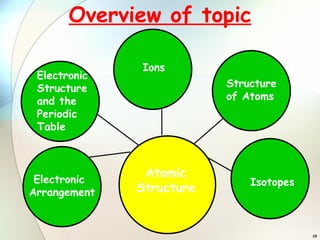
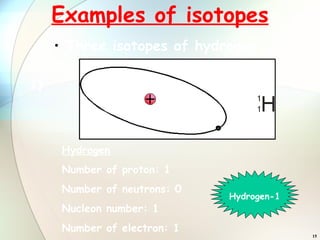
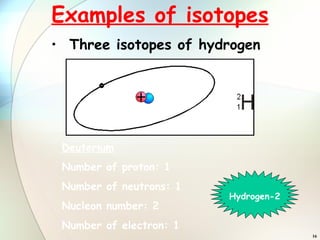
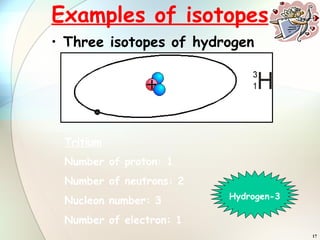
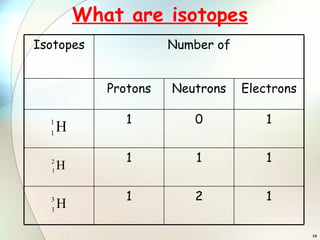
1) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
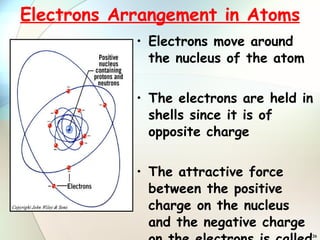
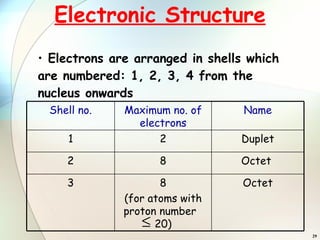
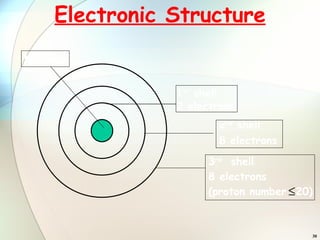
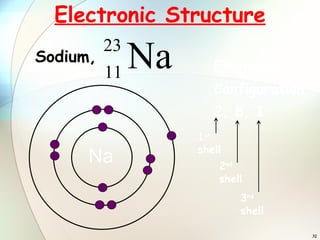
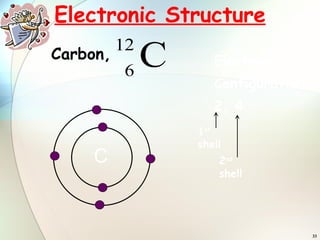
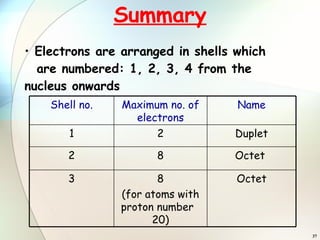
2) Electrons are arranged in shells around the nucleus numbered 1, 2, 3, etc. The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons and subsequent shells can hold up to 8 electrons.
3) To find an element's electronic configuration, electrons are filled into the lowest available energy shell first.