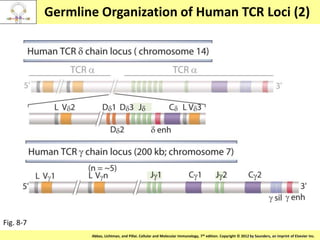
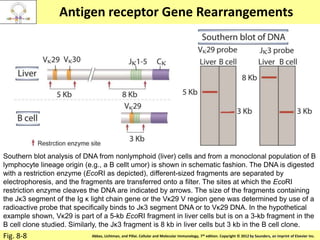
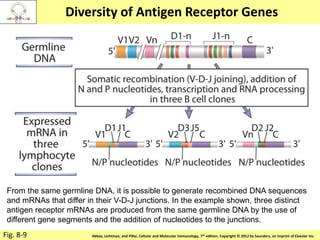
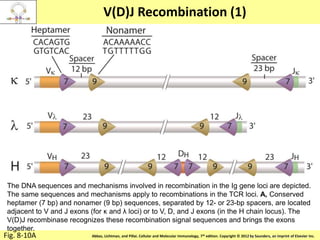
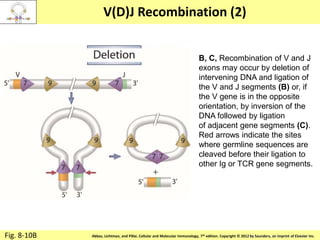
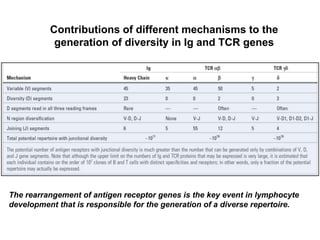
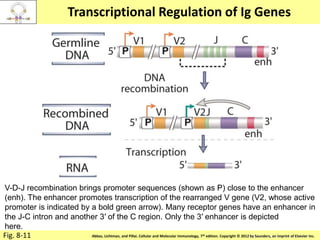
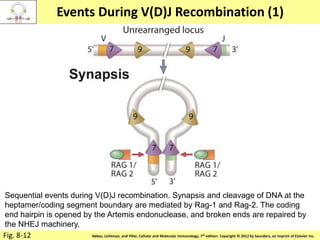
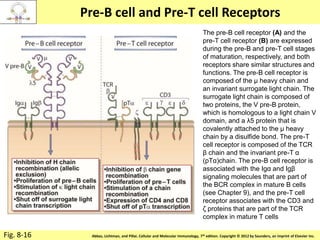
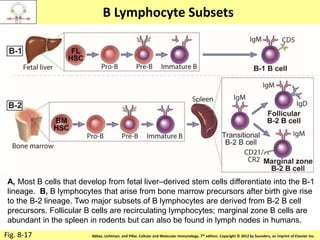
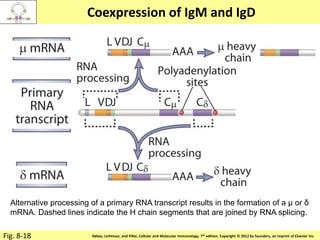
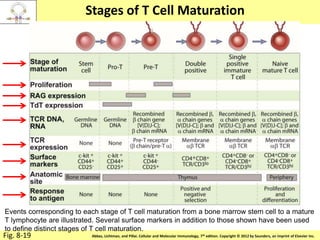
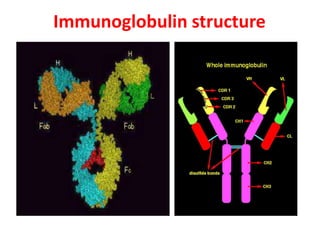
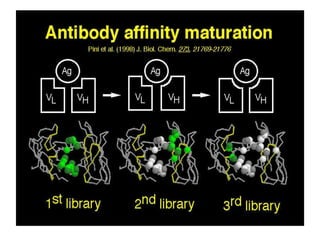
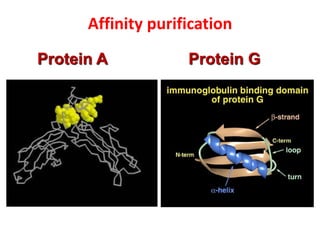
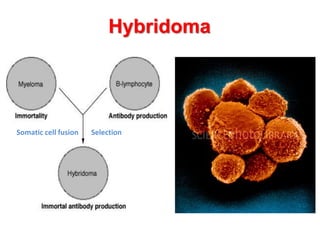
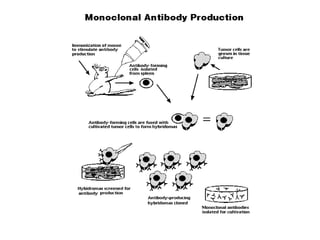
