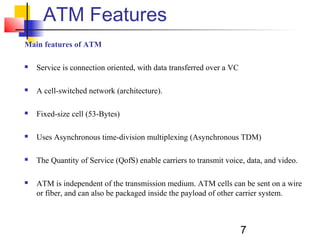
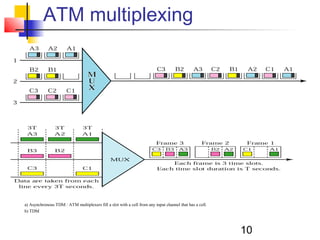
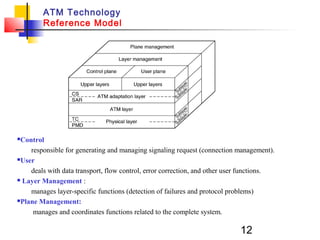
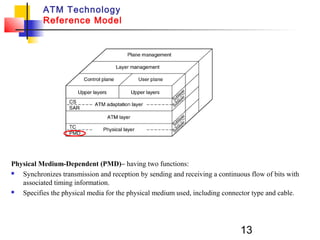
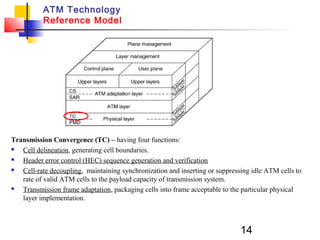
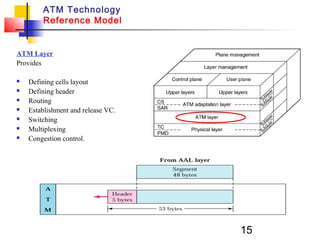
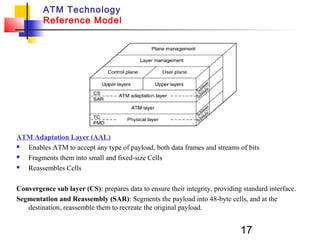
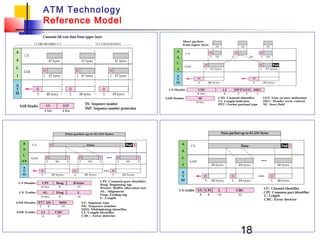
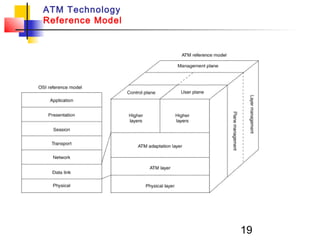
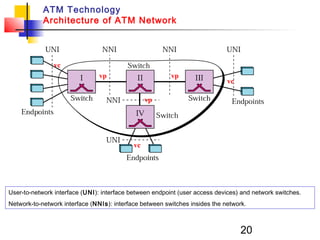
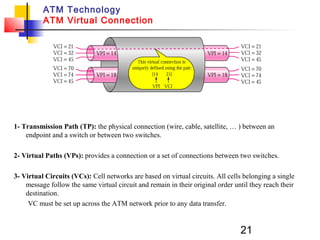
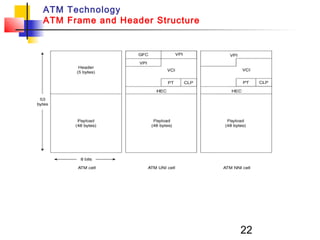
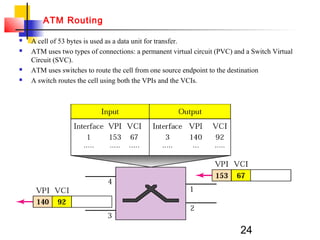
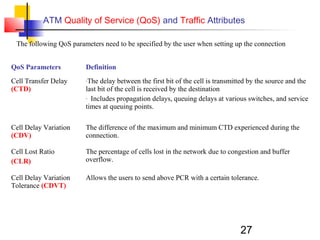
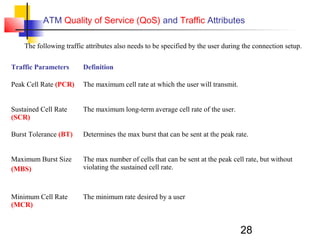
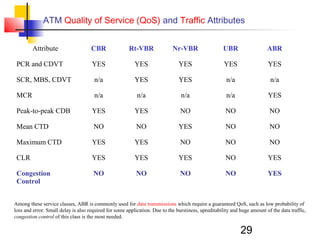
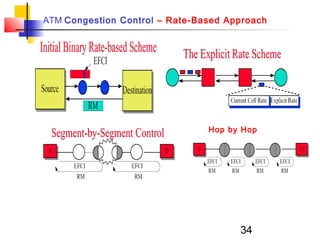
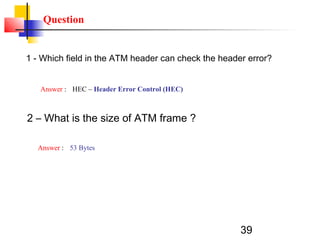
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a cell-switching and multiplexing technology that uses fixed-length packets called cells to carry different types of traffic like voice, video, and data. ATM works by segmenting data into these fixed-size cells which are then transmitted through virtual connections set up across an ATM network and reassembled at their destination. It provides benefits like high performance, Quality of Service guarantees, and the ability to handle different traffic types.