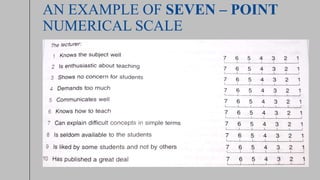
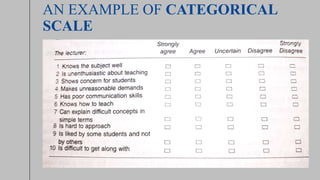
The document discusses different methods for measuring attitudes, including Likert scales, Thurstone scales, and Guttman scales. It provides details on the concepts and procedures for each scale. The Likert scale assumes statements have equal attitudinal value and uses summated ratings. The Thurstone scale uses statements rated by judges to calculate attitudinal weights. The Guttman scale orders statements hierarchically to measure extent of positive or negative attitudes. Examples of each scale are also included.