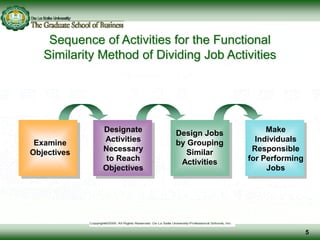
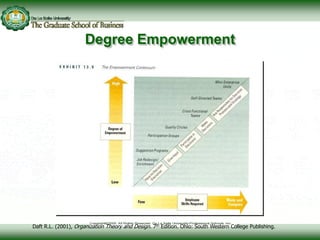
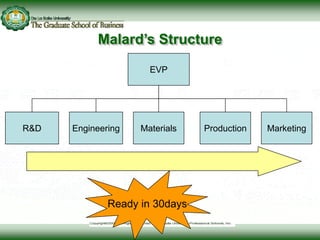
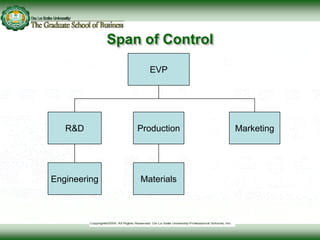
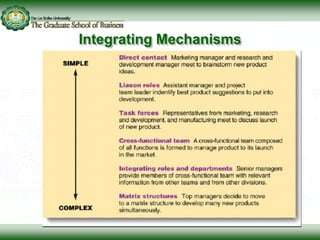
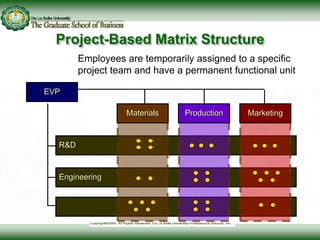
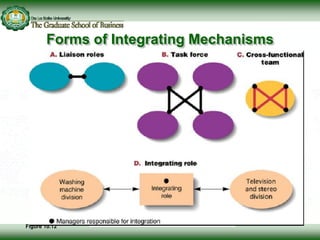
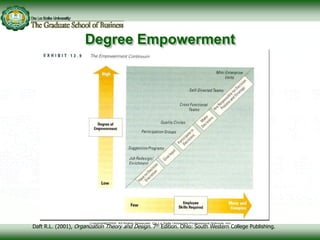
This document discusses concepts related to responsibility, authority, and delegation in organizations. It provides definitions and explanations of key terms:
- Responsibility is the obligation to perform assigned activities or duties.
- Authority is the right to perform or command others.
- Delegation is the process of assigning job activities and authority to specific individuals.
Effective delegation requires authority to be commensurate with responsibility, where subordinates have sufficient authority to perform their responsibilities without excessive supervision. Ultimate responsibility cannot be fully delegated.