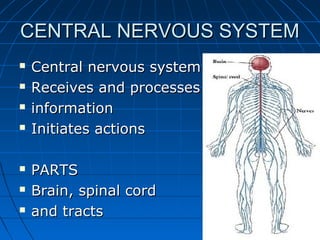
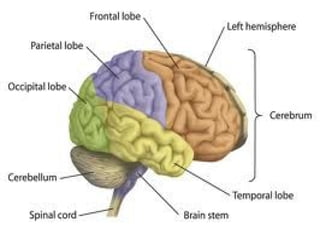
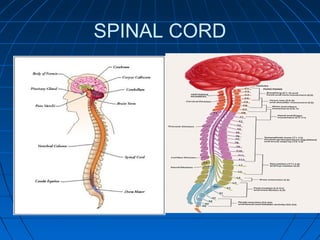
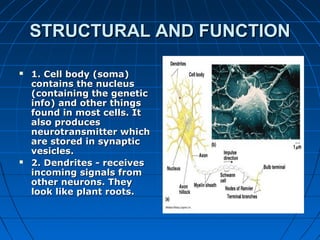
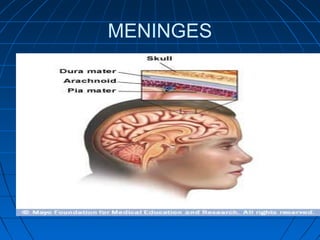
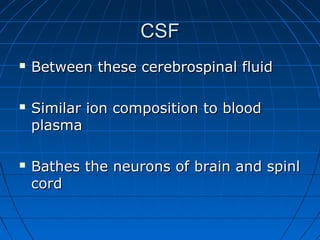
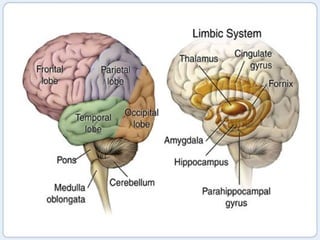
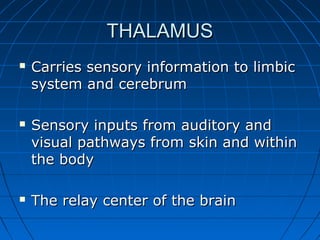
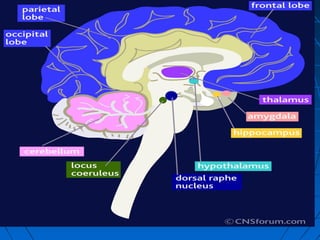
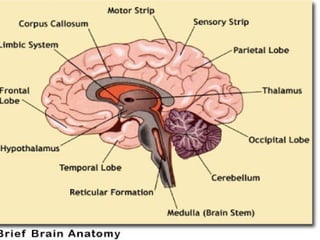
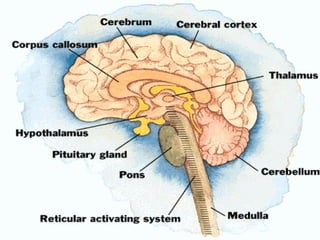
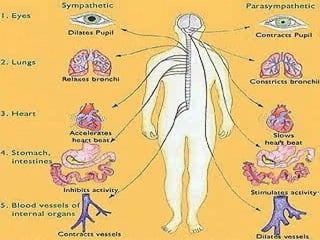
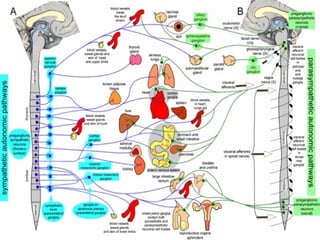
The document discusses the autonomic nervous system, which has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The sympathetic system prepares the body for fight or flight by increasing heart rate and blood pressure. The parasympathetic system then takes over once the stressor is gone, calming the body down.