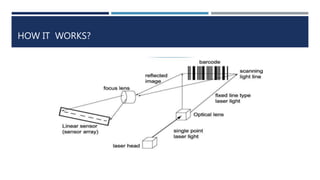
The document discusses barcodes, including what they are, their types and structure, how they work, characteristics, and technology. Barcodes are optical machine-readable representations of data that were invented in 1948 and use a series of bars and spaces to represent alphanumeric information binary code that can be decoded by barcode readers. Their basic structure includes quiet zones, start/stop patterns, data characters, and optionally check characters. Barcodes use binary coding and decoding where bars represent 1s and spaces represent 0s. Key properties are magnification, bar height, substrate, and bar widths. Barcode technology involves software to generate unique codes, special thermal printers to print them on products, thermal paper that changes color with heat, and barcode readers to scan