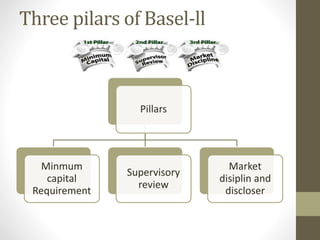
Basel II is an international banking standard that recommends regulations for how much capital banks must hold. It aims to make capital requirements more risk sensitive by aligning them with banks' financial and operational risks. The three pillars of Basel II are: 1) Minimum capital requirements based on credit, market, and operational risk; 2) Supervisory review of risk profiles and capital adequacy; 3) Market discipline through disclosure and transparency. Implementing Basel II poses challenges for Indian banks like additional capital requirements and favoring large banks with stronger risk management.