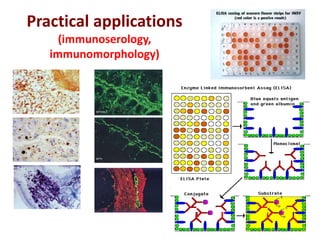
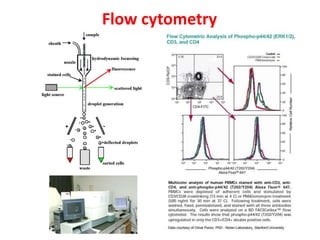
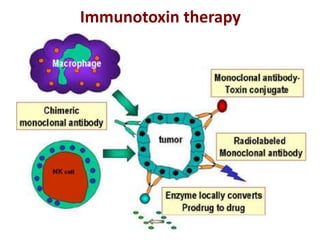
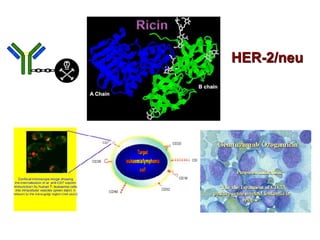
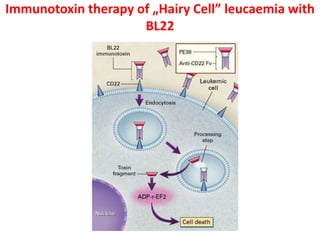
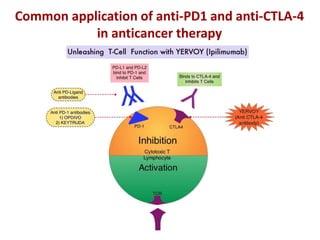
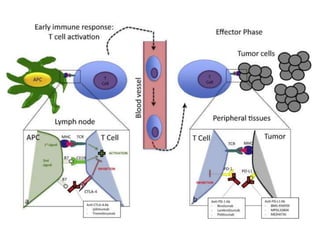
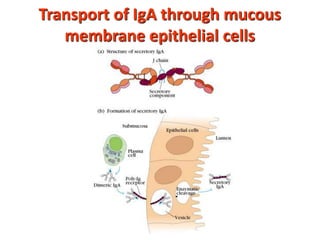
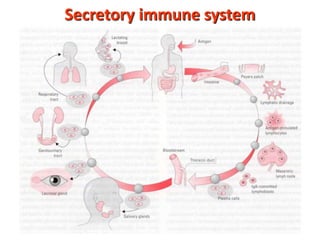
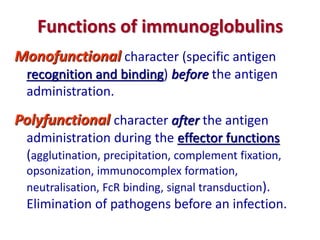
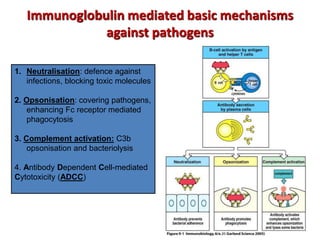
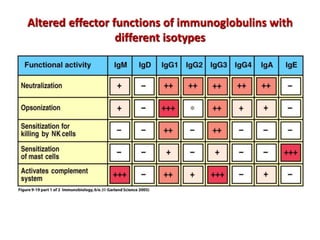
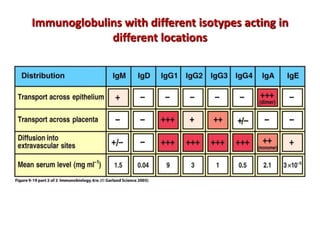
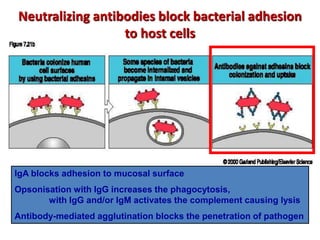
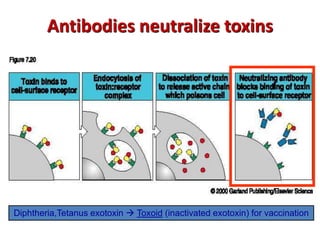
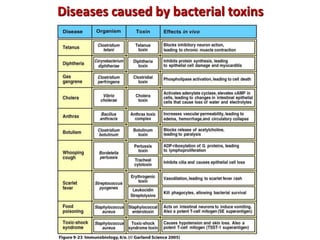
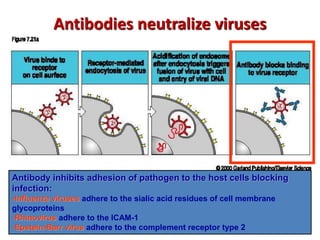
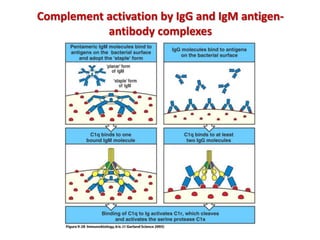
