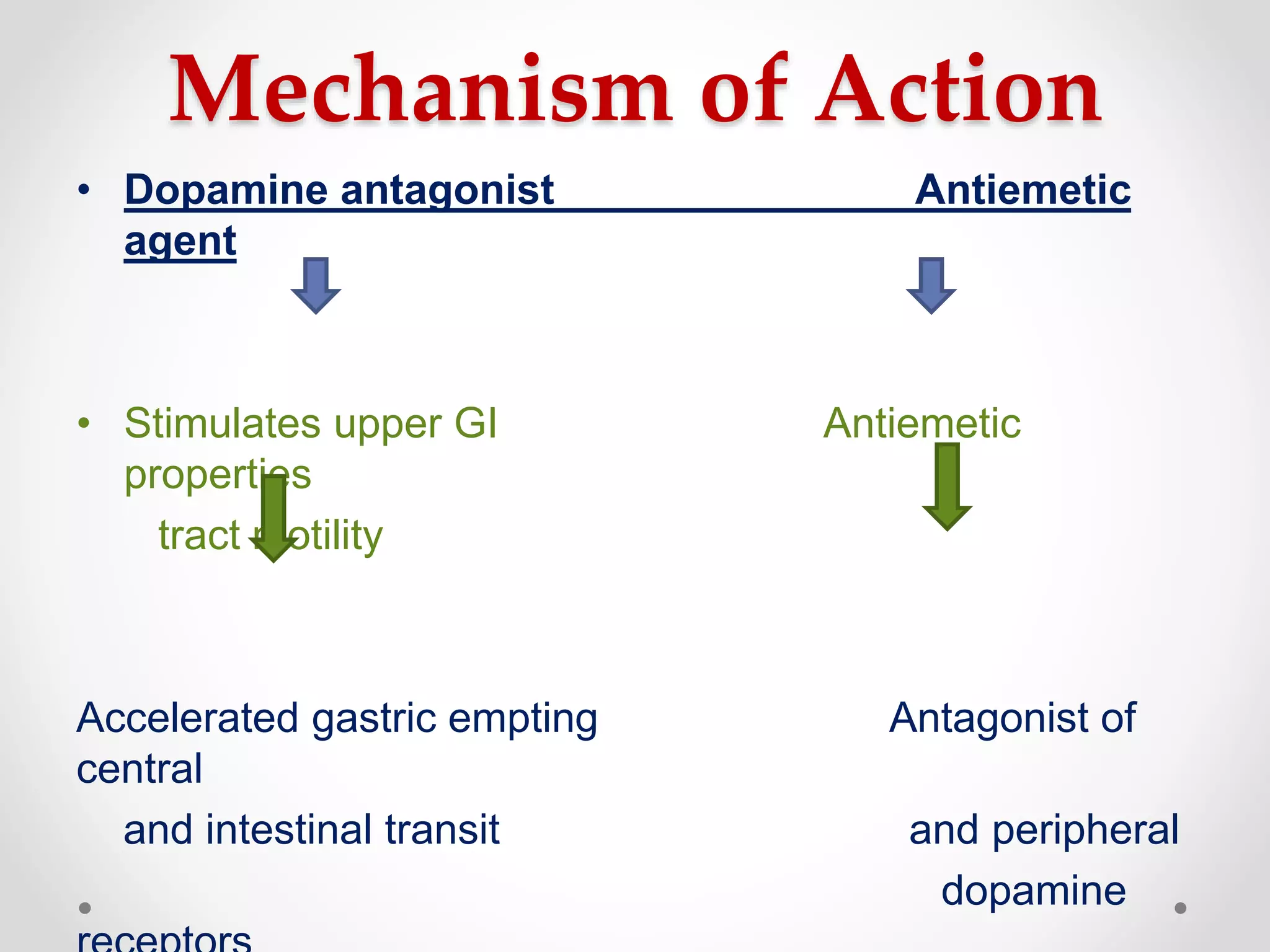
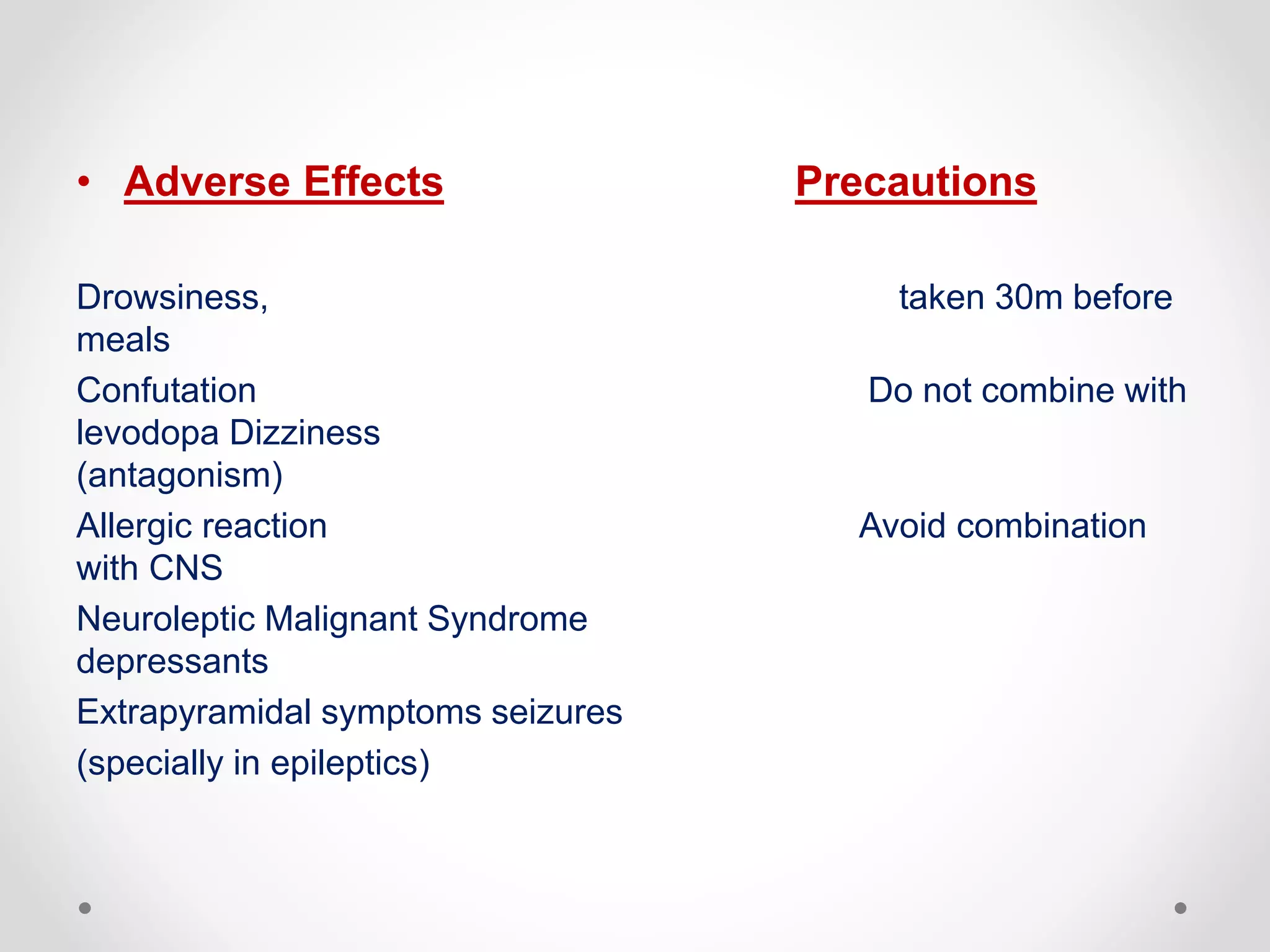
Metoclopramide is a prokinetic agent that increases stomach and upper intestine movements. It is used to treat certain stomach problems, nausea, and vomiting caused by chemotherapy. Metoclopramide works by antagonizing dopamine, stimulating upper GI tract motility, and accelerating gastric emptying and intestinal transit. It is available as tablets, injections, and oral solutions. Common uses include nausea and vomiting in adults, diabetic gastroparesis, GERD, and preventing postoperative nausea. Usual dosing is 15-30mg per day divided into three doses with at least 6 hours between doses.