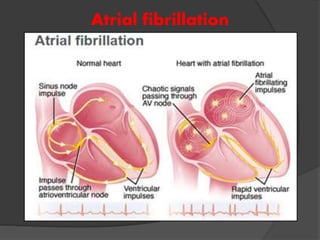
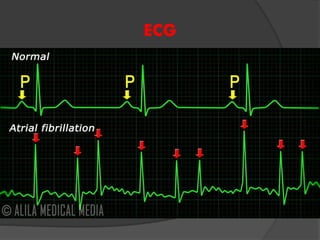
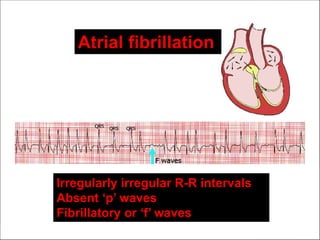
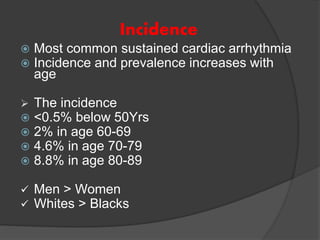
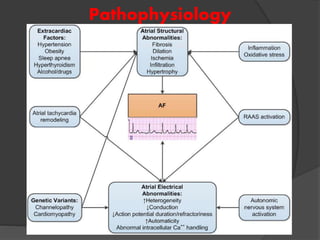
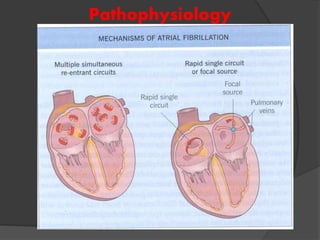
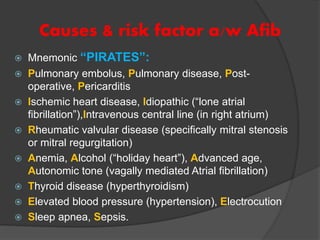
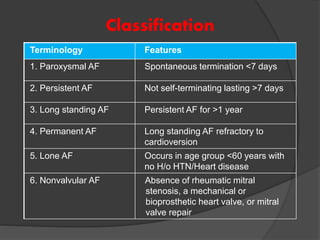
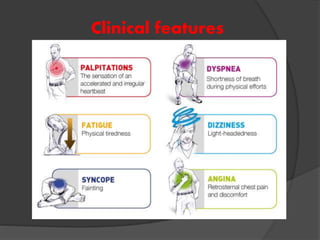
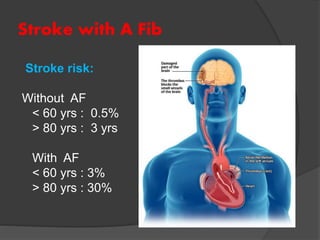
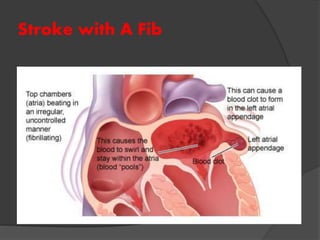
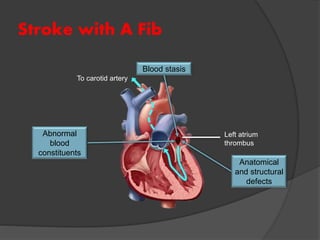
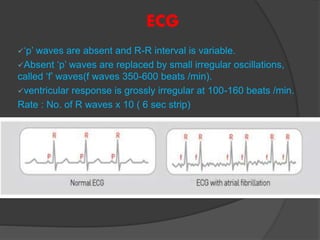
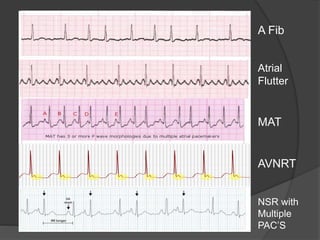
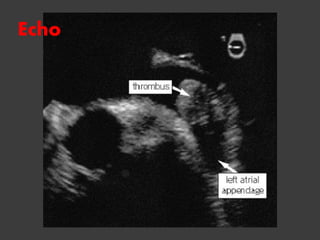
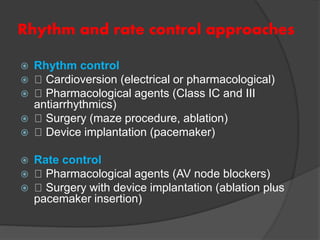
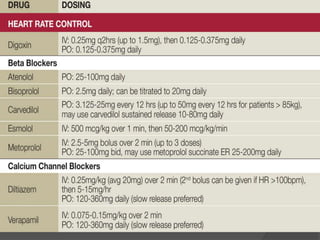
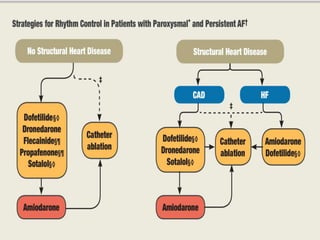
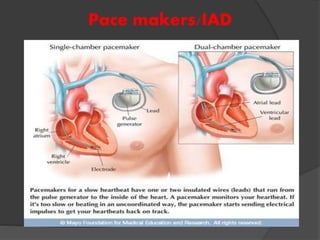
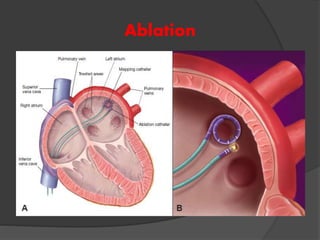
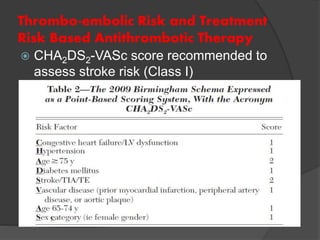
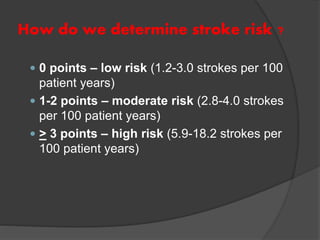
