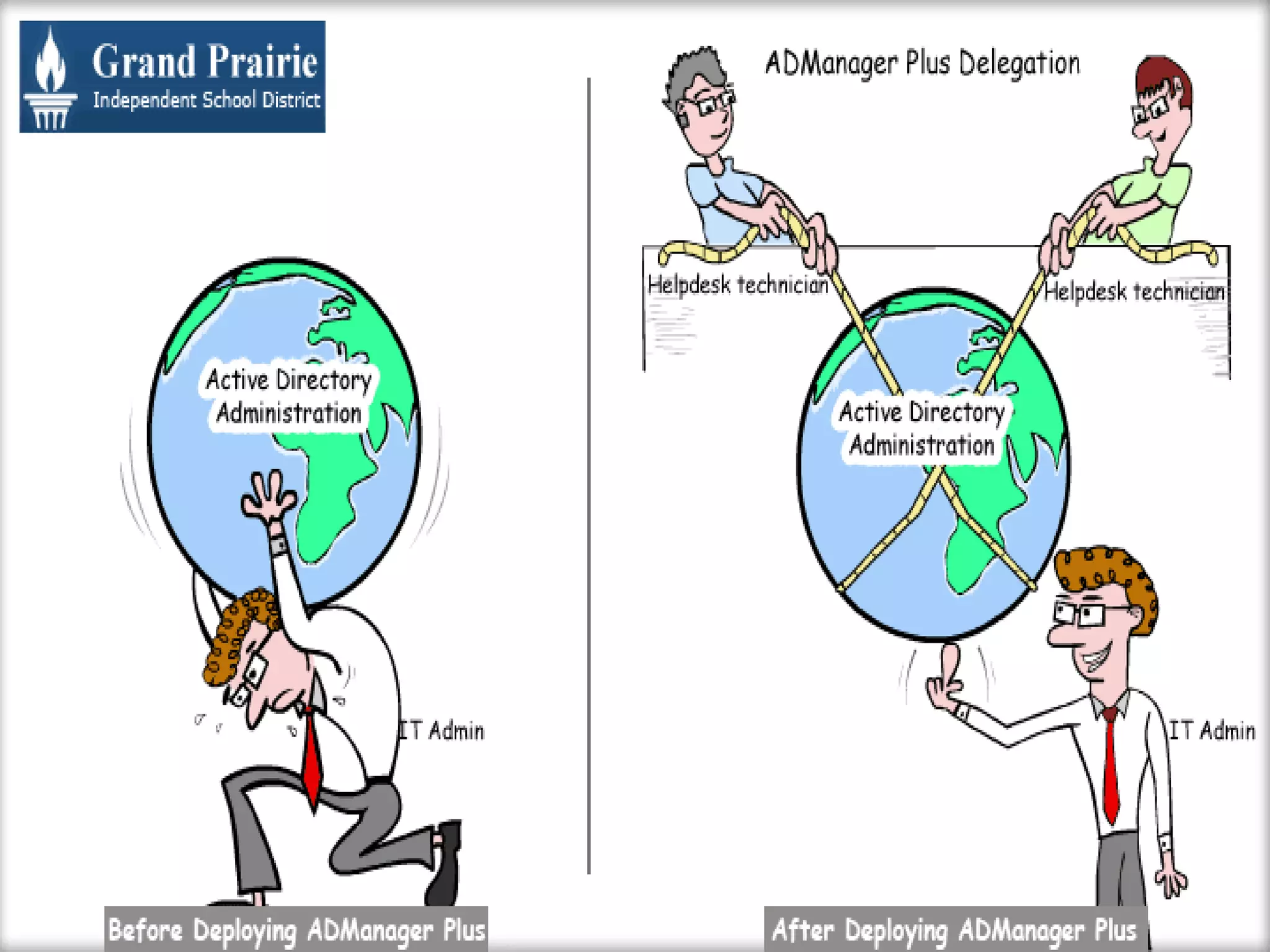
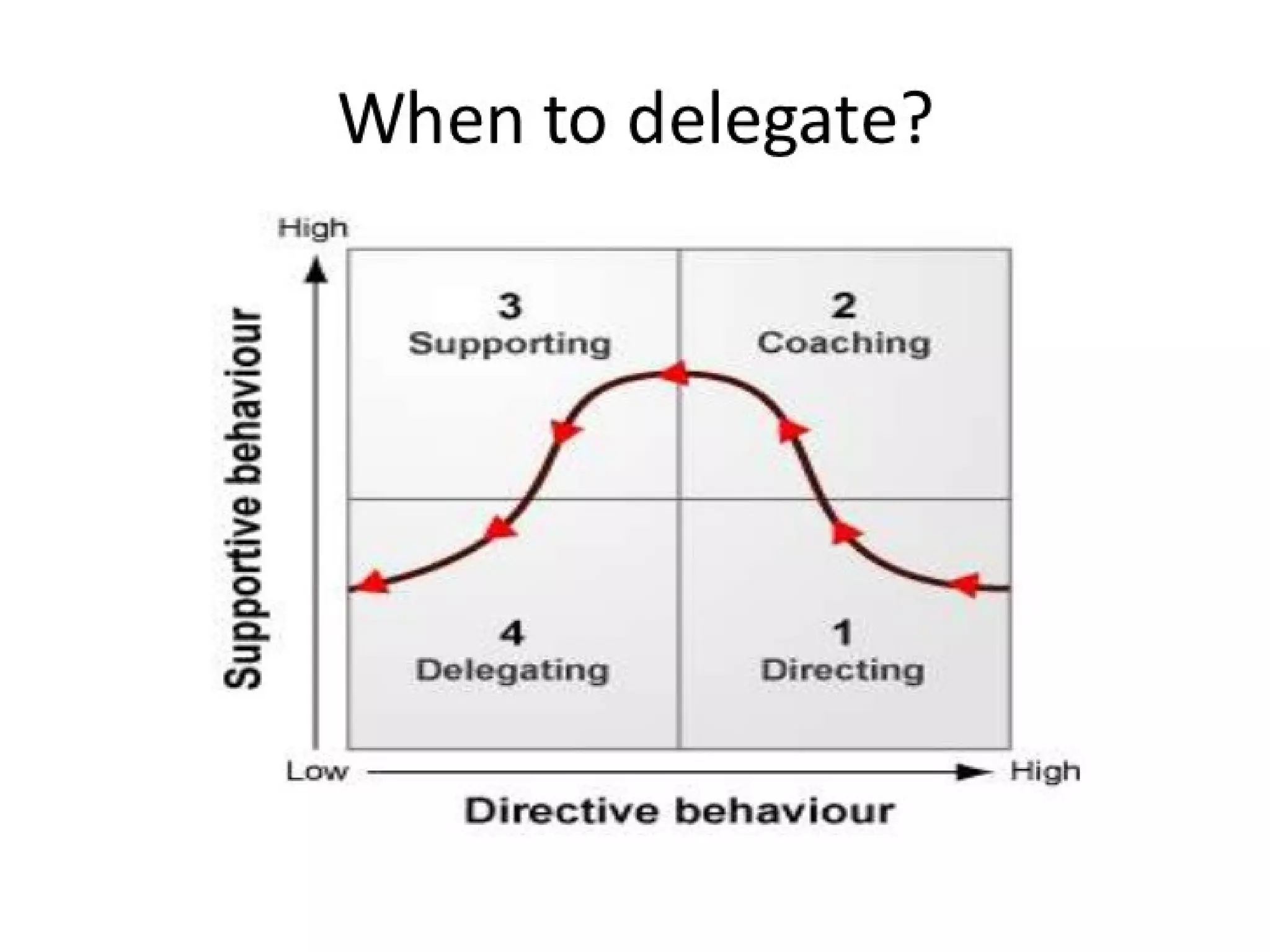
Delegation involves appointing someone to act on behalf of another, empowering them with authority and responsibility. Effective delegation saves time, develops skills, and improves team morale, while common pitfalls include under-delegation and lack of trust in subordinates. Successful delegation requires careful planning, selecting the right tasks and individuals, and providing adequate support and feedback.