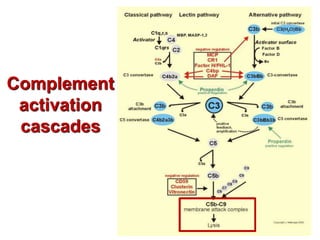
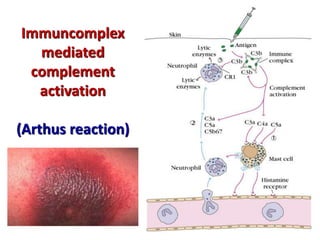
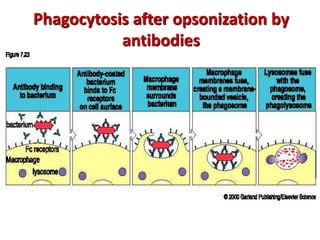
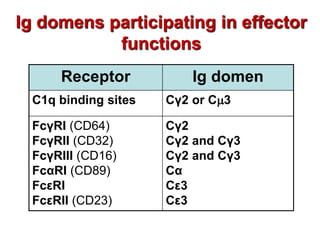
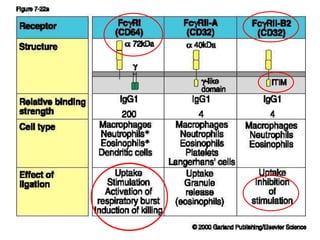
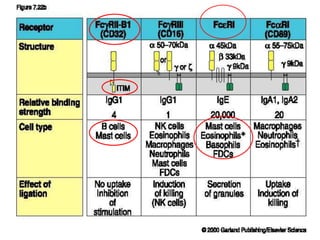
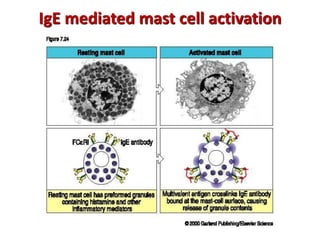
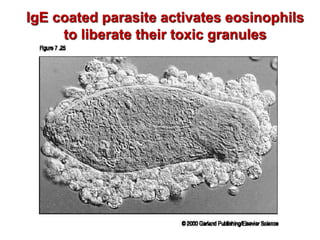
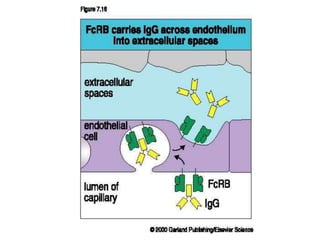
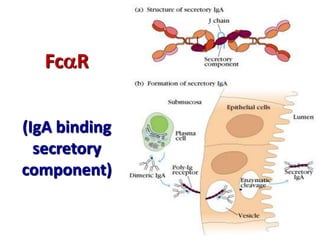
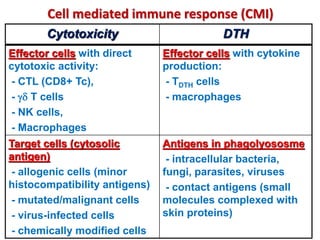
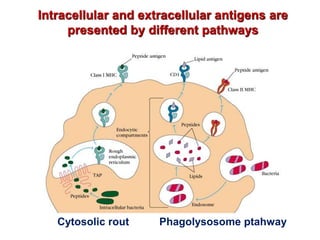
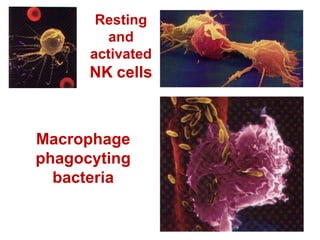
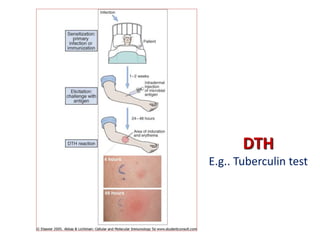
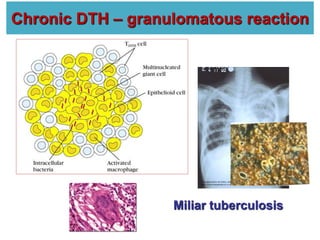
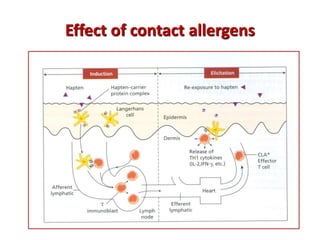
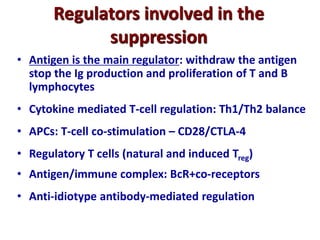
