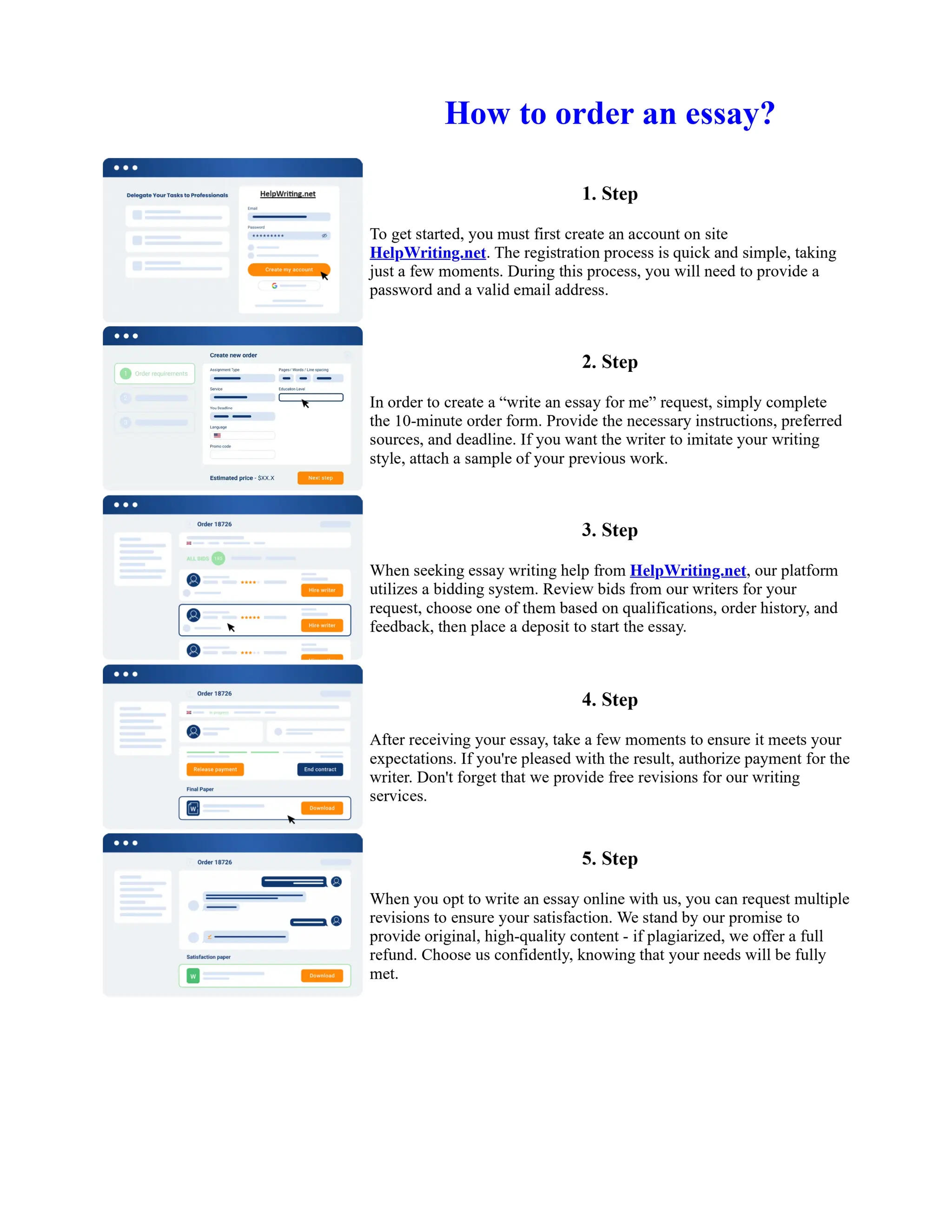
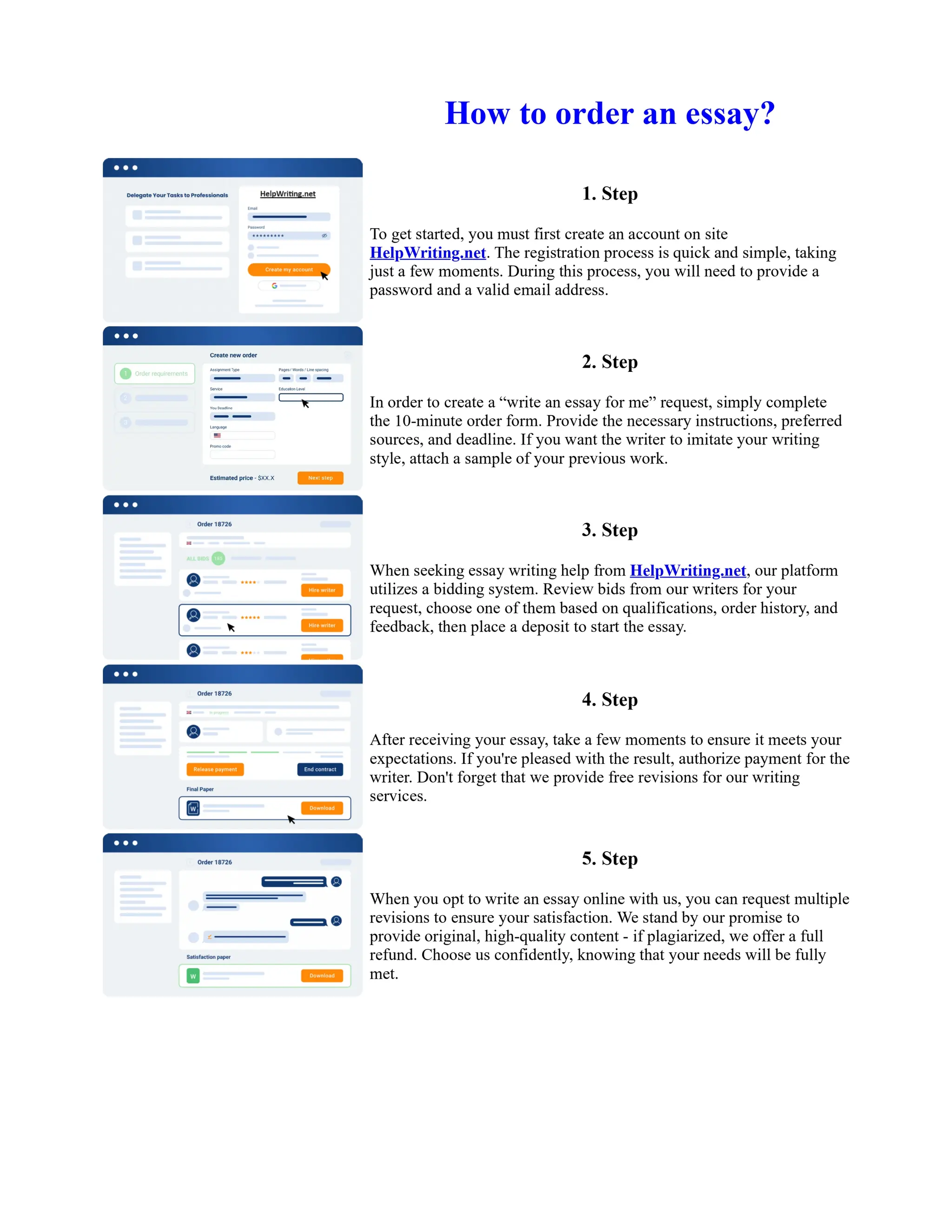
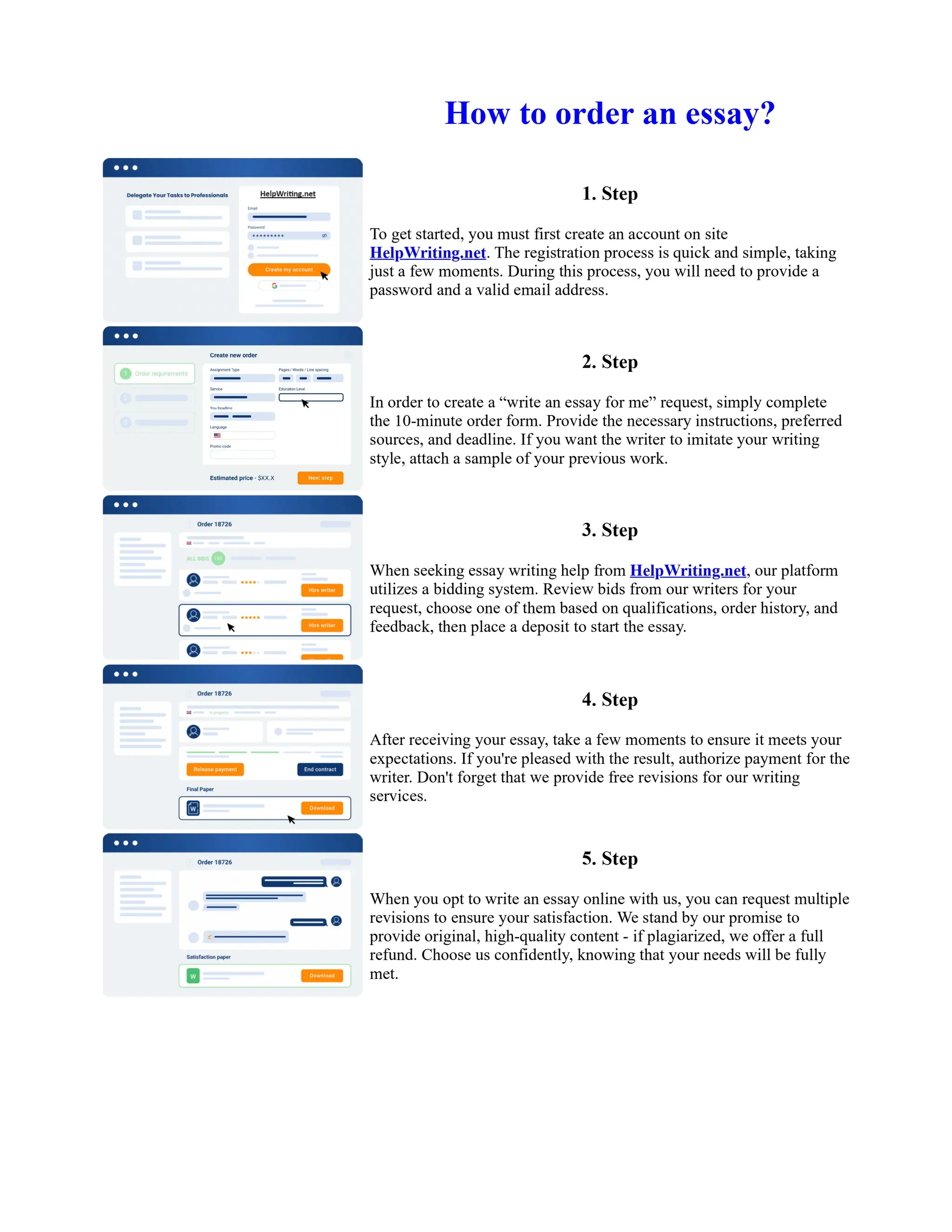
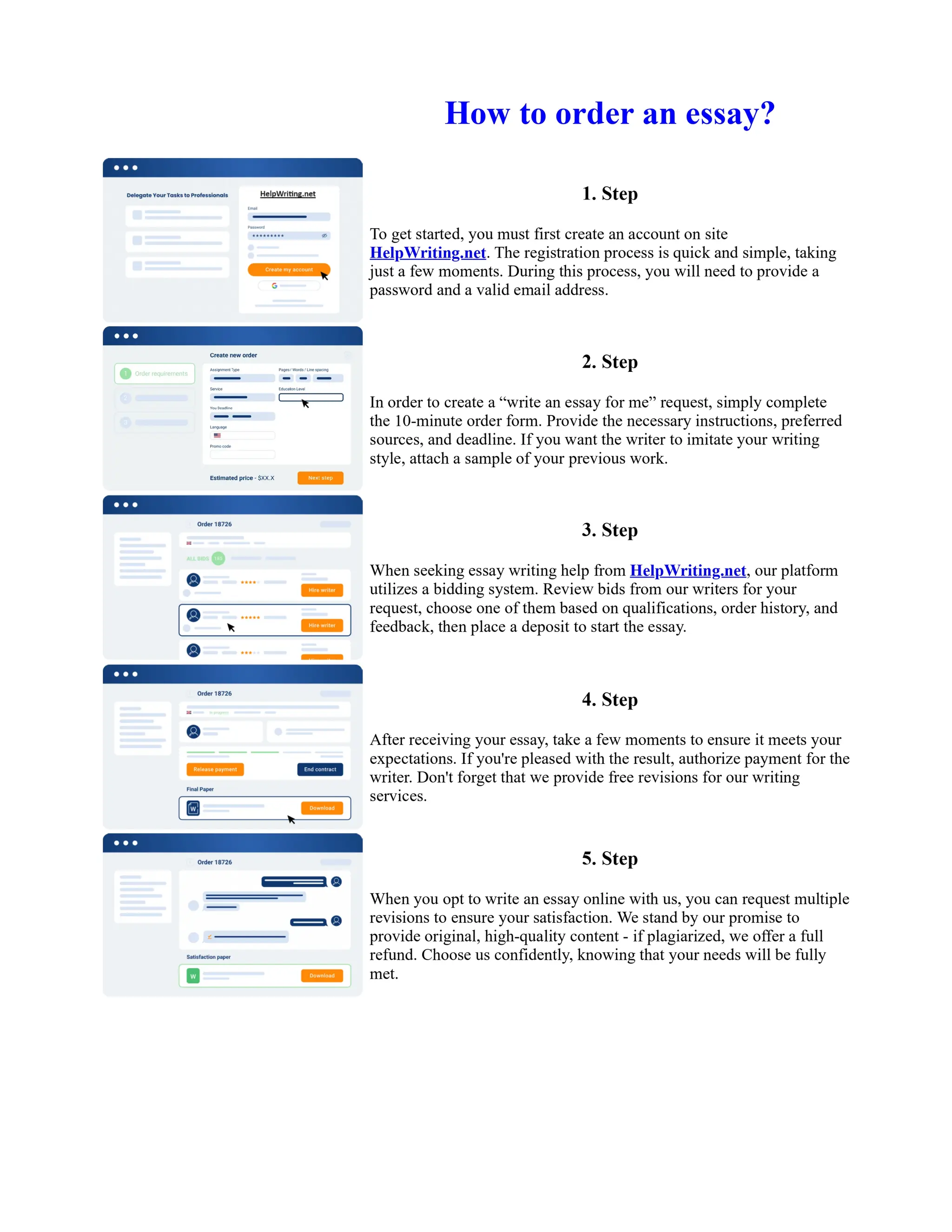
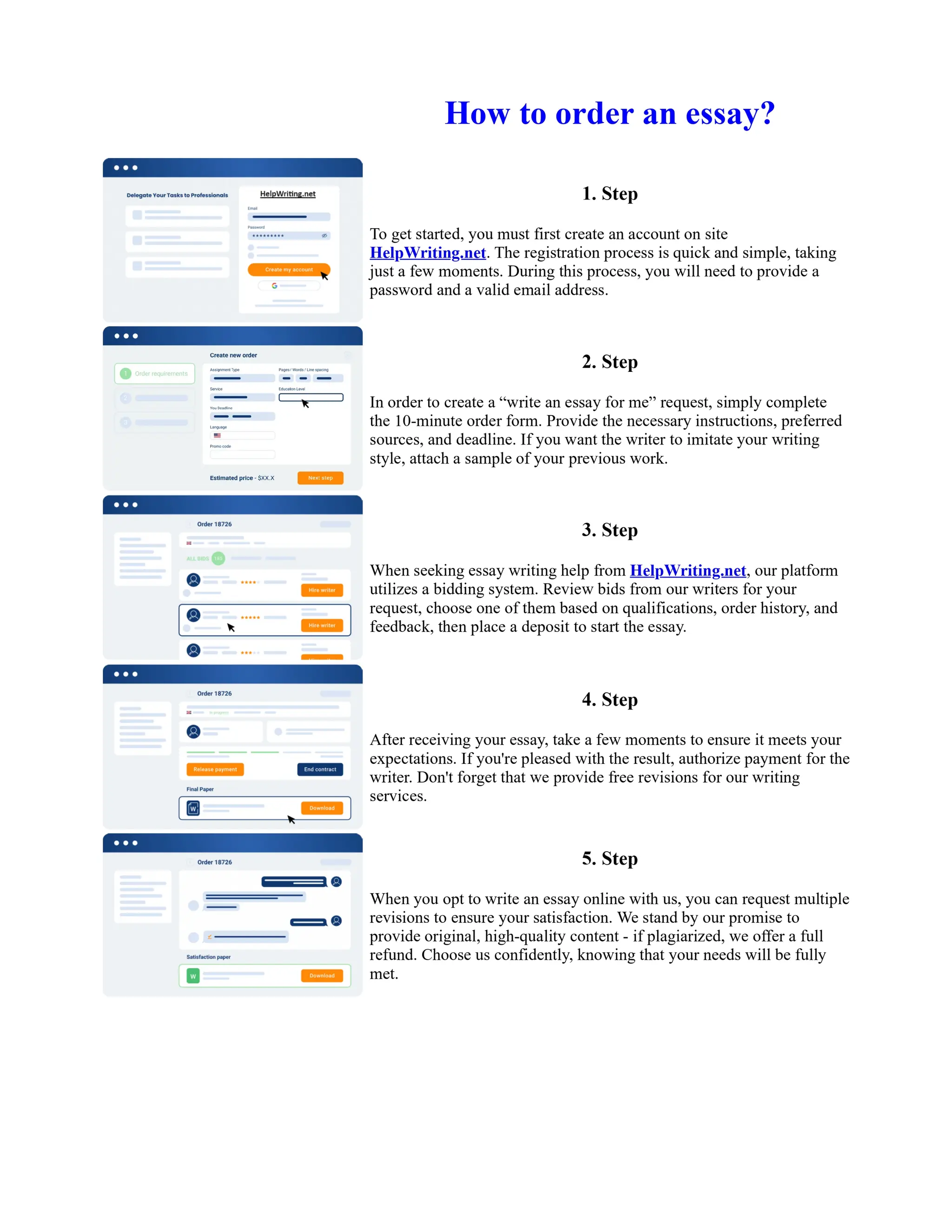
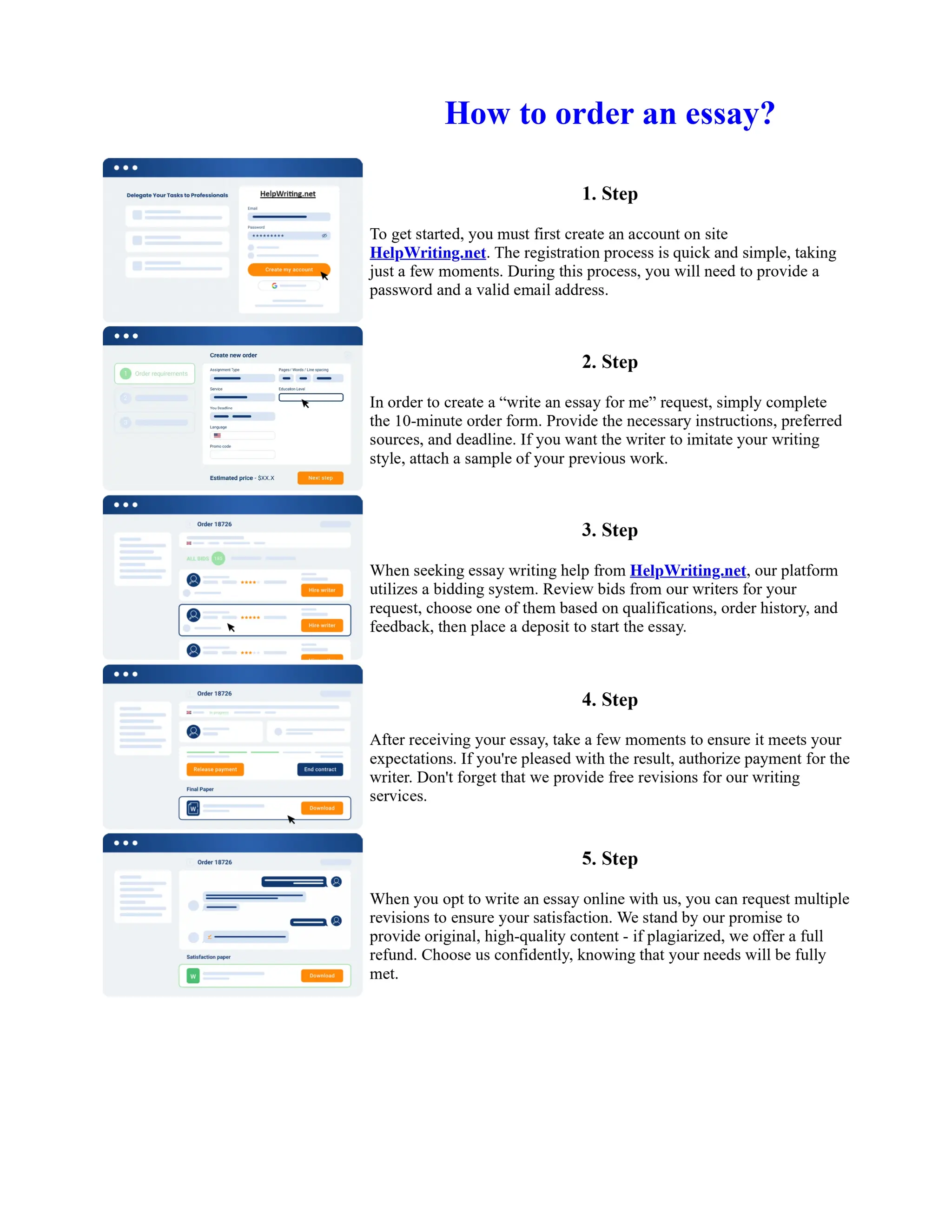
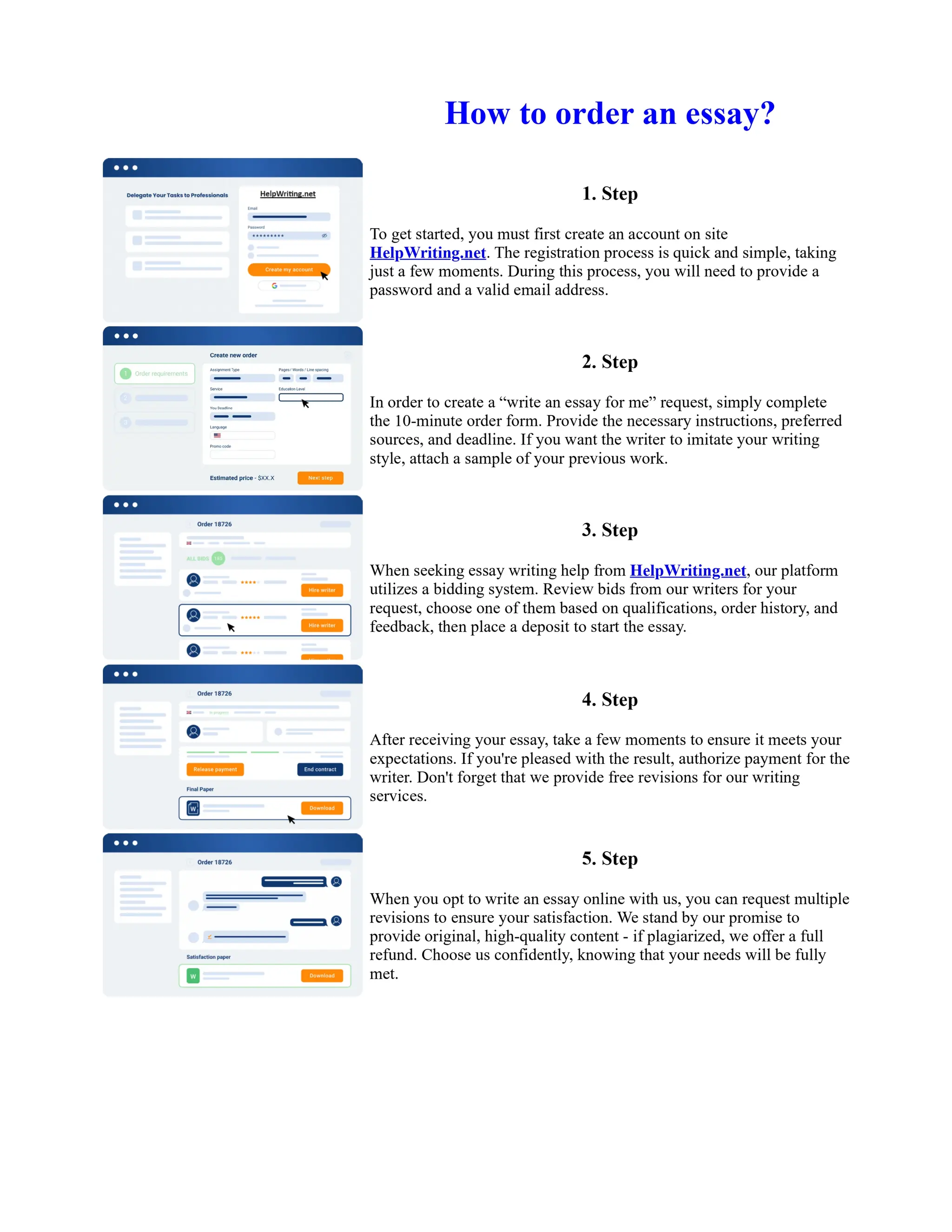
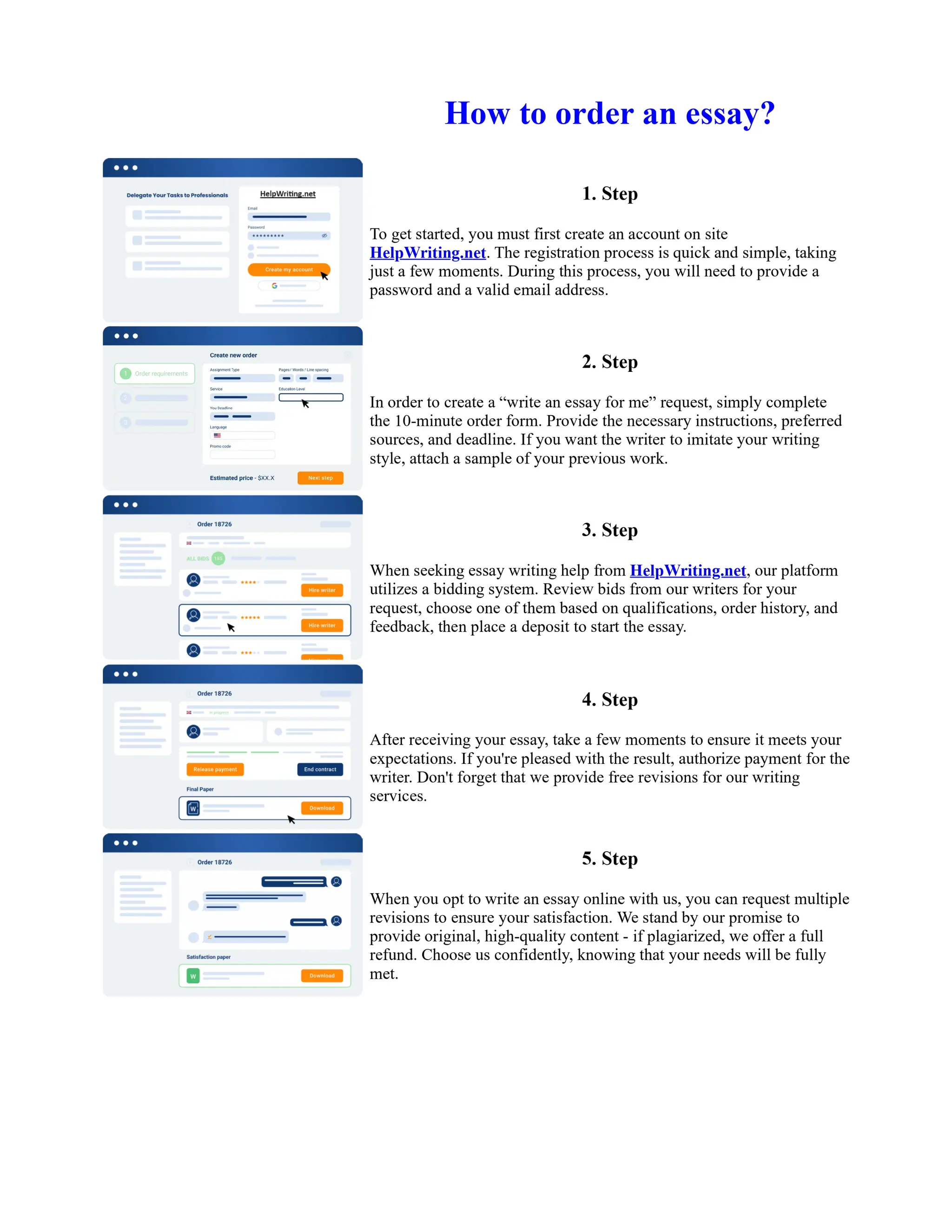
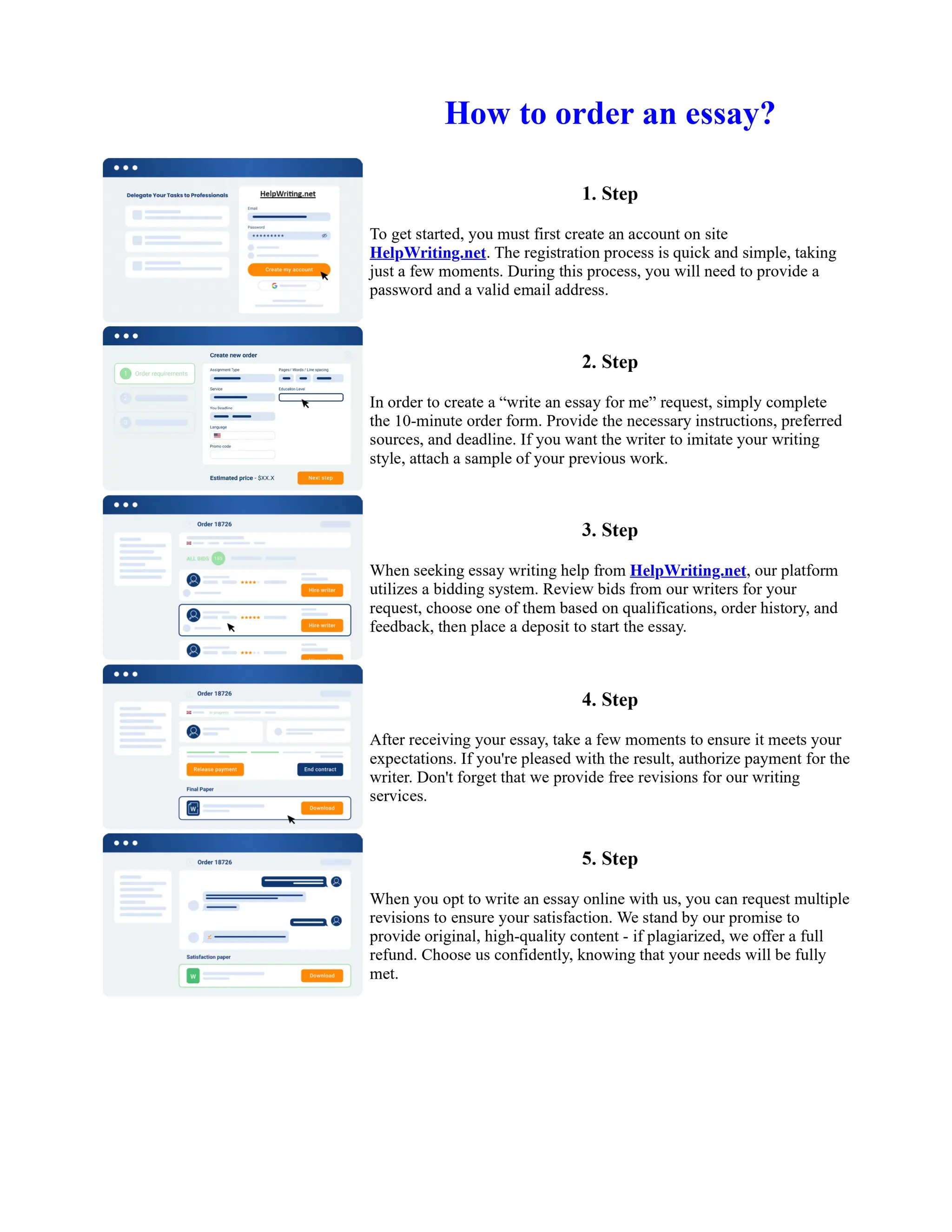
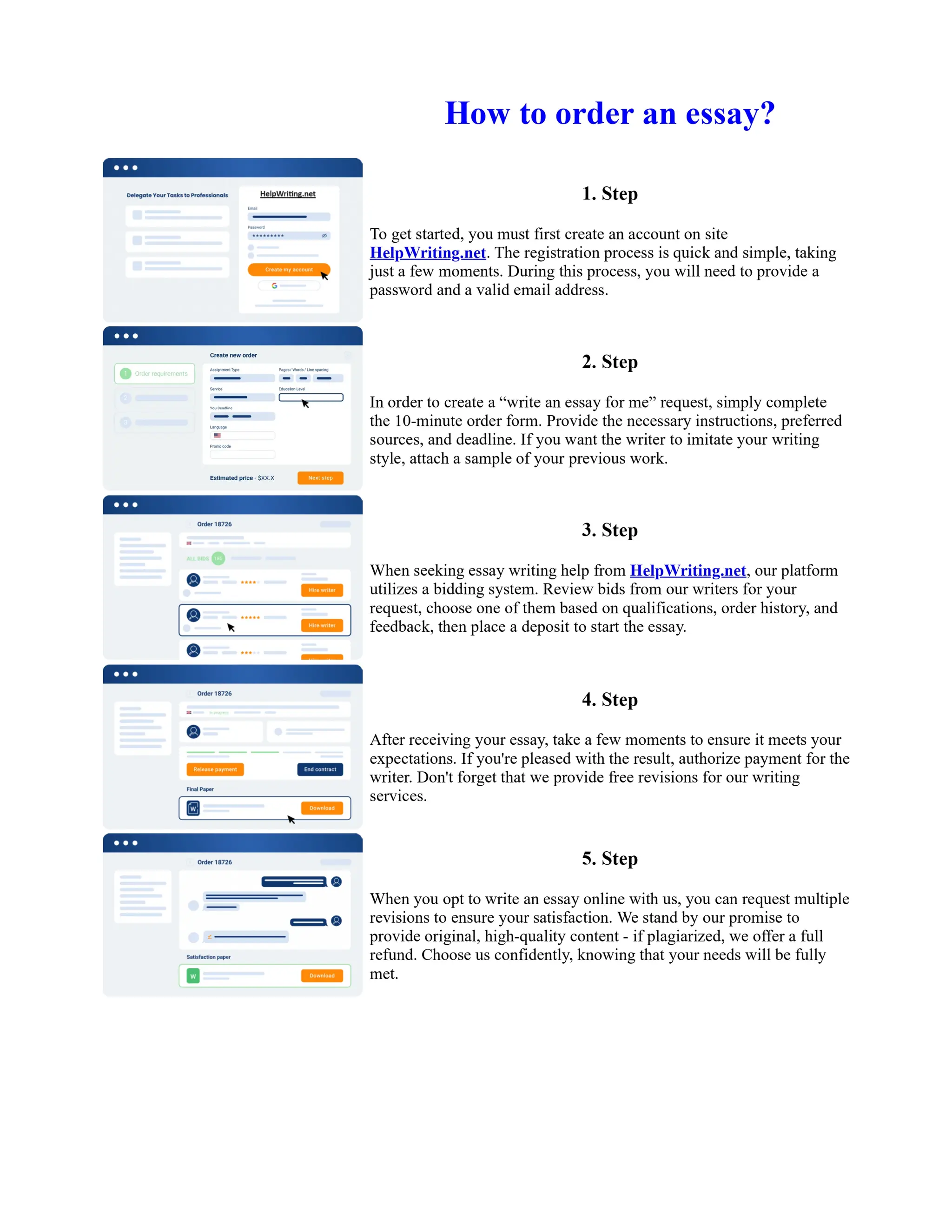
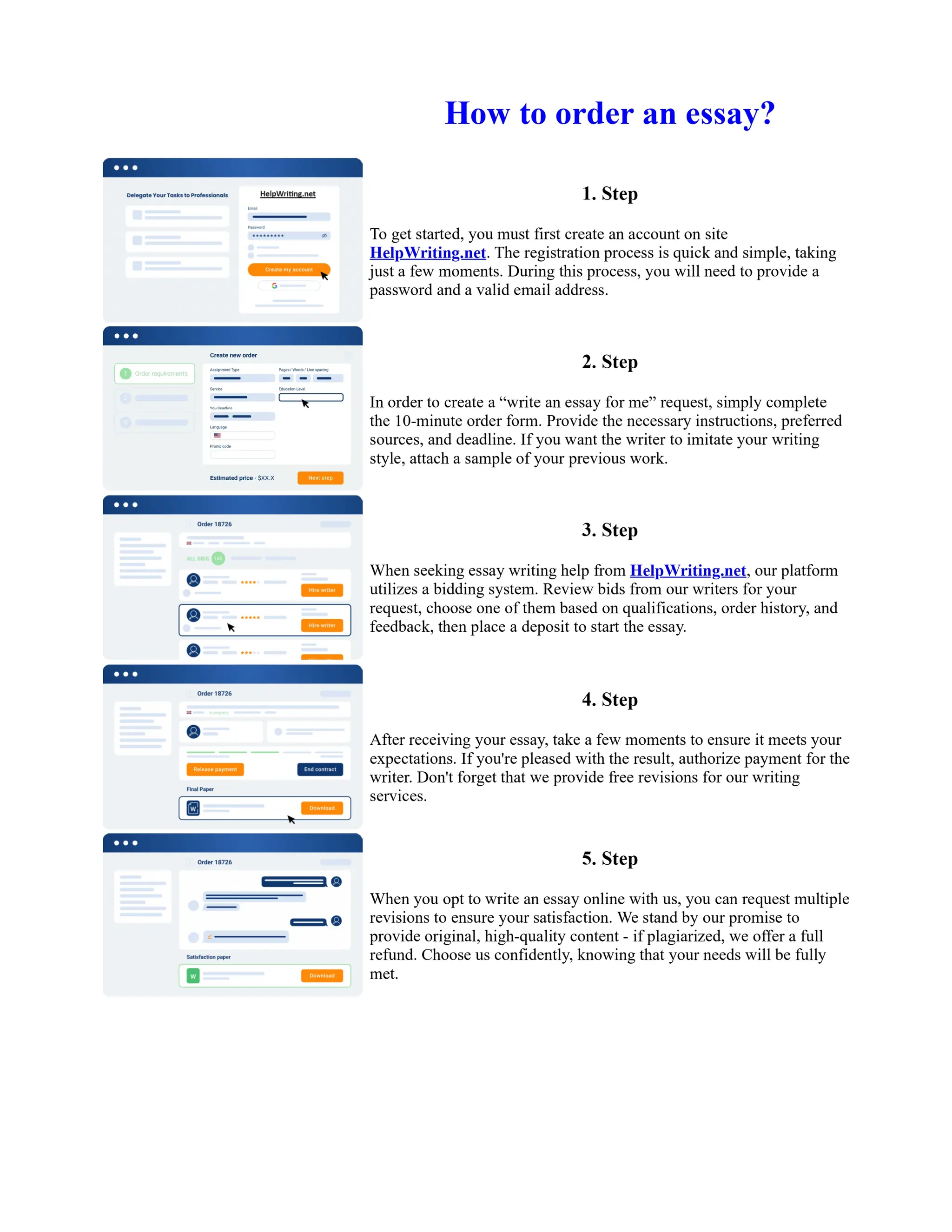
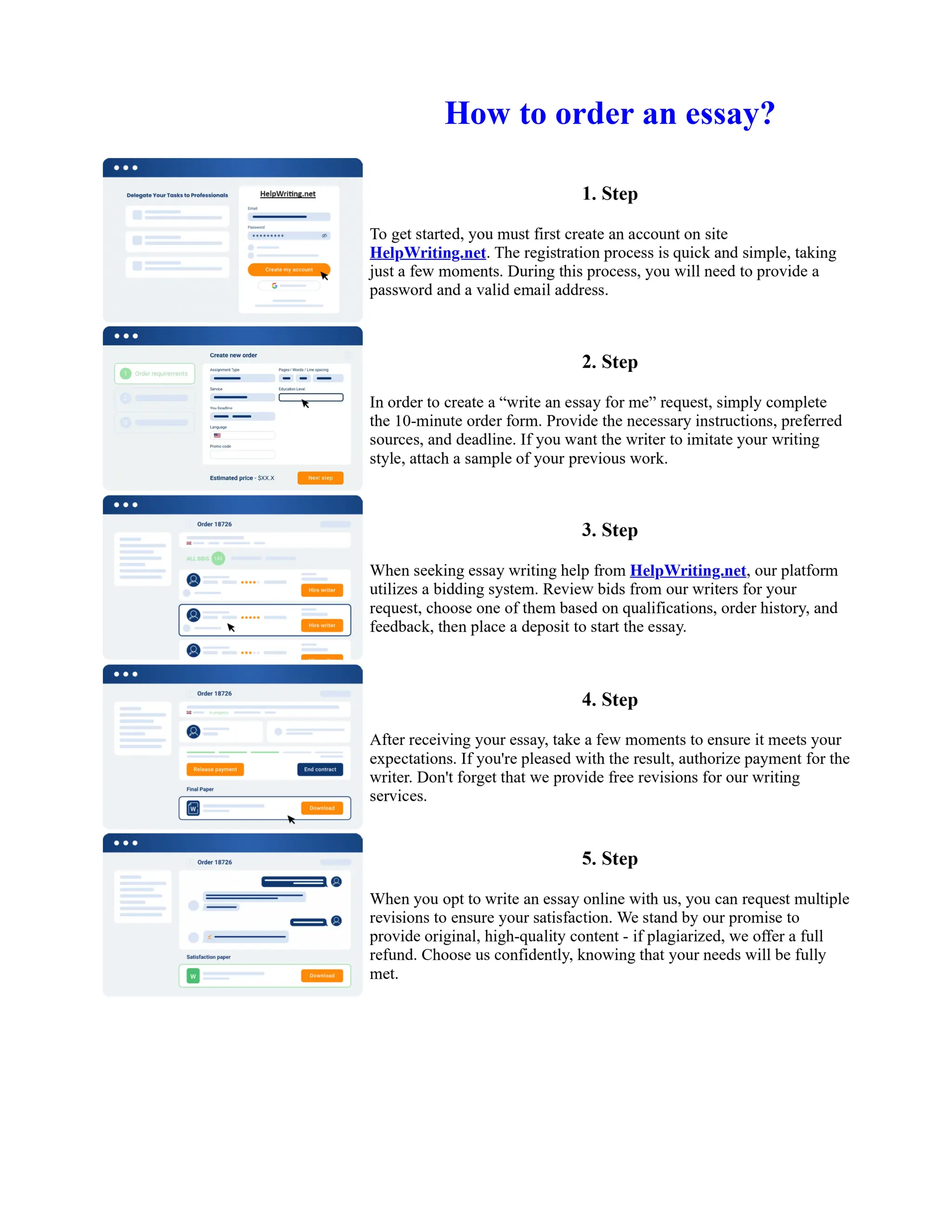
