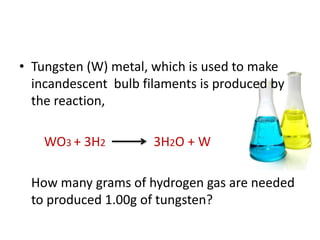
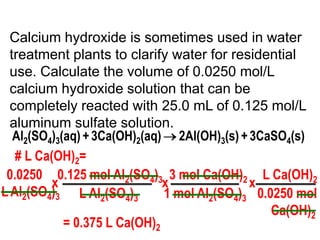
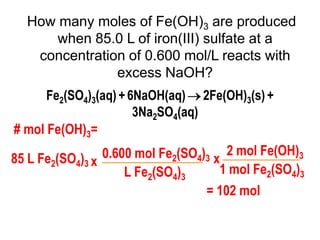
1) The document discusses key concepts in stoichiometry including moles, mole-mass relationships, balancing chemical equations, and using mole ratios to solve stoichiometry problems.
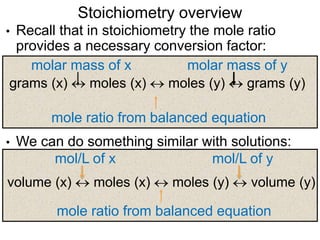
2) It provides steps for calculating molar mass, moles, mass from moles, and mass from mass using mole ratios from balanced chemical equations.
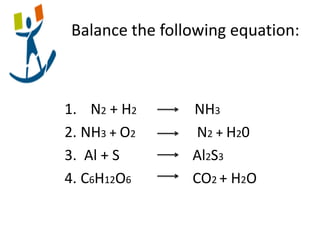
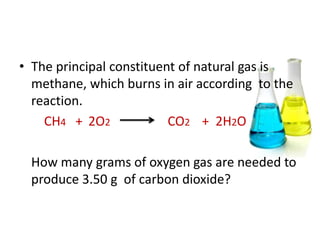
3) Several examples are presented to demonstrate solving for unknown quantities in chemical reactions using mole ratios from balanced equations.