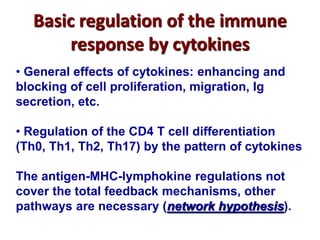
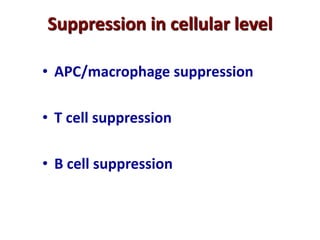
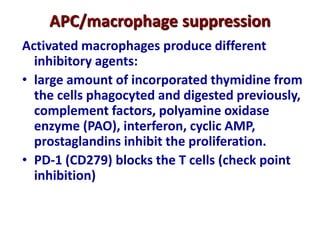
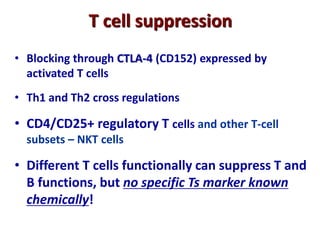
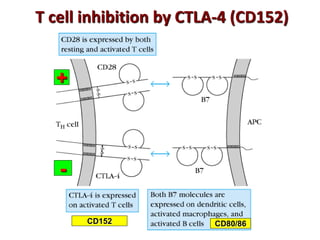
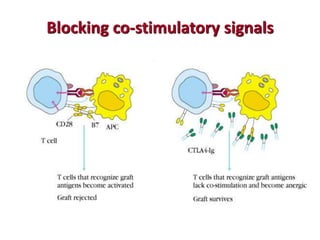
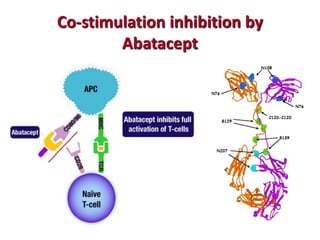
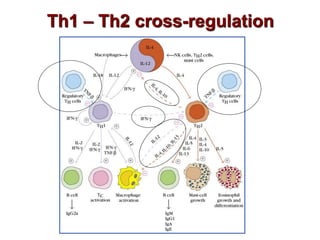
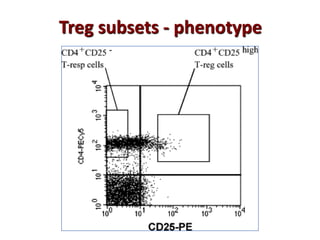
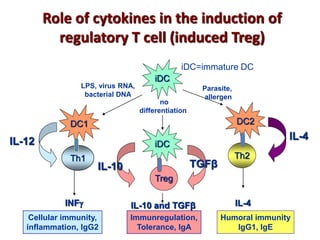
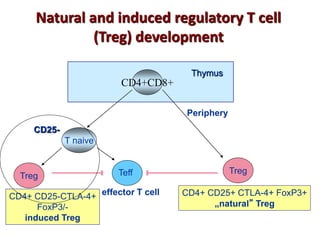
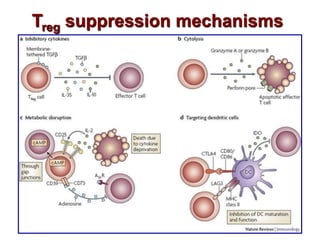
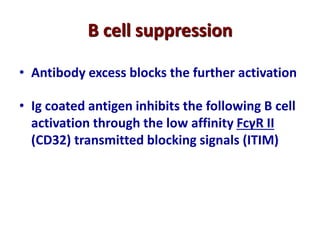
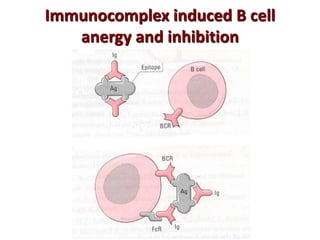
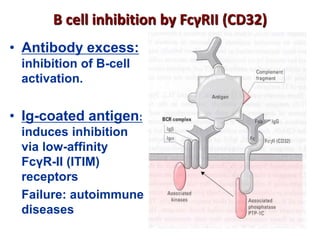
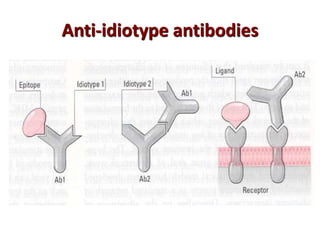
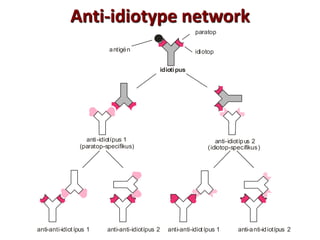