The document discusses the evolution of the Basel Accords from 1988 to the present. It highlights that:
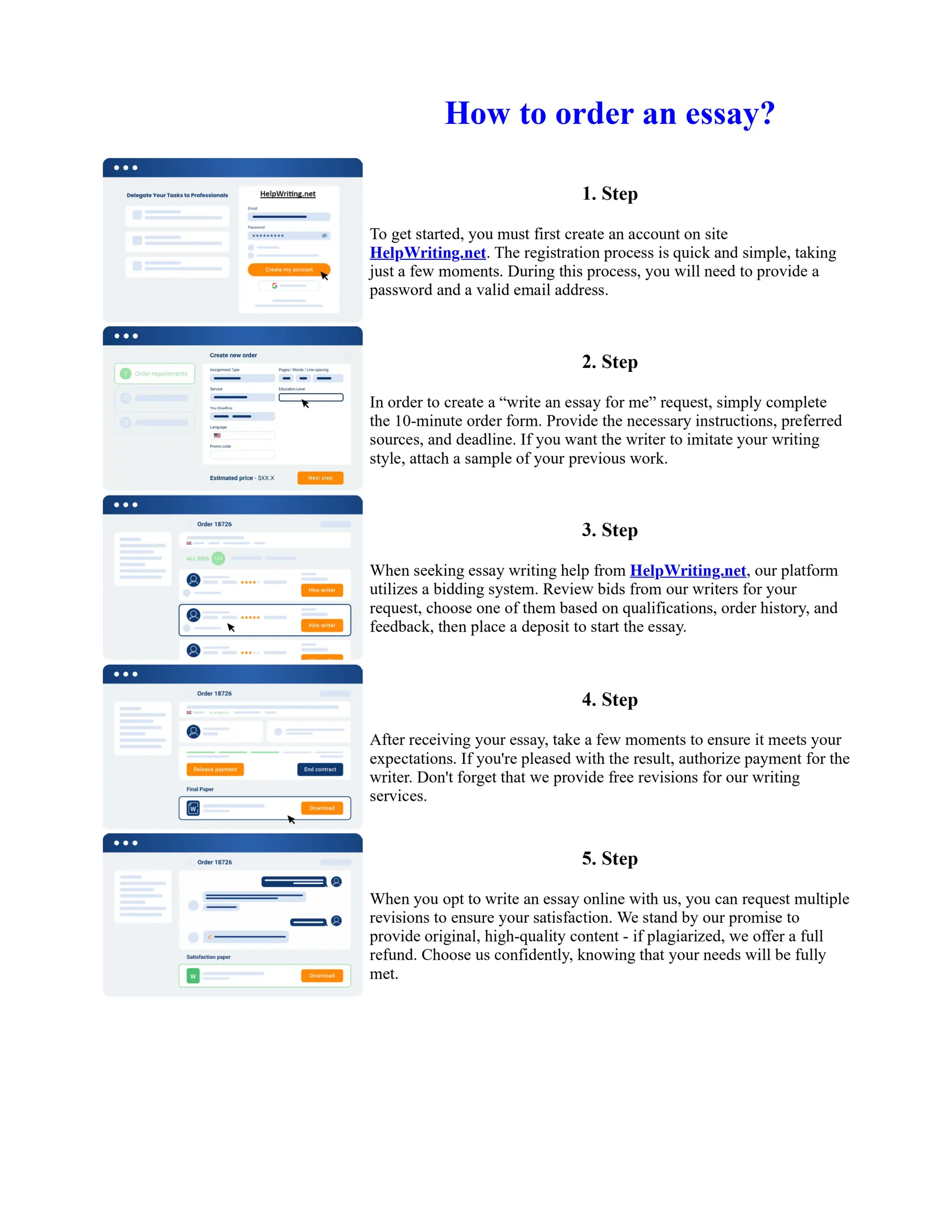
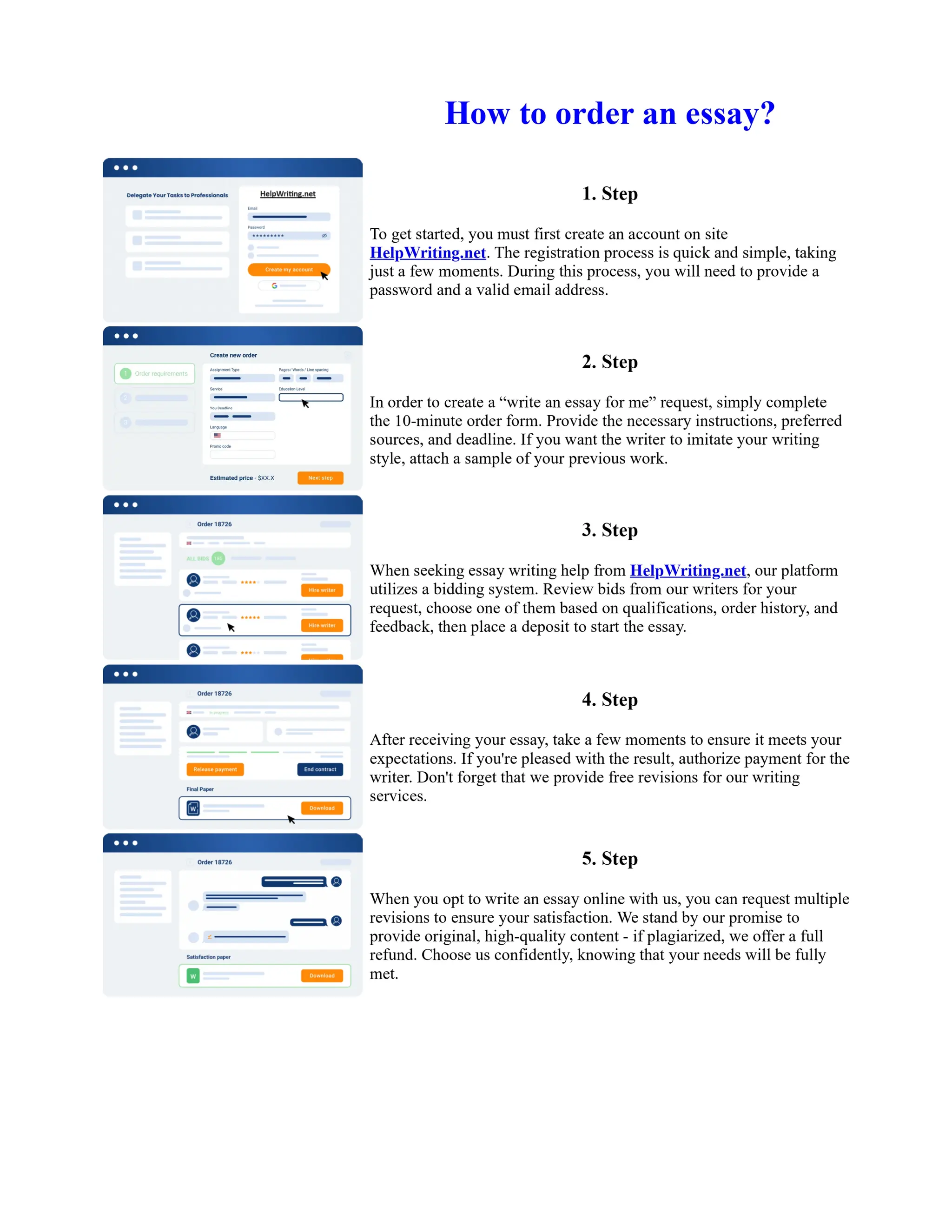
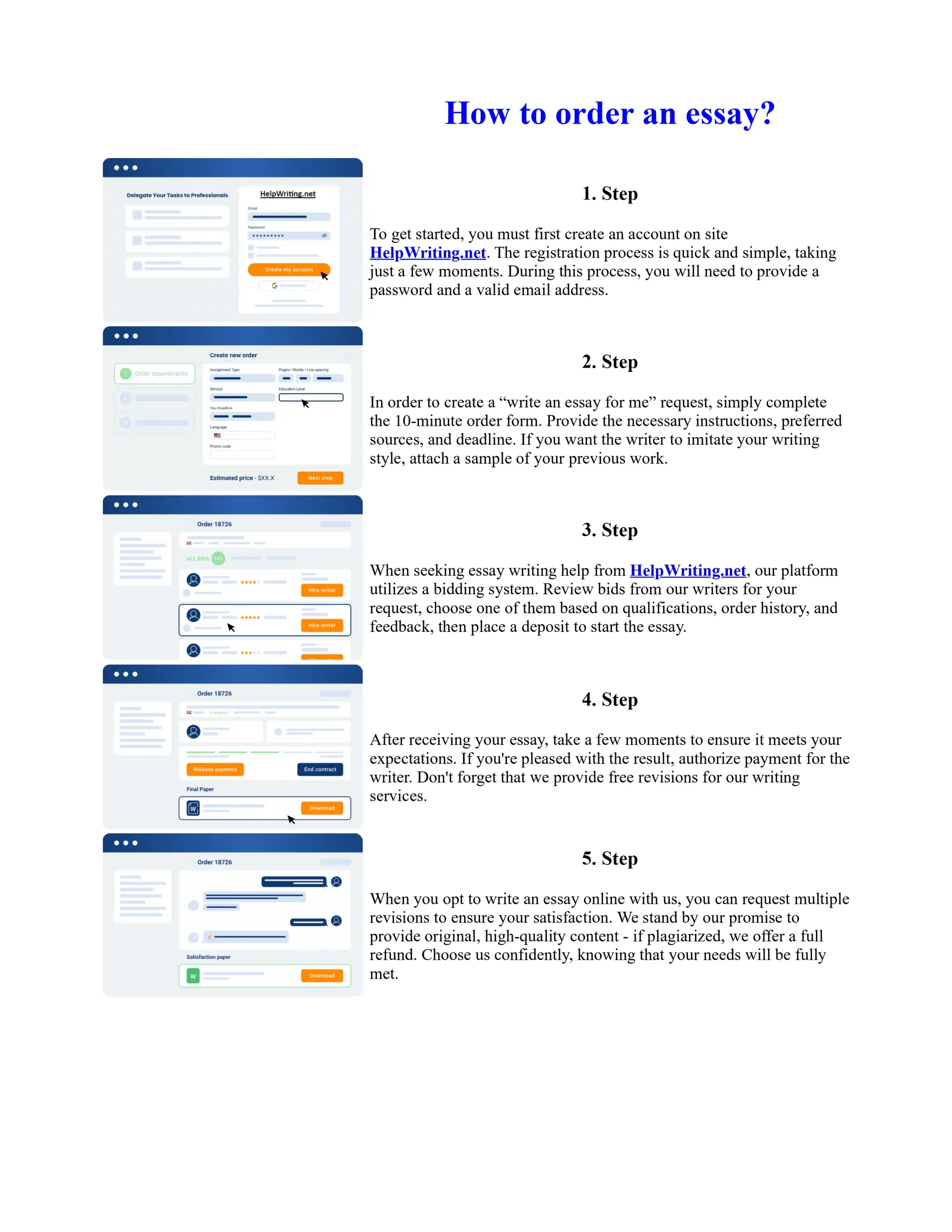
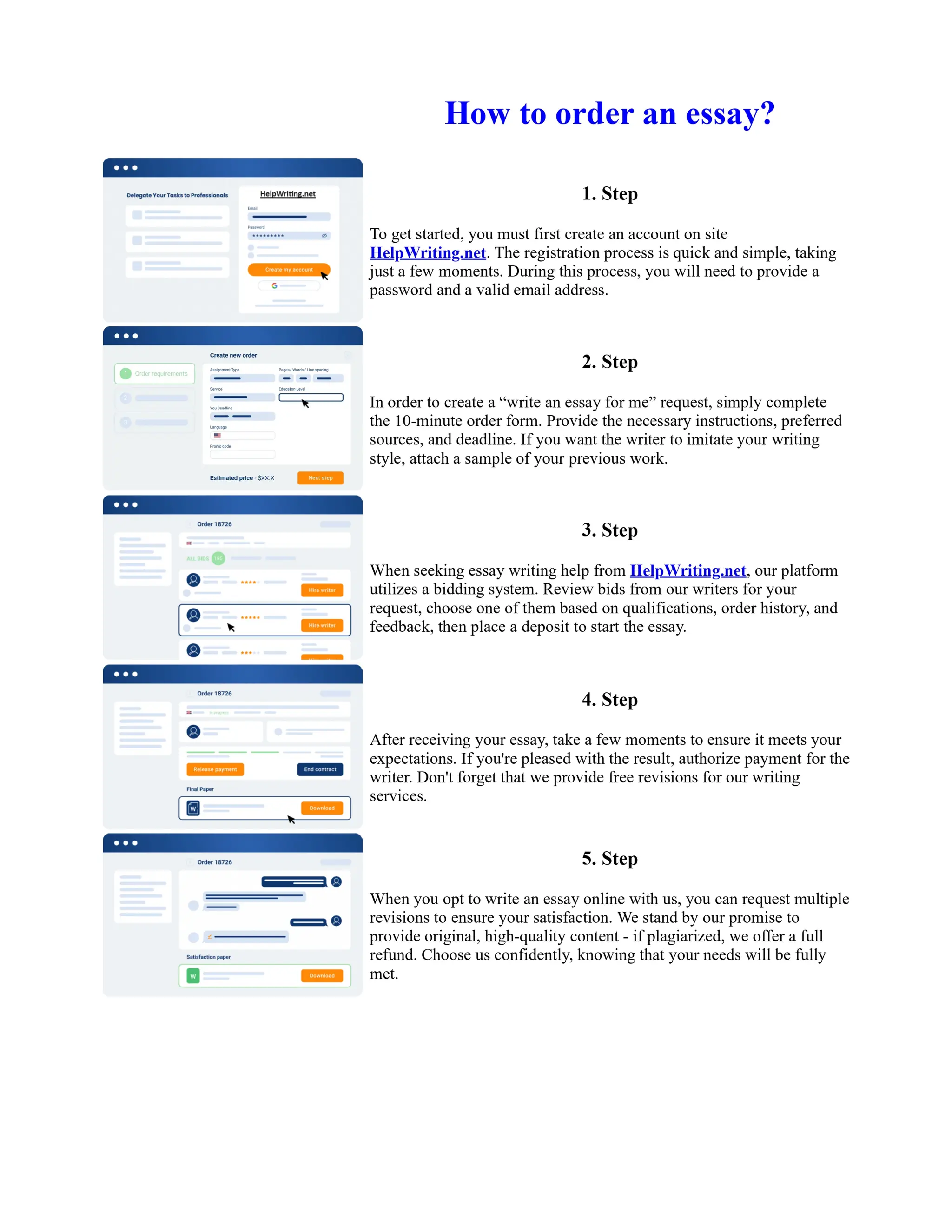
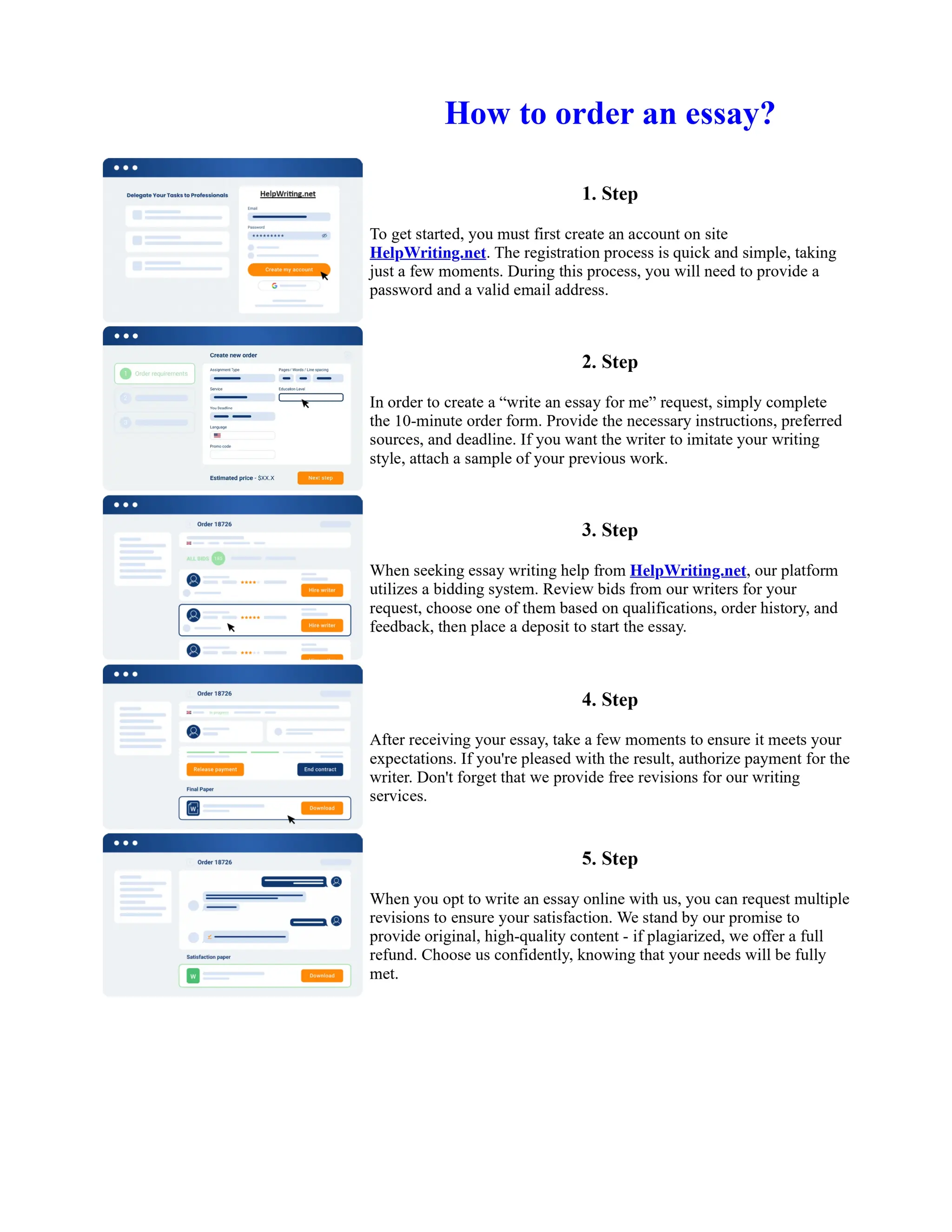
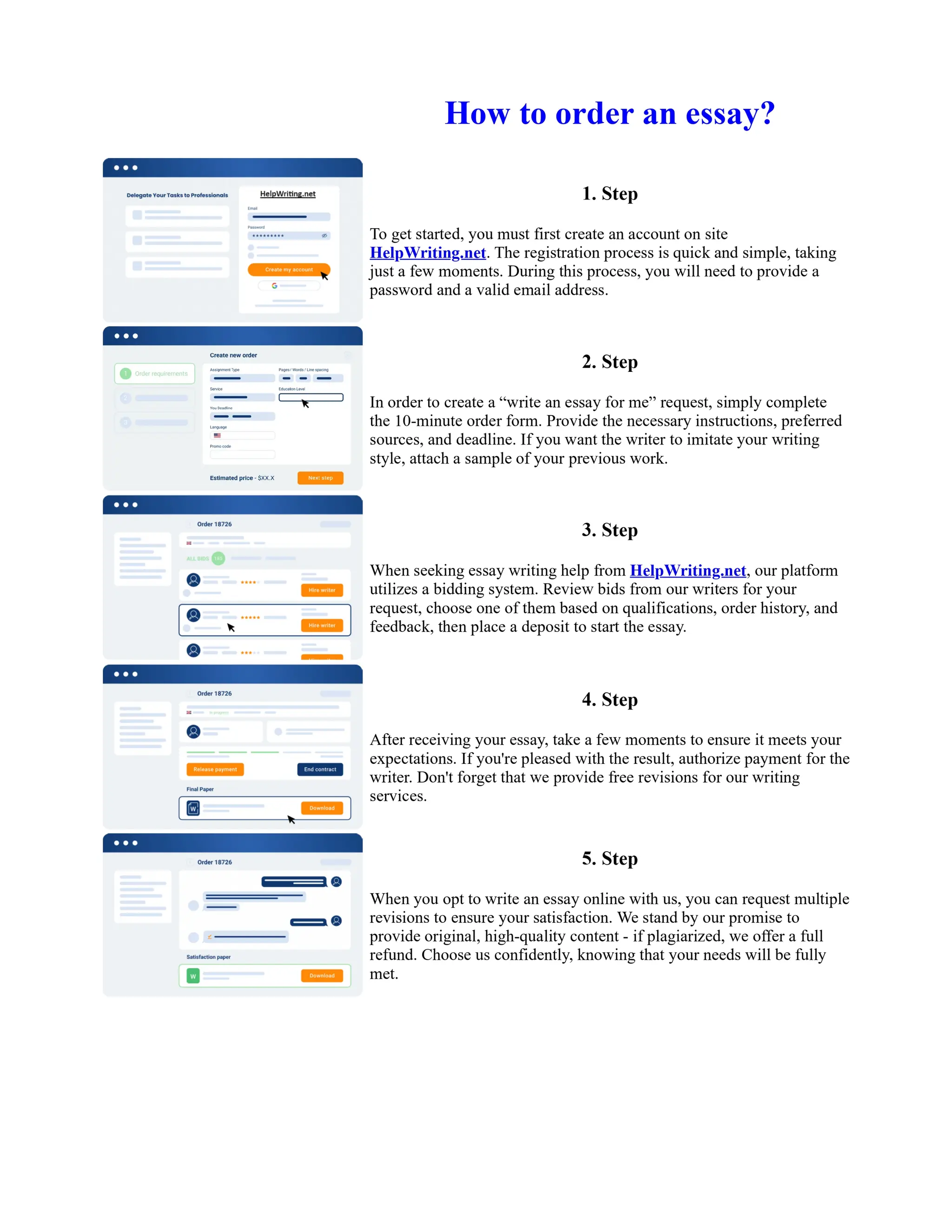
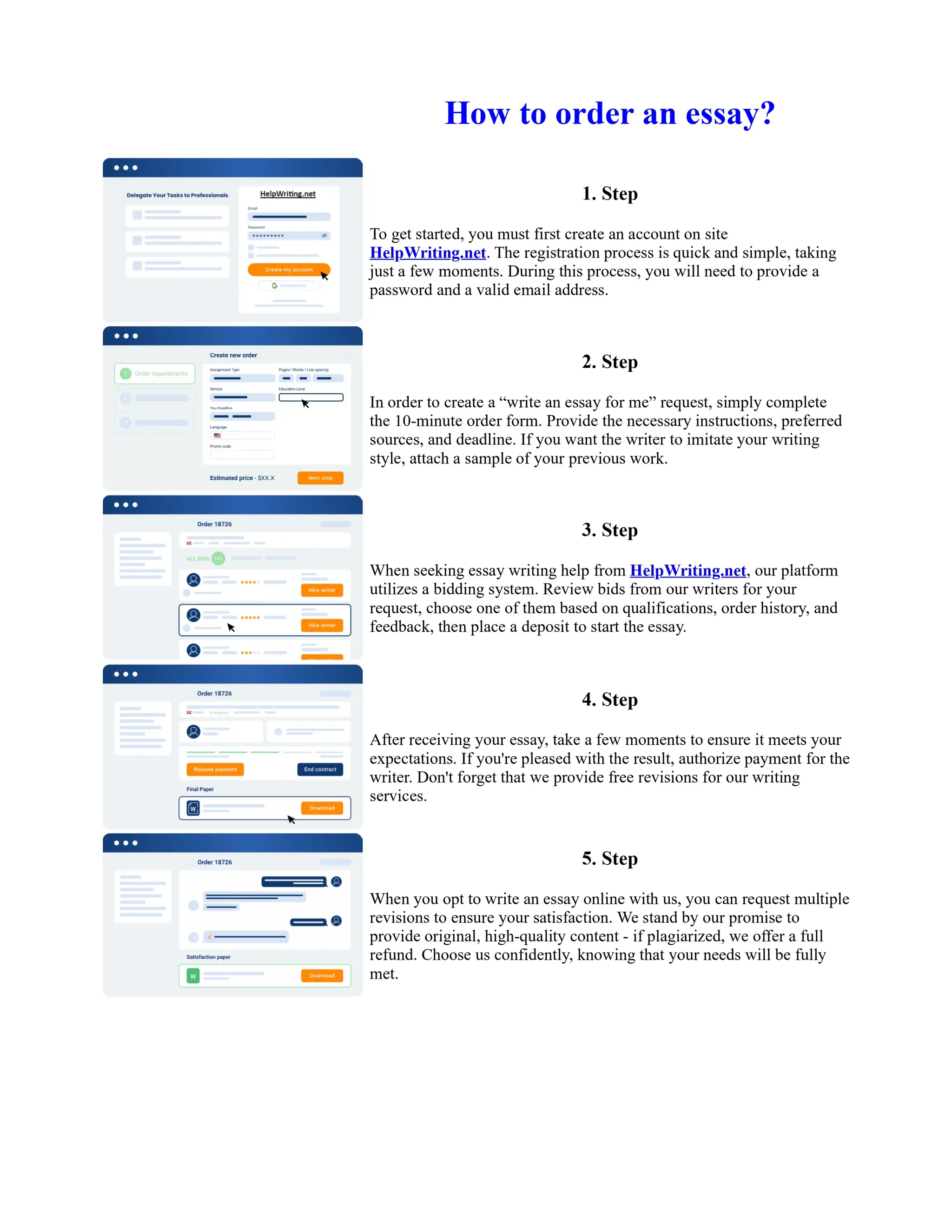
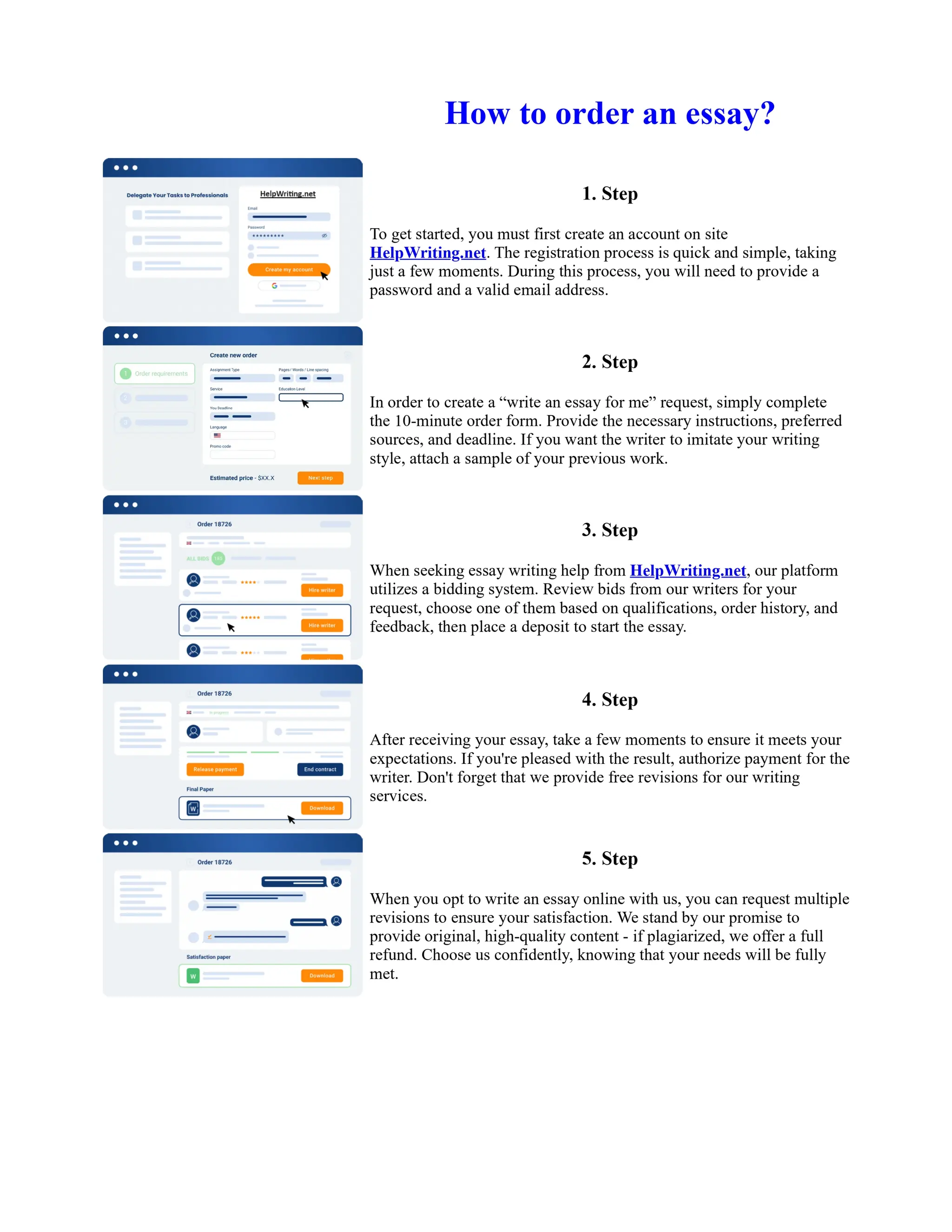
