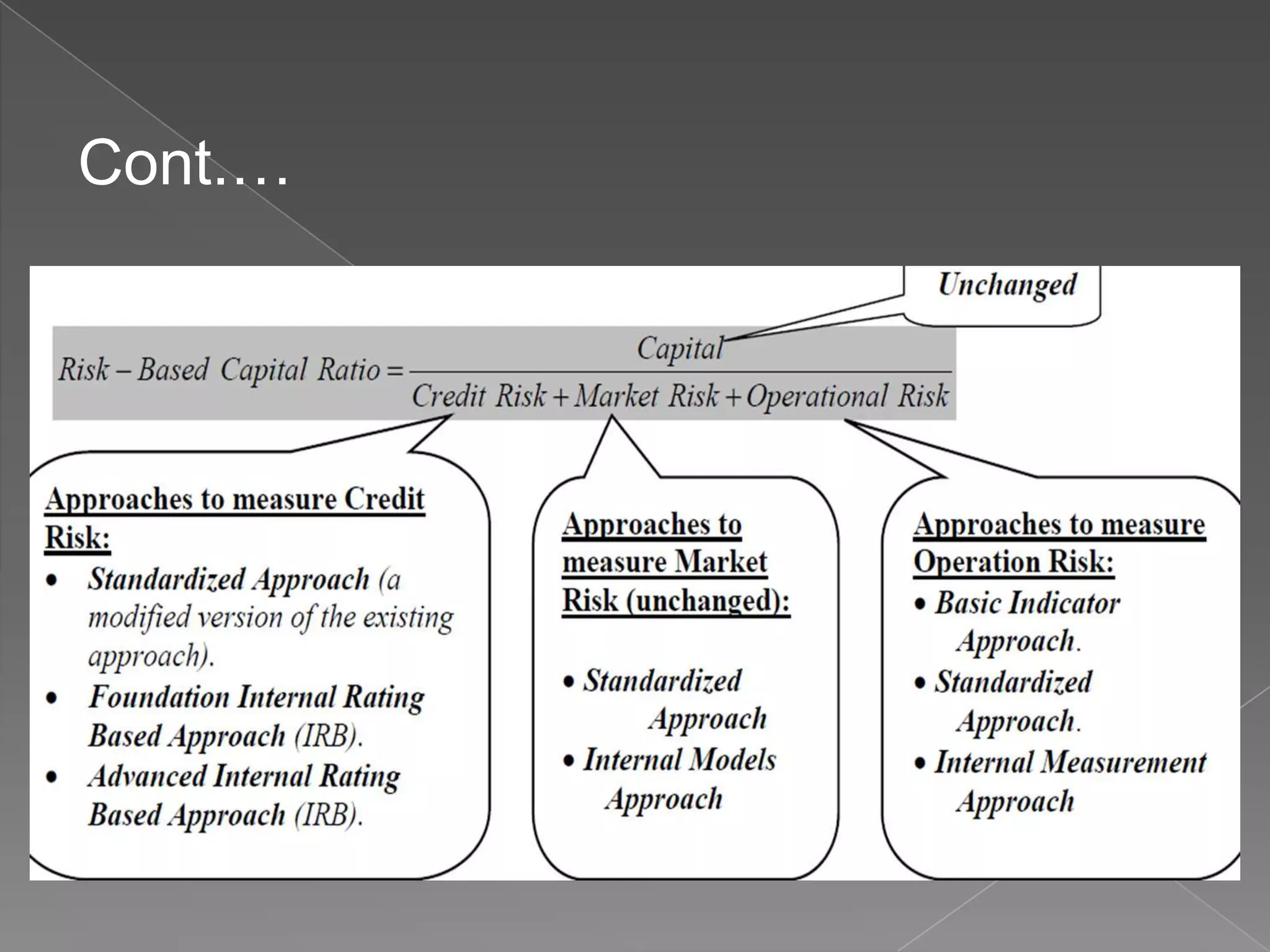
The document then discusses the key aspects of Basel I and Basel II accords. Basel I, introduced in 1998, required banks to hold capital equal to at least 8% of total assets, measured according to their riskiness across four buckets (0%, 20%, 50%, 100%). Basel II, published in 2004, consists of three pillars - minimum capital requirements, supervisory review, and market discipline. It introduced a risk