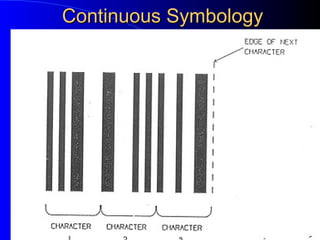
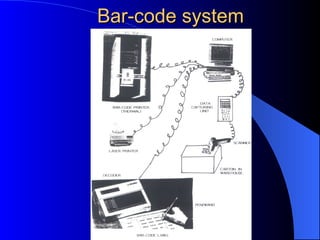
Bar code technology is an automatic identification system that utilizes dark bars and white spaces to represent specific information, enabling rapid and accurate data collection. It offers benefits such as reduced errors in data entry and improved resource management across various applications, including inventory control, retail, and healthcare. The document also describes bar code terminology, types of scanners, and applications in libraries, highlighting its importance in facilitating efficient operations.