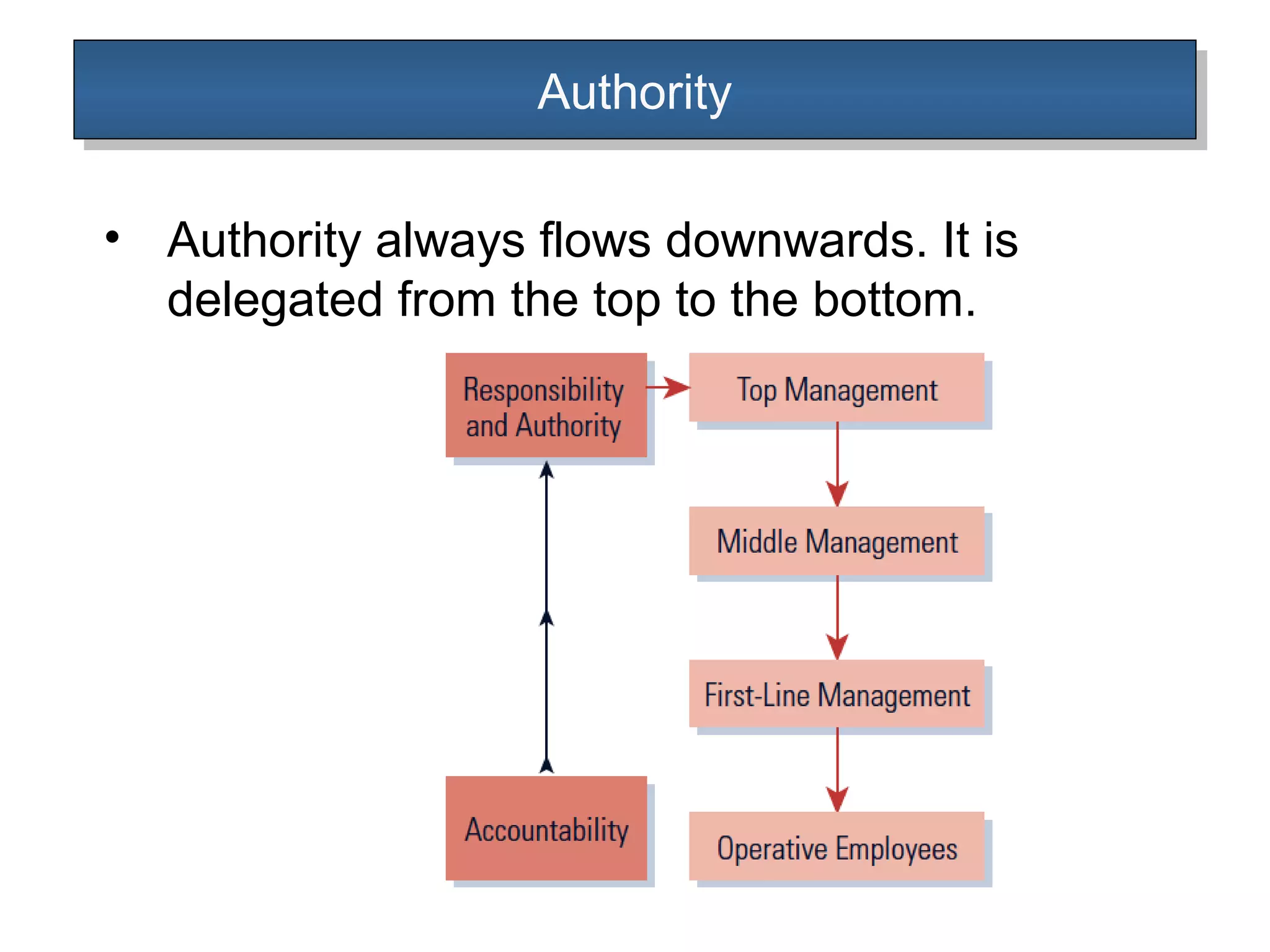
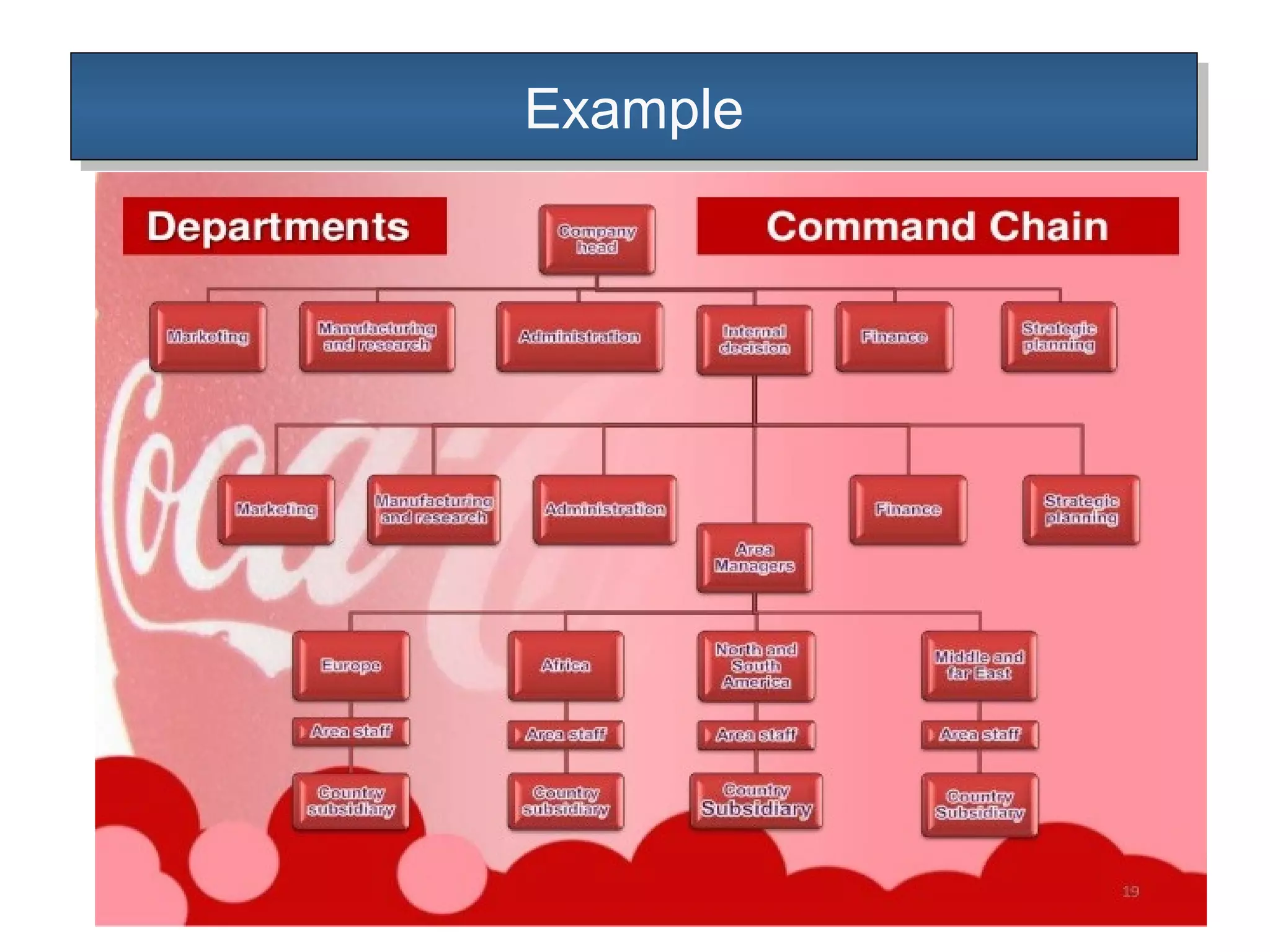
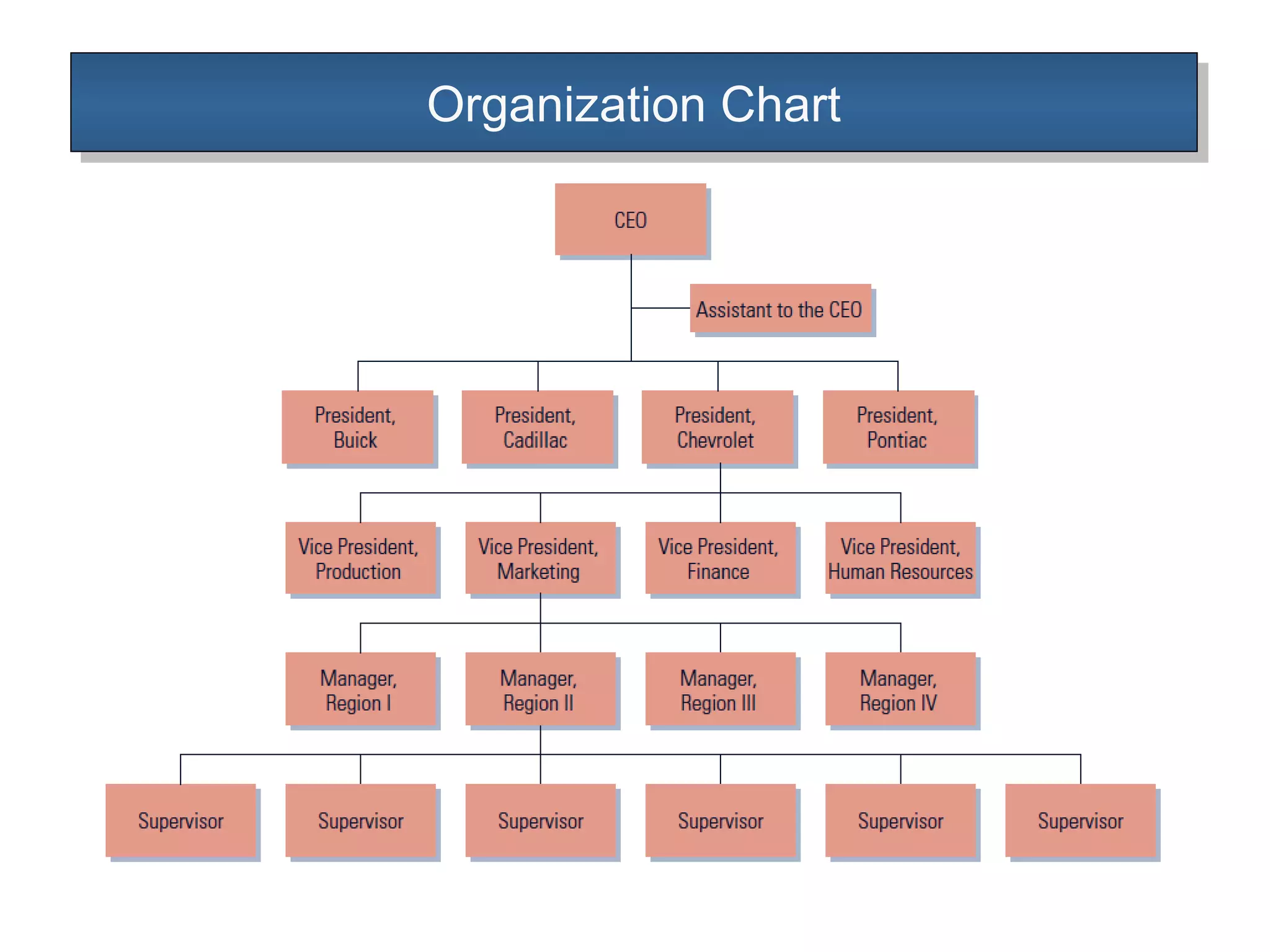
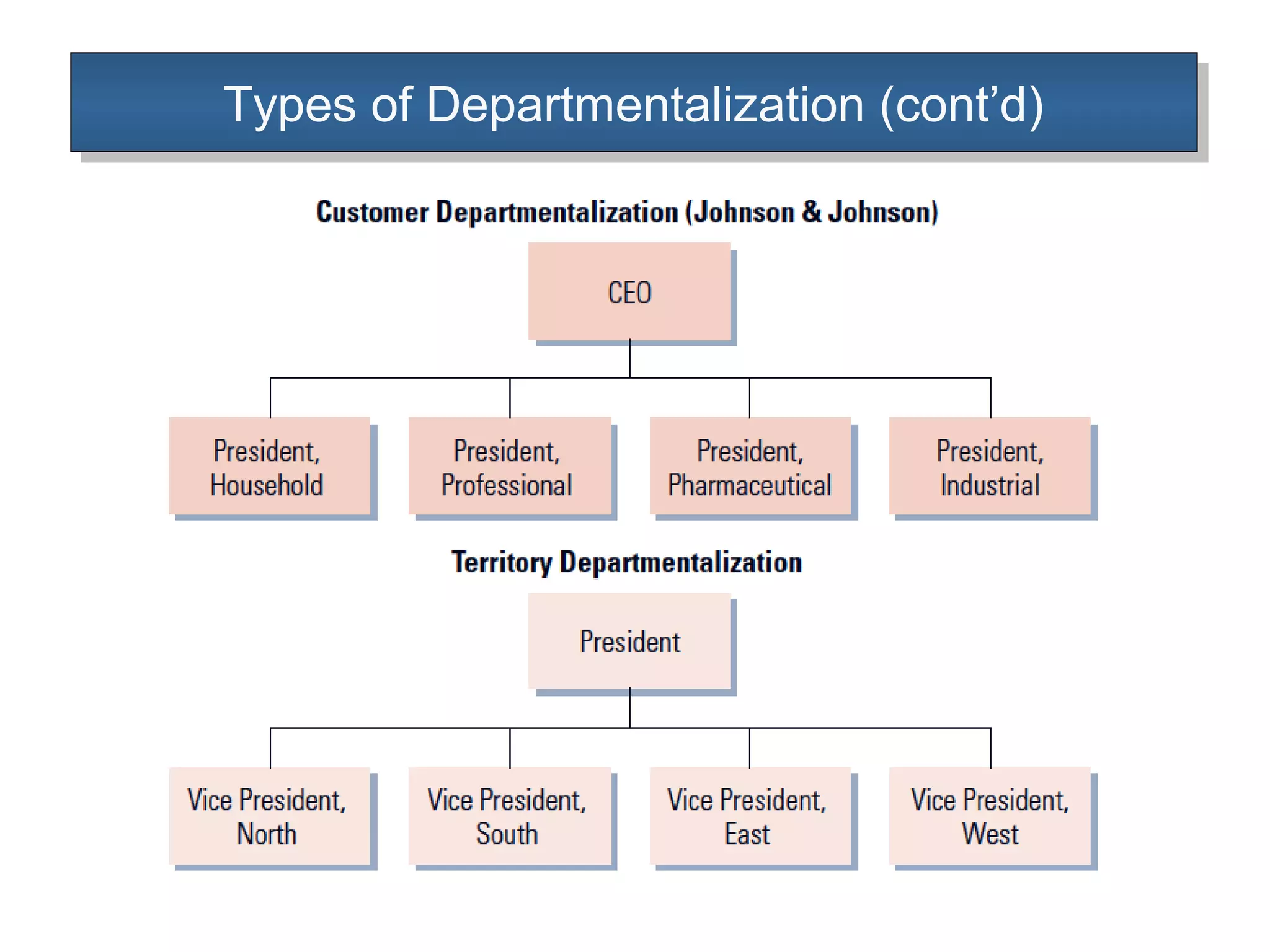
