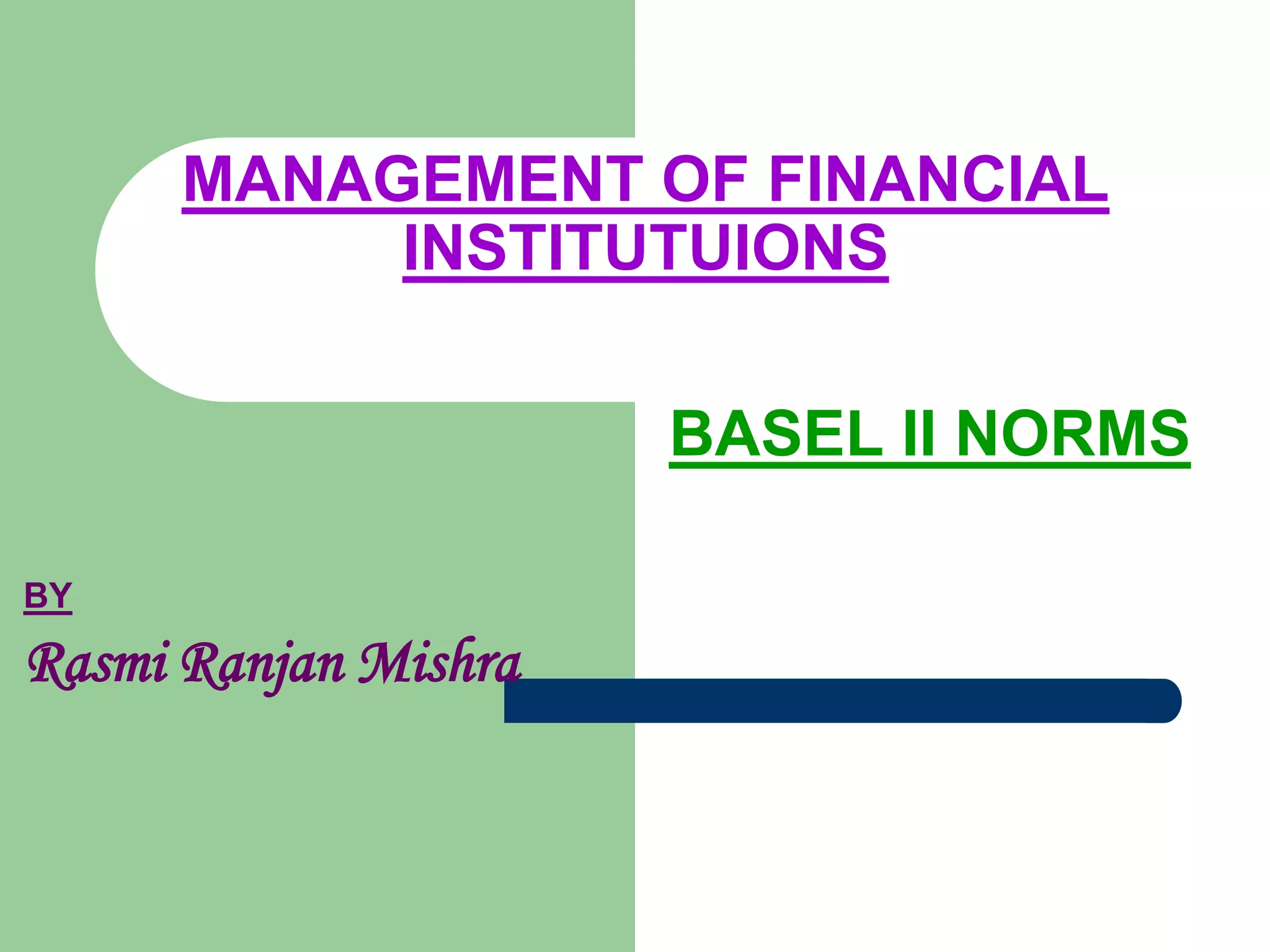
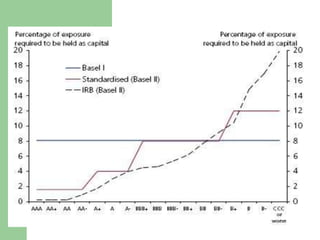
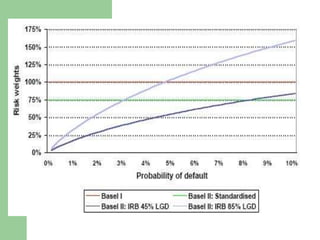
The document discusses the Basel II Accords, which establish international standards for banking regulations and capital requirements. Basel II aims to make capital requirements more risk-sensitive by measuring credit, operational, and market risks. It introduces a three pillar framework: Pillar 1 sets minimum capital standards; Pillar 2 establishes supervisory review; and Pillar 3 promotes market discipline through disclosure. Implementation of Basel II varies by country and bank sophistication in risk measurement. The overall goal is a safer, more stable global banking system.