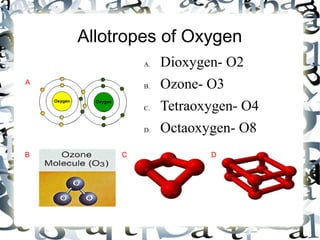
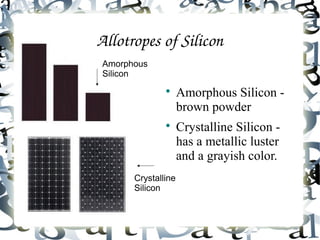
An allotrope is a variant form of an element with the same chemical composition but different molecular structure and properties. The document discusses several common allotropes including carbon (diamond, graphite), phosphorus (white, red), oxygen (O2, O3), sulfur (rhombic, monoclinic), boron (amorphous, crystalline), and silicon (amorphous, crystalline). Allotropes have substantial differences in their physical properties due to variations in atomic bonding arrangements.




![Allotropes of Carbon
A striking example of differing physical
properties among allotropes is the case
of carbon. Solid carbon exists in two
allotropic forms: diamond and graphite.
• Diamond is the hardest naturally occurring
substance and has the highest melting point
(more than 6,335°F [3,502°C]) of any
element.
• In contrast, graphite is a very soft material,
the substance from which the "lead" in lead
pencils is made.
The 8 Allotropes of Carbon are: a)
Diamond, b) Graphite, c)Lonsdaleite, d)
Buckminsterfullerene, e) C540, f)C70,
g)Amorphous, h) Carbon Nanotube](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allotropes-130423034502-phpapp02/85/Allotropes-5-320.jpg)