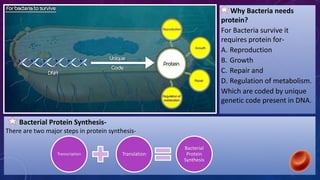
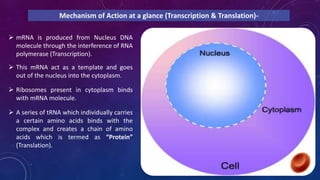
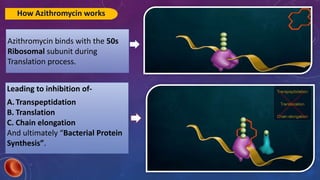
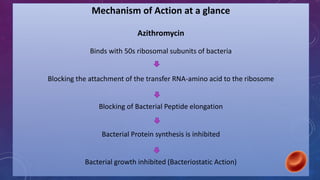
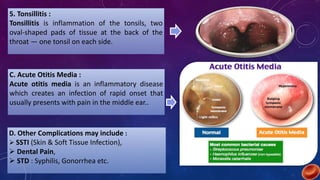
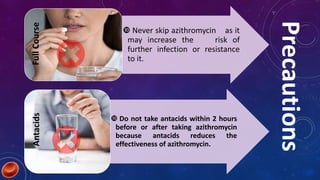
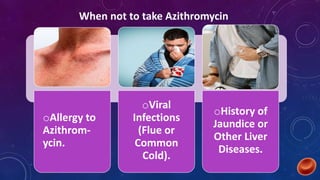
Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum macrolide antibiotic with bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic properties, effective against a range of bacterial infections, notably respiratory tract infections and enteric fever. It works by binding to the 50s ribosomal subunit, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis and resulting in bacterial growth inhibition. The medication is available in tablet and suspension forms, has a favorable dosing schedule, and is generally safe for use during pregnancy.