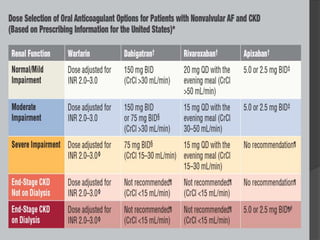
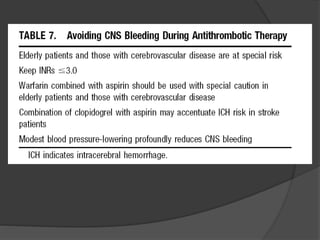
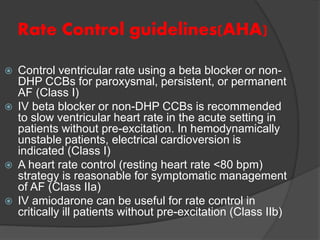
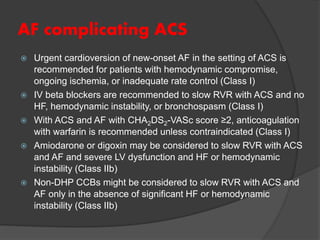
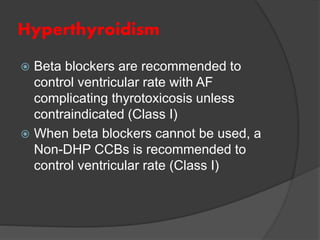
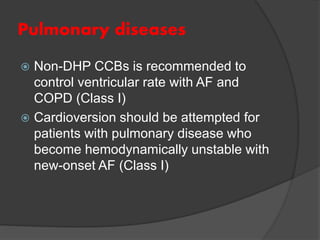
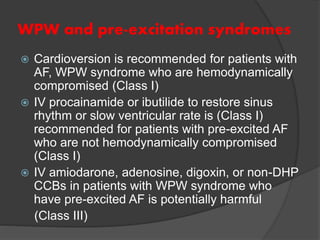
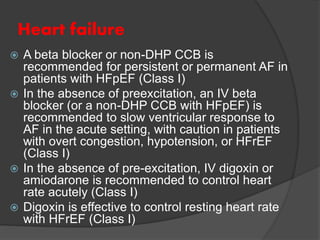
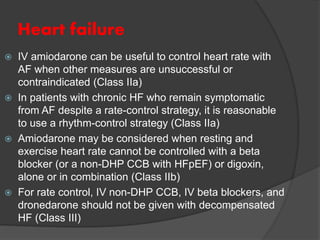
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common supraventricular arrhythmia characterized by an irregular heartbeat and specific ECG findings, with an incidence that increases with age. Key causes include structural heart abnormalities, ischemic heart disease, and various risk factors such as hypertension and hyperthyroidism. Management strategies focus on rate and rhythm control, anticoagulation to prevent thromboembolic events, and individualized treatment plans based on patient assessment.