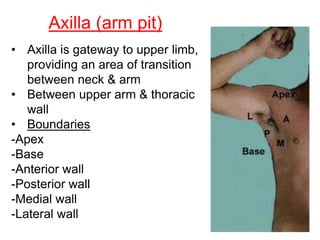
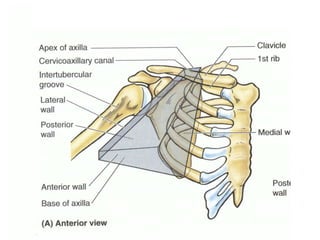
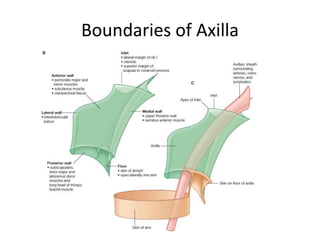
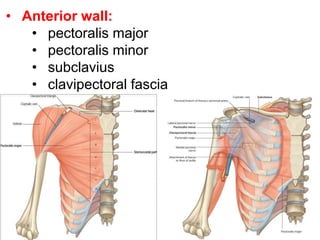
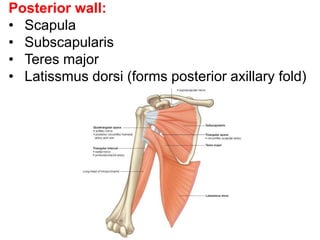
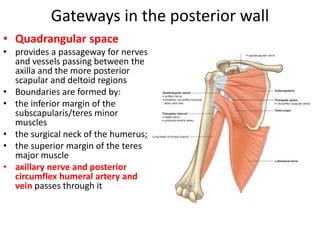
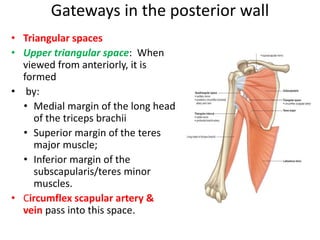
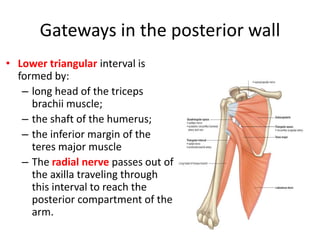
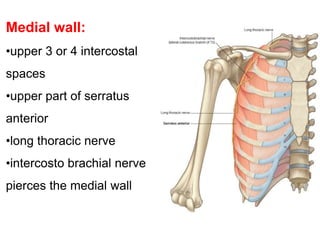
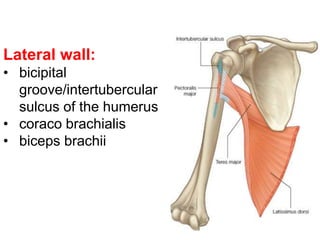
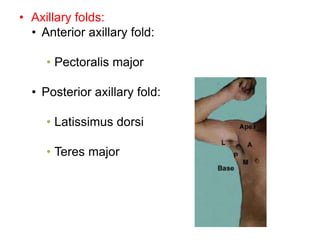
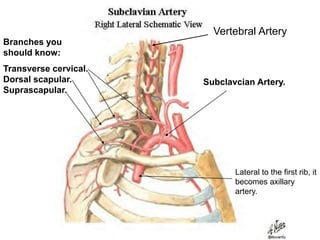
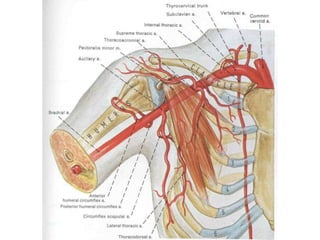
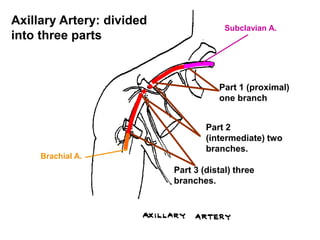
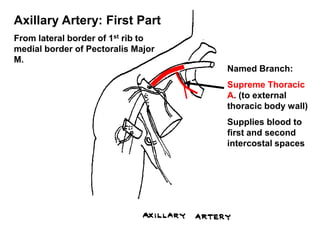
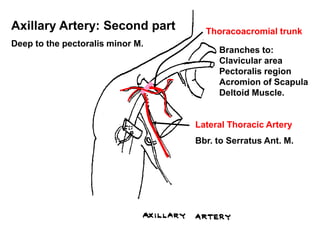
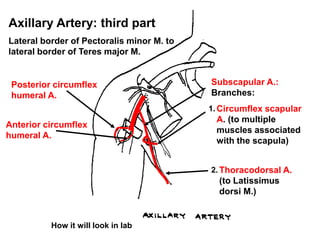
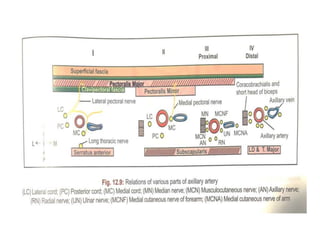
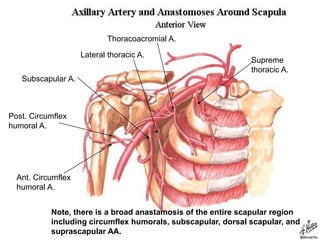
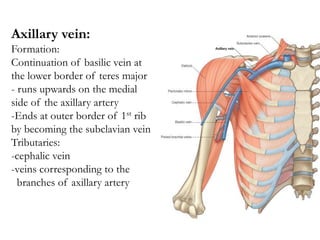
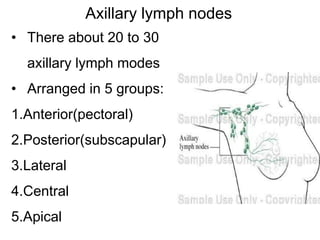
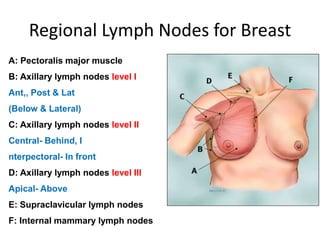
The document defines and describes the anatomy of the axilla, including its boundaries, contents, and structures that pass through it. The axilla is the region under the arm bounded by the first rib, scapula, and thoracic wall. It contains the axillary vessels and brachial plexus, as well as fat and lymph nodes. Gateways in the posterior wall allow passage of nerves and vessels between the axilla and scapular regions.