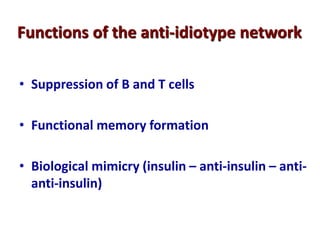
The document discusses lymphocyte development and antigen receptor gene rearrangement. It covers the following key points:
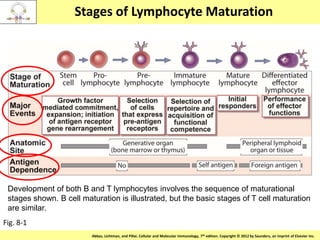
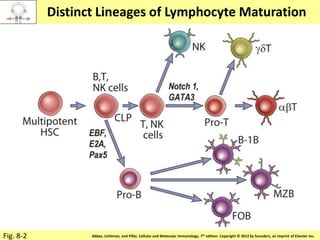
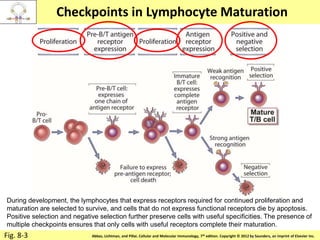
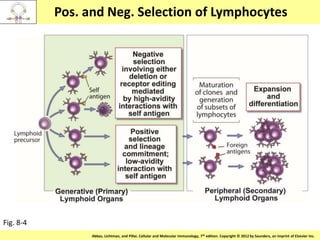
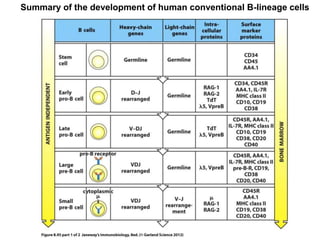
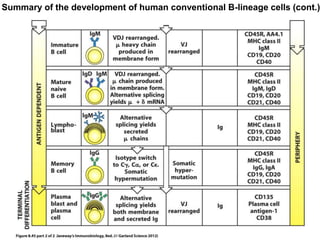
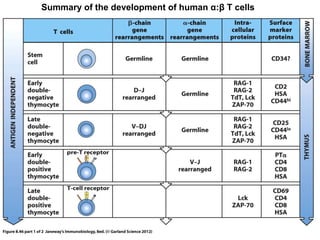
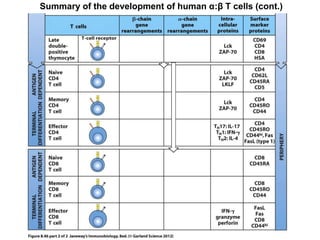
1. Lymphocyte development involves commitment to the B or T cell lineage, proliferation of progenitors, rearrangement of antigen receptor genes, selection checkpoints, and differentiation into distinct subpopulations.
