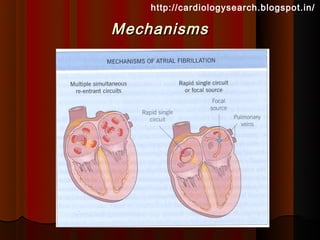
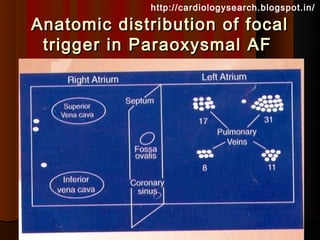
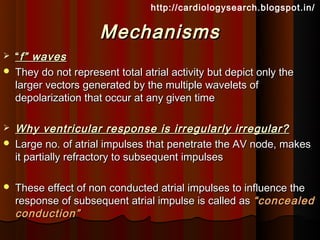
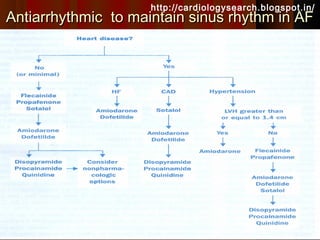
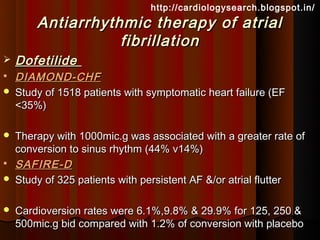
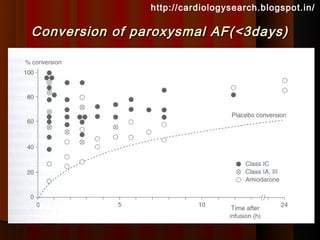
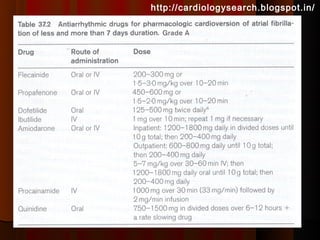
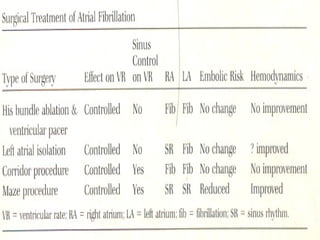
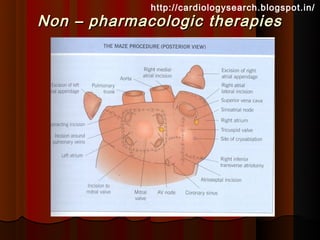
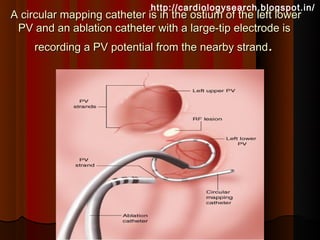
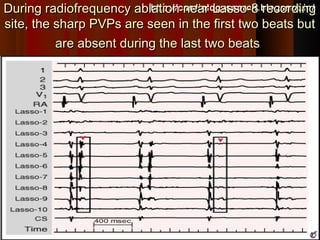
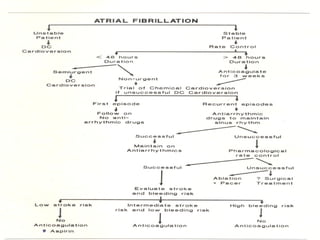
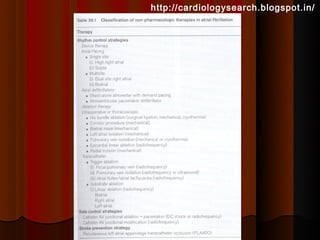
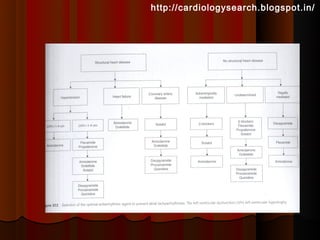
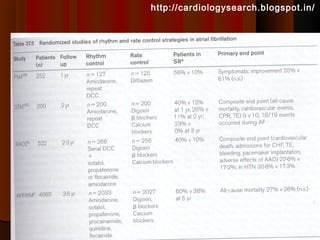
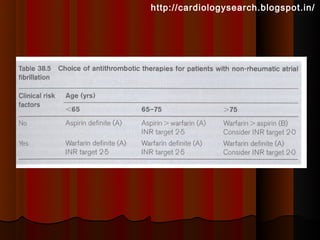
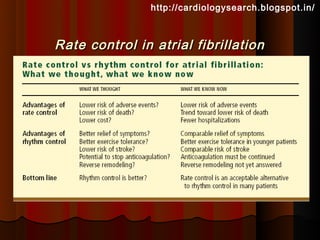
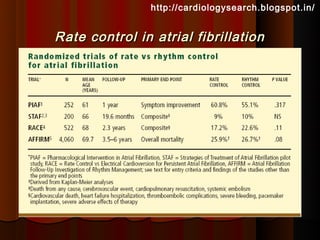
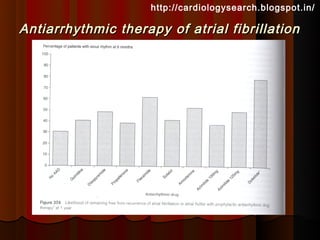
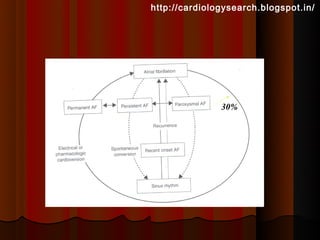
This document discusses atrial fibrillation (AF), including its classification, mechanisms, and management. AF is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity seen on ECG as irregular baseline undulations. The ventricular response rate is irregularly irregular between 100-160 bpm. AF can be classified as first detected, paroxysmal lasting <7 days, persistent lasting >7 days, or permanent lasting >1 year. The mechanism involves multiple reentrant wavelets propagating randomly through the atria. Management strategies include pharmacological or electrical cardioversion for acute termination, antiarrhythmic drugs to prevent recurrence, and rate control medications.