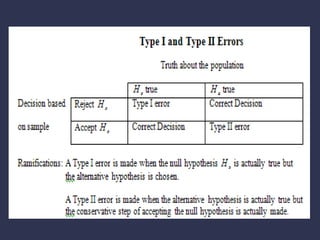
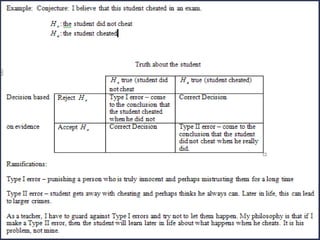
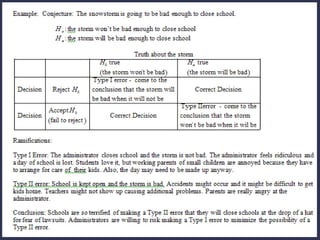
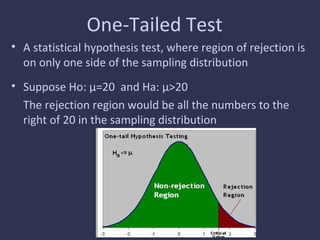
Statistical hypothesis testing involves formal procedures to accept or reject statistical hypotheses about population parameters based on sample data. It involves stating the null and alternative hypotheses, analyzing sample data using test statistics, and interpreting results to either reject the null hypothesis if the test statistic is unlikely or fail to reject it if it is not significant based on the p-value and significance level. Type I and II errors can occur, with the significance level setting the probability of a Type I error and the power test measuring the probability of avoiding a Type II error. Hypothesis tests can use one-tailed or two-tailed regions of rejection depending on the alternative hypothesis.