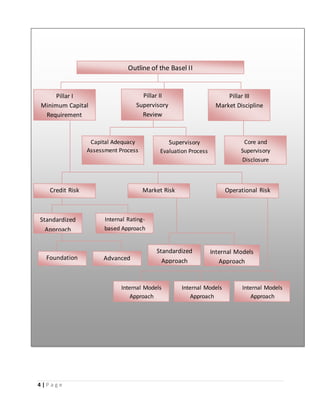
Basel II and III are international banking regulatory accords that establish capital requirements and risk management standards. Basel II, established in 1988, focused on credit risk but did not adequately address operational and market risk. Basel III, developed after the 2008 crisis, strengthened capital and liquidity requirements and introduced leverage and liquidity ratios. The Basel accords aim to ensure banks maintain adequate capital reserves to absorb losses and promote stable, risk-sensitive banking globally.