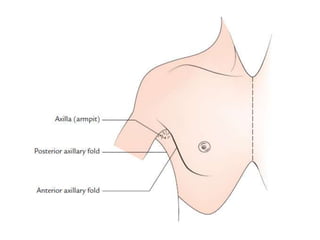
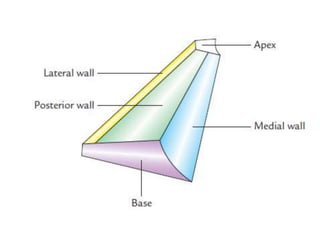
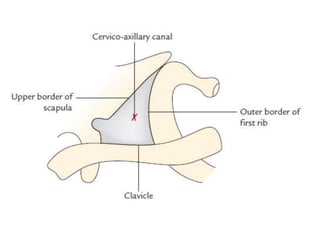
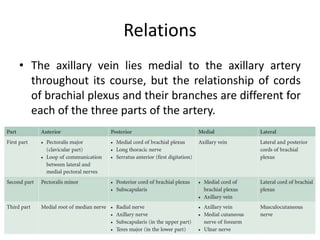
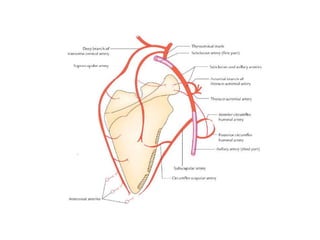
The axilla contains the brachial plexus, axillary vessels, and lymph nodes. It has boundaries formed by muscles and acts as a passage from the neck to the upper limb. The axillary artery passes through the axilla in three parts, giving off branches. The axillary vein lies medial to the artery, draining the upper limb. Lymph nodes in the axilla drain the arm and breast. The scapular anastomosis connects arterial branches to ensure circulation if main vessels are blocked.