Embed presentation
Downloaded 58 times







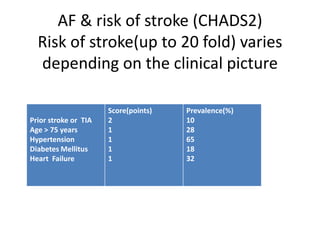
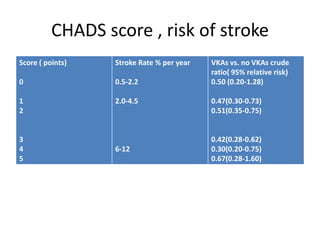
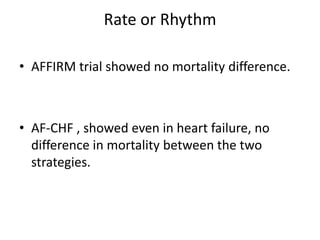




Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained arrhythmia, with a lifetime risk of 25% for those over 40, affecting millions, primarily in older adults. AF significantly increases the risk of stroke, with rates as high as 20-fold depending on clinical factors, and it accounts for 15% of all strokes, particularly in women over 75. Anticoagulation options include VKAs and newer agents like ximelagatran and idraparinux, which have shown comparable efficacy to warfarin but with varying bleeding risks.