1) Basel I, adopted in 1988, aimed to strengthen bank stability and create equal competition. However, it only considered credit risk and encouraged regulatory arbitrage.
2) Basel II, introduced in 2004, aimed to make capital requirements more risk-sensitive by incorporating banks' internal risk management. It included three pillars for minimum capital, supervisory review, and market discipline.
3) While Basel III, finalized in 2010 after the financial crisis, aims to mitigate past damage, the results of its stricter capital standards are still to be seen as countries implement its guidelines.
















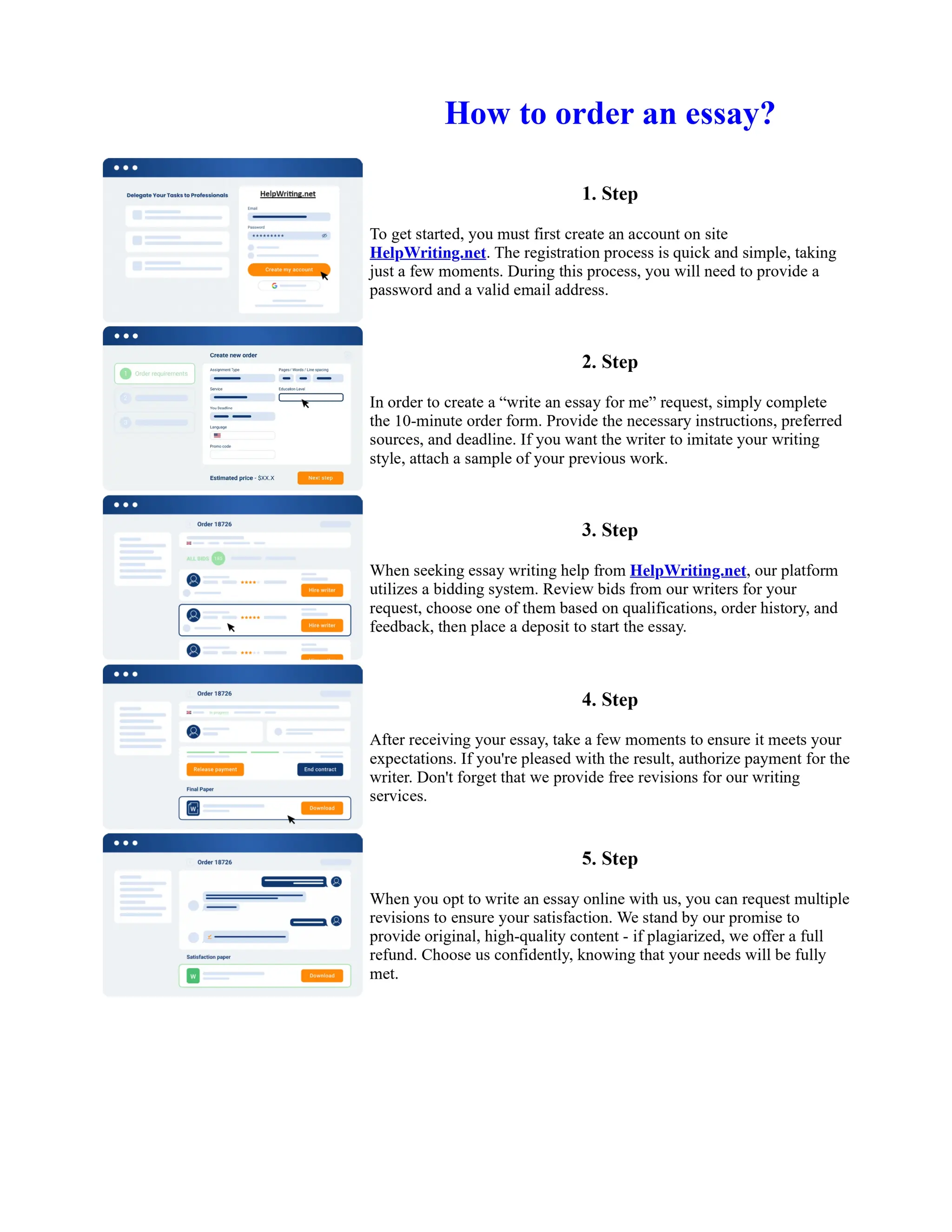
![Too Big to Fail Essay
Too big to fail?
In this essay I will be addressing the "Too Big To Fail" (TBTF) problem in the current banking
system. I will be discussing the risks associated with this policy, and the real problems behind it. I
will then examine some solutions that have been proposed to solve the "too big to fail" problem. The
policy 'too big to fail' refers to the idea that a bank has become so large that its failure could cause a
