water intake.
- 5. Urethra 5 • The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body for disposal. • The urethra is the only urologic organ that shows any significant anatomic difference between males and females; all other urine transport structures are identical. • Female: Its short length, about 4 cm (1.57”), is less of a barrier to fecal bacteria than the longer male urethra and the best explanation for the greater incidence of UTI in women. • Males: The length of the male urethra varies between men but averages 20 cm (7.87”) in length.
- 6. Bladder 6 • The urinary bladder collects urine from both ureters. The bladder is partially retroperitoneal (outside the peritoneal cavity) with its peritoneal-covered “dome” projecting into the abdomen when the bladder is distended with urine. • The bladder’s strength diminishes with age. • Micturition proper term for urination or voiding. • Incontinence: loss of ability to control micturition
- 7. Ureters 7 • The kidneys and ureters are completely retroperitoneal, and the bladder has a peritoneal covering only over the dome. • As urine passes through the ureter, it does not passively drain into the bladder but rather is propelled by waves of peristalsis. • The ureters are approximately 30 cm long.
- 8. Kidneys 8 • The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. • Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs. • Each kidney weighs about 125–175 g in males and 115–155 g in females. They are about 11–14 cm in length, 6 cm wide, and 4 cm thick, and are directly covered by a fibrous capsule composed of dense, irregular connective tissue that helps to hold their shape and protect them. • Nephrons are the “functional units” of the kidney; they cleanse the blood and balance the constituents of the circulation.
- 9. Kidney Failure Symptoms 9 • Weakness • Lethargy • Shortness of Breath • Widespread Edema • Anemia • Metabolic Acidosis • Metabolic Alkalosis • Heart Arrhythmias • Uremia • Loss of appetite • Fatigue • Excessive urination • Oliguria
- 10. Transport Mechanisms 10 • Mechanisms by which substances move across membranes for reabsorption or secretion include active transport, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, secondary active transport, and osmosis. • Active transport utilizes energy, to move a substance across a membrane from a low to a high concentration. • Simple diffusion moves a substance from a higher to a lower concentration down its concentration gradient. It requires no energy and only needs to be soluble. • Facilitated diffusion is similar to diffusion in that it moves a substance down its concentration gradient.
- 11. Renal Blood Flow 11 • It is vital that the flow of blood through the kidney be at a suitable rate to allow for filtration. This rate determines how much solute is retained or discarded, how much water is retained or discarded, and ultimately, the osmolarity of blood and the blood pressure of the body. • Reduction of sympathetic stimulation results in vasodilation and increased blood flow through the kidneys during resting conditions. When the frequency of action potentials increases, the arteriolar smooth muscle constricts (vasoconstriction), resulting in diminished glomerular flow, so less filtration occurs. • Under conditions of stress, sympathetic nervous activity increases, resulting in the direct vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles (norepinephrine effect) as well as stimulation of the adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla, in turn, produces a generalized vasoconstriction through the release of epinephrine. • Angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor that actively causes vasoconstriction and stimulates aldosterone release by the adrenal cortex. • This includes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles, further reducing the volume of blood flowing through the kidneys. This process redirects blood to other organs with more immediate needs. If blood pressure falls, the sympathetic nerves will also stimulate the release of renin. • Additional renin increases production of the powerful vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II, as discussed above, will also stimulate aldosterone production to augment • The kidneys are very effective at regulating the rate of blood flow over a wide range of blood pressures. Your blood pressure will decrease when you are relaxed or sleeping. It will increase when exercising. Yet, despite these changes, the filtration rate through the kidney will change very little.
- 12. Antidiuretic Hormone 12 • Several hormones have specific, important roles in regulating kidney function. • They act to stimulate or inhibit blood flow. Some of these are endocrine, acting from a distance, whereas others are paracrine, acting locally. • Diuretics are drugs that can increase water loss by interfering with the recapture of solutes and water from the forming urine. They are often prescribed to lower blood pressure. • Coffee, tea, and alcoholic beverages are familiar diuretics. • ADH promotes the recovery of water, decreases urine volume, and maintains plasma osmolarity and blood pressure.
- 13. Urinary System and Homeostasis 13 • All systems of the body are interrelated. A change in one system may affect all other systems in the body, with mild to devastating effects • . A failure of urinary continence can be embarrassing and inconvenient, but is not life threatening. • The loss of other urinary functions may prove fatal. • Vitamin D synthesis: Activated vitamin D is important for absorption of Ca++ in the digestive tract, its reabsorption in the kidney, and the maintenance of normal serum concentrations of Ca++ and phosphate. • Calcium is vitally important in bone health, muscle contraction, hormone secretion, and neurotransmitter release. Inadequate Ca++ leads to disorders like osteoporosis and osteomalacia in adults and rickets in children.
- 14. Urinary System and Homeostasis 14 • Blood pressure regulation: Due to osmosis, water follows where Na+ leads. Much of the water the kidneys recover from the forming urine follows the reabsorption of Na+. • Normally, all of the glucose is recovered, but loss of glucose control (diabetes mellitus) may result in an osmotic dieresis severe enough to produce severe dehydration and death. • A loss of renal function means a loss of effective vascular volume control, leading to hypotension (low blood pressure) or hypertension (high blood pressure), which can lead to stroke, heart attack, and aneurysm formation. • The reabsorption of Na+ helps to raise and maintain blood pressure over a longer term. • Regulation of Osmolarity: If the kidney glomeruli are damaged by an autoimmune illness, large quantities of protein may be lost in the urine. • The resultant drop in serum osmolarity leads to widespread edema that, if severe, may lead to damaging or fatal brain swelling. • Severe hypertonic conditions may arise with severe dehydration from lack of water intake, severe vomiting, or uncontrolled diarrhea. • When the kidney is unable to recover sufficient water from the forming urine, the consequences may be severe (lethargy, confusion, muscle cramps, and finally, death) .
- 15. Recovery of Electrolytes 15 • Sodium, calcium, and potassium must be closely regulated. • To modify the plasma makeup in the production of urine the following has to take place: absorption; filtration; and secretion.