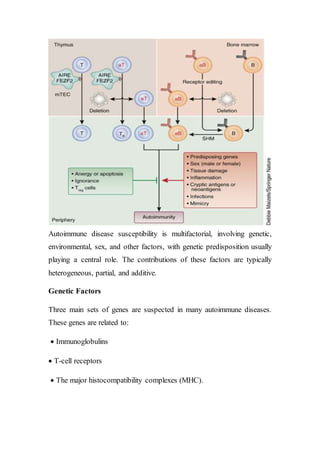
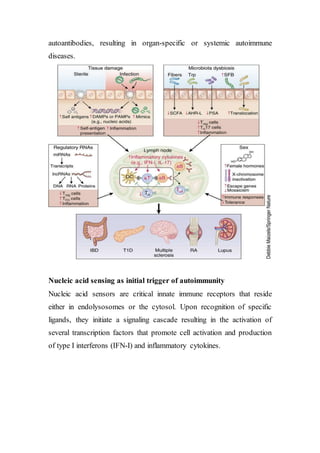
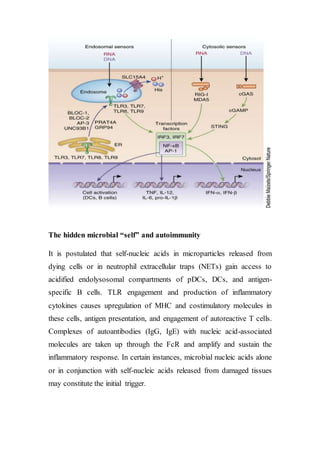
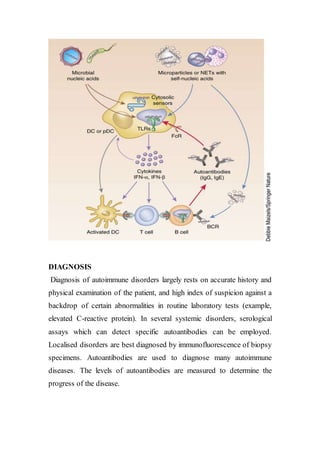
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system attacks the body's own cells and tissues. They represent a significant health burden, affecting 3-9% of the population. The immune system normally maintains tolerance to self-antigens but in autoimmunity this tolerance fails. Autoimmune diseases can be systemic, targeting ubiquitous antigens, or organ-specific, targeting particular tissues. Genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors all contribute to autoimmune disease susceptibility. Treatments aim to suppress the immune system or its inflammatory responses.