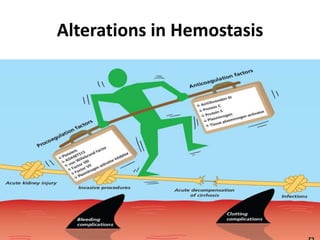
This document discusses coagulopathy in patients with cirrhosis. It notes that cirrhosis was traditionally viewed as a hypocoagulable state, but patients also have a high risk of thrombosis. Coagulation is complexly altered in cirrhosis through effects on platelets, coagulation factors, natural anticoagulants, fibrinolysis and inflammation. Prevention of bleeding focuses on vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, platelets and new thrombopoietin receptor agonists which may increase platelet counts before procedures.