The document provides information on Basel committees and accords. It discusses the following:
- The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision was founded in 1974 by central bank governors of G10 countries to focus on banking supervision and ensure adequate supervision.
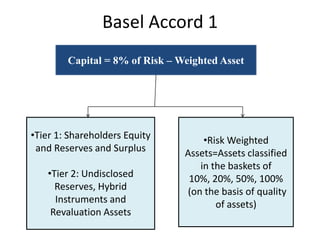
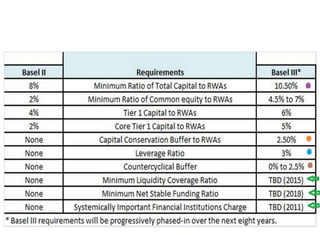
- Basel I, introduced in 1988, required banks to hold capital equal to 8% of risk-weighted assets. It aimed to ensure adequate capital levels and competitive banking markets.
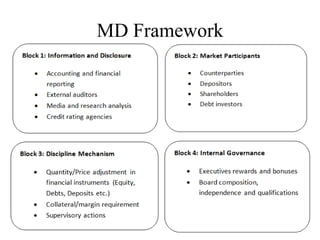
- Basel II, introduced capital requirements for credit risk, operational risk and market risk using standardized and internal ratings-based approaches. It also included a supervisory review process and introduced requirements for market discipline and transparency.
- Basel III further strengthened bank capital requirements and introduced new regulatory standards on