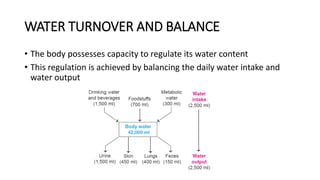
This document discusses water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance in the human body. It covers several key points:
- Water makes up about 60% of the human body and is essential for biochemical reactions and transport. The body carefully regulates water intake, output, and distribution between intracellular and extracellular fluid.
- Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are important for maintaining fluid balance and osmotic pressure. The kidneys play a key role in regulating electrolyte concentrations through hormones.
- Acid-base balance is critical and maintained through buffers, respiratory and renal systems that regulate bicarbonate and carbon dioxide levels to keep blood pH between 7.35-7.45. Dis