disastrous effect to the rest of the economy, and so the government will provide assistance, in the
form of perhaps a bailout/oversee a merger, to prevent this from happening. This is to protect the
creditors and allow the bank to continue operating. If a bank does fail then this could cause a
domino effect throughout ... Show more content on Helpwriting.net ...
Market risk is the risk associated with an investors day to day investments, that are affected by
constant fluctuations in the markets. With investment banking, a banks reputation is a critical in its
success, reputational risk describes the trustworthiness of a business. A firm with a poor reputation
will not get as much business, meaning a bad reputation results in a loss in revenue. Concentration
Risk is the risk showing the spread of a banks' accounts to various debtors to whom the bank has
lent to. The Basel II accord stated that 'operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate
or failed internal processes, people and systems, or from external events'. This risk covers the very
wade basis of a company's operations, there are many different factors involved here: people,
employees actions and company processes.
Systemic Risk is the risk of the collapse of the entire financial system, Kay (2008) defined it as 'the
tendency for the failure of a financial services business to have an impact on many other businesses.'
[ 16 ] The key to solving the problem of systemic risk is by naming and taxing the TBTF firms and
this will minimize systemic risk and it will level the playing field for firms who do not have the
same guarantee of financial support as TBTF firms do.
During the recent financial crisis, in the autumn of 2008, the Lehman Brothers bank collapsed. It
was the biggest bankruptcy in history
... Get more on HelpWriting.net ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/baselnorms-231119224828-f50b2f5d/75/Basel-Norms-33-2048.jpg)