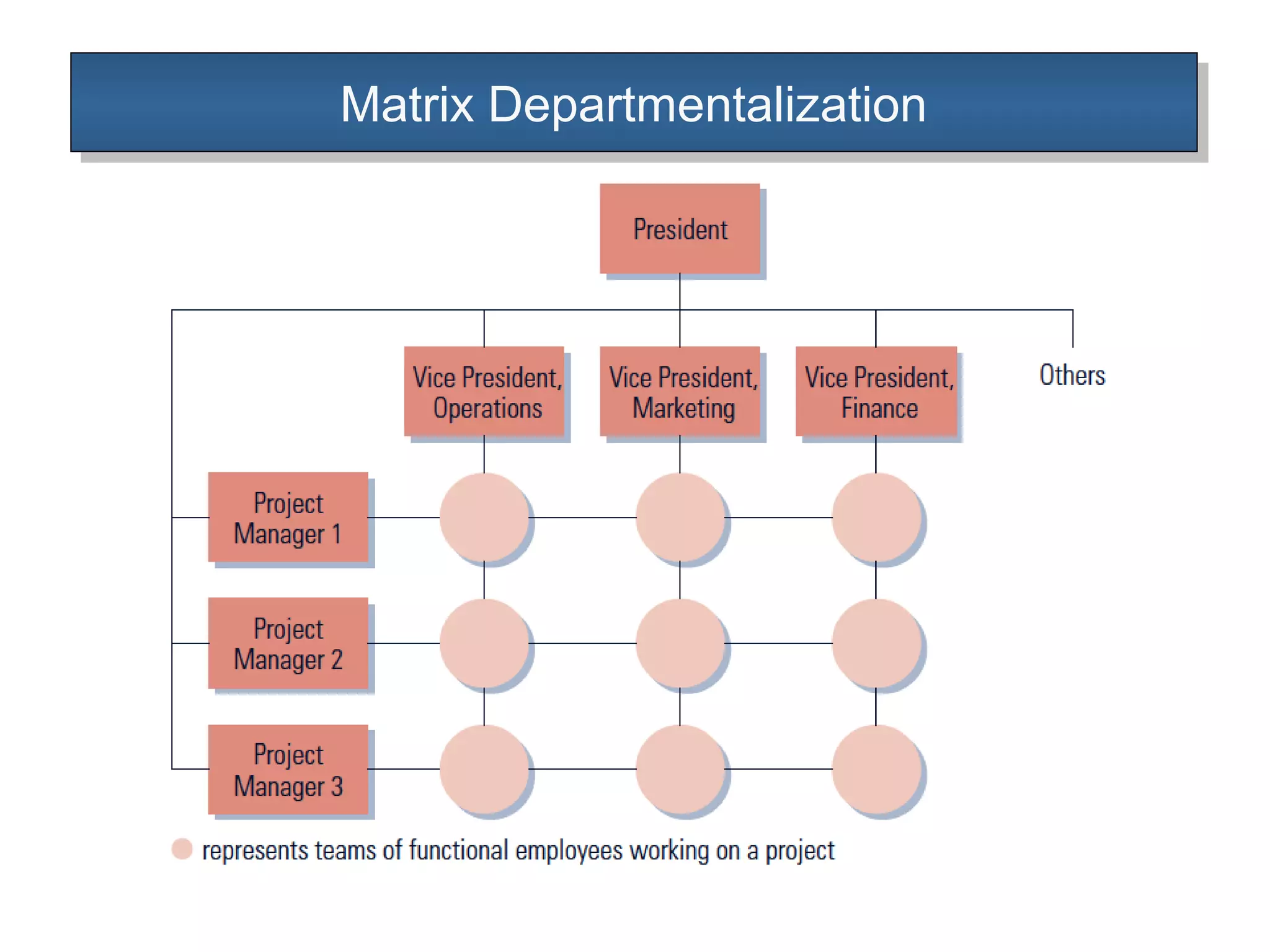
The document outlines the concepts of authority and power within an organization, emphasizing that authority is the formal right to command and flows downwards, while power is the personal ability to influence others and can flow in any direction. It discusses the delegation of authority, the differences between centralized and decentralized authority, and the benefits of delegating responsibility to improve organizational efficiency. Additionally, it touches upon organizational charts and types of departmentalization, including matrix departmentalization.