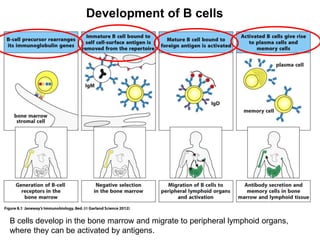
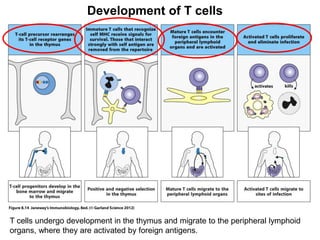
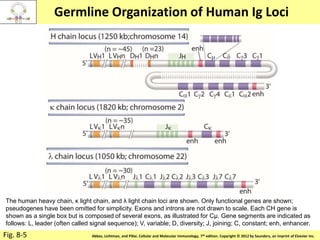
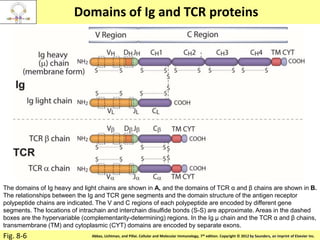
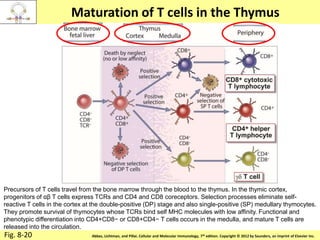
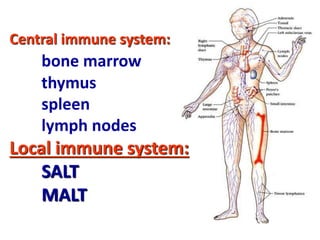
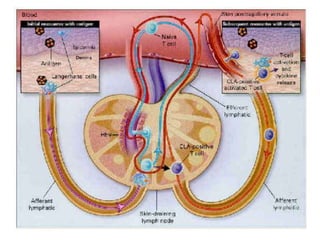
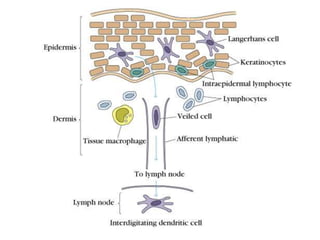
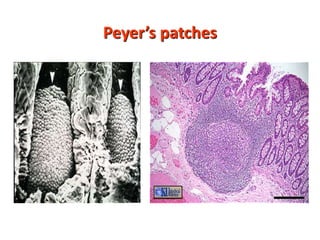
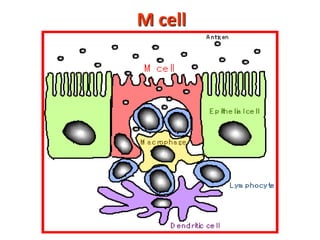
2. B cells undergo gene rearrangement and development in the bone marrow before migrating to peripheral lymphoid organs. T cells develop through similar processes in the thymus.
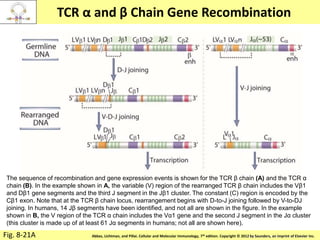
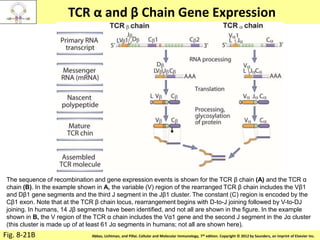
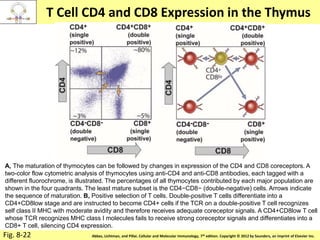
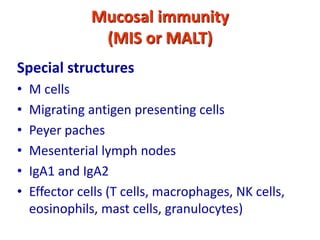
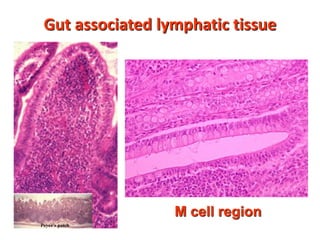
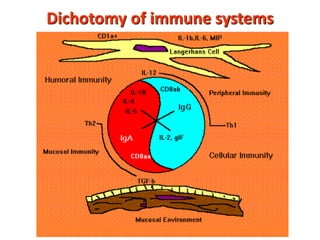
3. During development, gene rearrangement generates diversity in antigen receptor genes, and selection checkpoints ensure that only lymphocytes with functional receptors will mature and enter the peripheral immune system.