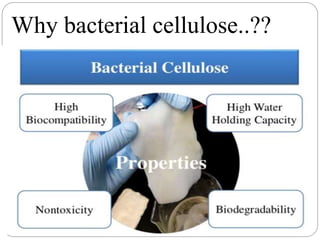
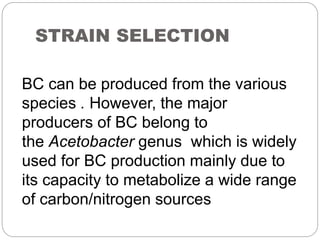
Bacterial cellulose is produced by certain bacteria through a four step process: strain selection, culture medium preparation, cultivation, and downstream processing. The conventional culture medium contains glucose, peptone and yeast extract. Recent studies have shown that adding ethanol and acetic acid to this medium can improve bacterial cellulose yield up to 279%. Bacterial cellulose has many applications including use in facial masks, food packaging, biomedical devices, and artificial meat.